This is the tiny developer documentation for Hono.
# Start of Hono documentation
# Hono
Hono —— _**在日语中意为火焰🔥**_ —— 是一个基于 Web 标准构建的小巧、简单且极速的 Web 应用框架。
它能够运行在任意 JavaScript 运行时:Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、Vercel、Netlify、AWS Lambda、Lambda@Edge,以及 Node.js。
快,而且不止于快。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hono!'))
export default app
```
## 快速上手
只需运行下列命令之一:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono@latest
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono@latest
```
:::
## 核心特性
- **极速性能** 🚀 —— `RegExpRouter` 路由器拥有极致性能,没有线性循环,真正的快。
- **轻量体积** 🪶 —— `hono/tiny` 预设压缩后小于 14kB。Hono 没有任何依赖,只使用 Web 标准。
- **多运行时** 🌍 —— 兼容 Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、AWS Lambda 与 Node.js,同一份代码跑遍所有平台。
- **电池全配** 🔋 —— 内置中间件、可自定义中间件、第三方中间件与助手函数,开箱即用。
- **愉悦的开发体验** 😃 —— API 简洁清晰,对 TypeScript 提供一流支持,如今还拥抱了完备的类型系统。
## 适用场景
Hono 是一个类似 Express 的纯后端 Web 应用框架,没有前端层。
它可以在 CDN 边缘运行,与中间件组合即可搭建更大的应用。
以下是几个典型案例:
- 构建 Web API
- 作为后端服务器的代理
- CDN 边缘的入口层
- 边缘计算应用
- 库或框架的基础服务器
- 全栈应用
## 谁在使用 Hono?
| 项目 | 平台 | 用途 |
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com) | Cloudflare Workers | 免费开源的 CDN 服务,_Hono 被用于提供 API 服务_。 |
| [Cloudflare D1](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/d1/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器 SQL 数据库,_Hono 被用于内部 API 服务_。 |
| [Cloudflare Workers KV](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/workers-kv/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器键值数据库,_Hono 被用于内部 API 服务_。 |
| [BaseAI](https://baseai.dev) | 本地 AI 服务器 | 带有记忆功能的无服务器 AI Agent 流水线开源框架,_使用 Hono 搭建 API 服务器_。 |
| [Unkey](https://unkey.dev) | Cloudflare Workers | 开源的 API 鉴权与授权平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
| [OpenStatus](https://openstatus.dev) | Bun | 开源的网站与 API 监控平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
| [Deno Benchmarks](https://deno.com/benchmarks) | Deno | 基于 V8 的安全 TypeScript 运行时,_Hono 用于基准测试_。 |
| [Clerk](https://clerk.com) | Cloudflare Workers | 开源的用户管理平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
还有以下团队也在生产环境中使用 Hono:
- [Drivly](https://driv.ly/) - Cloudflare Workers
- [repeat.dev](https://repeat.dev/) - Cloudflare Workers
想了解更多?请访问 [Who is using Hono in production?](https://github.com/orgs/honojs/discussions/1510)。
## 一分钟体验 Hono
以下演示展示了如何使用 Hono 在 Cloudflare Workers 上创建应用。

## 极速表现
**在 Cloudflare Workers 的各类路由器中,Hono 是最快的。**
```
Hono x 402,820 ops/sec ±4.78% (80 runs sampled)
itty-router x 212,598 ops/sec ±3.11% (87 runs sampled)
sunder x 297,036 ops/sec ±4.76% (77 runs sampled)
worktop x 197,345 ops/sec ±2.40% (88 runs sampled)
Fastest is Hono
✨ Done in 28.06s.
```
查看 [更多基准测试](/docs/concepts/benchmarks)。
## 轻量体积
**Hono 非常小。**在使用 `hono/tiny` 预设并压缩后,体积 **低于 14KB**。
拥有众多中间件和适配器,但只会在使用时才打包。作为对比,Express 的体积为 572KB。
```
$ npx wrangler dev --minify ./src/index.ts
⛅️ wrangler 2.20.0
--------------------
⬣ Listening at http://0.0.0.0:8787
- http://127.0.0.1:8787
- http://192.168.128.165:8787
Total Upload: 11.47 KiB / gzip: 4.34 KiB
```
## 多款路由器
**Hono 提供多种路由器实现。**
**RegExpRouter** 是 JavaScript 世界中最快的路由器。它在派发前先构建一个巨大的正则表达式,用以匹配路由。配合 **SmartRouter**,即可支持所有路由模式。
**LinearRouter** 能够极快地注册路由,适用于每次请求都会初始化应用的运行时。**PatternRouter** 则以简单的方式添加并匹配路由模式,让体积更小。
查看 [更多关于路由的信息](/docs/concepts/routers)。
## Web 标准
得益于 **Web 标准**,Hono 可以运行在众多平台上。
- Cloudflare Workers
- Cloudflare Pages
- Fastly Compute
- Deno
- Bun
- Vercel
- AWS Lambda
- Lambda@Edge
- 以及更多
通过使用 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server),Hono 也能在 Node.js 上运行。
查看 [更多关于 Web 标准的信息](/docs/concepts/web-standard)。
## 中间件与助手
**Hono 拥有大量中间件与助手函数**,真正实现“写得更少,做得更多”。
开箱即用的中间件与助手包括:
- [Basic Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)
- [Bearer Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/bearer-auth)
- [Body Limit](/docs/middleware/builtin/body-limit)
- [Cache](/docs/middleware/builtin/cache)
- [Compress](/docs/middleware/builtin/compress)
- [Context Storage](/docs/middleware/builtin/context-storage)
- [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
- [CORS](/docs/middleware/builtin/cors)
- [ETag](/docs/middleware/builtin/etag)
- [html](/docs/helpers/html)
- [JSX](/docs/guides/jsx)
- [JWT Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/jwt)
- [Logger](/docs/middleware/builtin/logger)
- [Language](/docs/middleware/builtin/language)
- [Pretty JSON](/docs/middleware/builtin/pretty-json)
- [Secure Headers](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers)
- [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
- [Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
- [GraphQL Server](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/graphql-server)
- [Firebase Authentication](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/firebase-auth)
- [Sentry](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/sentry)
- 以及更多!
例如,在 Hono 中仅需几行代码就能加入 ETag 与请求日志:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { etag } from 'hono/etag'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(etag(), logger())
```
查看 [更多关于中间件的信息](/docs/concepts/middleware)。
## 开发者体验
Hono 带来令人愉悦的“**开发者体验**”。
得益于 `Context` 对象,可以轻松获取 Request/Response。
此外,Hono 采用 TypeScript 编写,自带“**类型**”。
例如,路径参数会被推断为字面量类型。
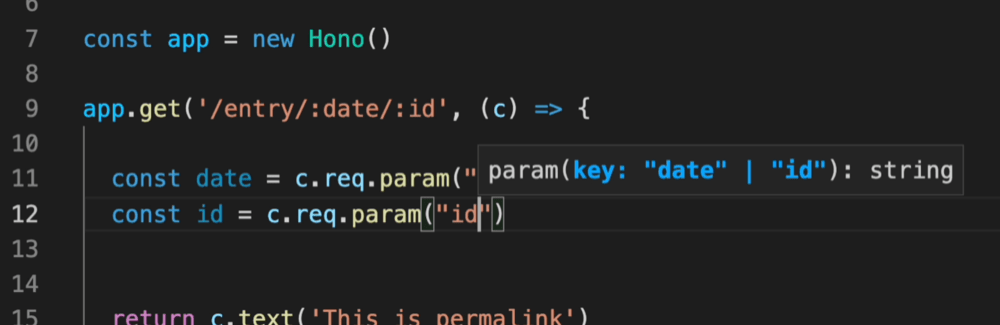
借助 Validator 与 Hono Client `hc`,可以启用 RPC 模式。
在该模式下,你可以继续使用自己喜爱的校验器(如 Zod),轻松在服务端与客户端之间共享 API 规范,从而构建类型安全的应用。
查看 [Hono Stacks](/docs/concepts/stacks)。
# 最佳实践
Hono 十分灵活,你可以按照自己的偏好编写应用。
不过,仍然有一些更值得遵循的最佳实践。
## 尽量不要创建“控制器”
能不写“Ruby on Rails 风格的控制器”时,就别写。
```ts
// 🙁
// 类似 RoR 的控制器
const booksList = (c: Context) => {
return c.json('list books')
}
app.get('/books', booksList)
```
问题出在类型上。例如,如果不写复杂的泛型,控制器内部无法推断路径参数。
```ts
// 🙁
// 类似 RoR 的控制器
const bookPermalink = (c: Context) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // 无法推断路径参数
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
}
```
因此你完全没必要写 RoR 风格的控制器,直接在路径定义后编写处理函数即可。
```ts
// 😃
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // 可以正确推断路径参数
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
})
```
## 使用模式验证请求
如果需要验证请求,请使用模式验证器,而不要手写验证逻辑。
```ts
import { z } from 'zod'
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
app.post(
'/auth',
zValidator(
'json',
z.object({
email: z.string().email(),
password: z.string().min(8),
})
),
async (c) => {
const { email, password } = c.req.valid('json')
return c.json({ email, password })
}
)
```
## 在调用 `app.get()` 之前定义配置
这是来自 JavaScript 模块的最佳实践:
在调用函数之前先定义配置对象。
```ts
const route = {
method: 'GET',
path: '/',
}
app.get(route, (c) => c.text('Hello'))
```
## 不要为了分组而重复使用 `app.route`
只有在需要为同一路径提供多个 HTTP 方法时,才应该使用 `app.route`。
如果只是想划分路由分组,就会显得多此一举。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const books = app.route('/books')
books.get('/', (c) => c.json(['Hello']))
books.get('/:id', (c) => c.json({ id: c.req.param('id') }))
```
在这种情况下就显得冗余了。直接写成下面这样能得到相同的效果。
```ts
app.get('/books', (c) => c.json(['Hello']))
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => c.json({ id: c.req.param('id') }))
```
## 更倾向使用 `app.on` 而不是 `app.xxx`
Hono 提供了 `app.on`,可以为同一路径定义多个 HTTP 方法。建议使用 `app.on`,而不是 `app.xxx`。
```ts
app.on(['GET', 'POST'], '/books', (c) => {
return c.json(['Hello'])
})
```
## 使用 `c.req.param()` 而非 `c.req.param['id']`
请使用函数形式的 `c.req.param()`,而不是访问器 `c.req.param['id']`,以避免触发 getter。
```ts
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id')
return c.json({ id })
})
```
## 用模板字符串拼接响应
拼接响应文本时,请使用模板字符串,而不是字符串相加。
```ts
app.get('/hello/:name', (c) => {
const { name } = c.req.param()
return c.text(`Hello ${name}!`)
})
```
## 日志
使用 `console.log` 和 `console.error` 输出日志信息。
```ts
app.get('/hello', async (c) => {
const start = Date.now()
const res = await c.req.parseBody()
const end = Date.now()
console.log(`[${c.req.method}] ${c.req.path} - ${end - start}ms`)
return c.json(res)
})
```
## 用 `c.var` 复用逻辑
如果有重复使用的逻辑,可以通过 `c.set` 和 `c.var` 进行复用。
```ts
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
c.set('database', await getDatabase())
await next()
})
app.get('/users', async (c) => {
const db = c.var.database
const users = await db.users.findMany()
return c.json(users)
})
```
## 等待 Response
`Response` 只能读取一次。等待响应会消耗它。
```ts
app.get('/', async (c) => {
const res = await fetch('https://example.com')
const json = await res.json()
return c.json(json)
})
```
# Create-hono
以下是 `create-hono` 支持的命令行选项。这个项目初始化工具会在你执行 `npm create hono@latest`、`npx create-hono@latest` 或 `pnpm create hono@latest` 时运行。
> [!NOTE]
> **为什么需要这篇文档?** 安装与快速上手示例通常只展示最精简的 `npm create hono@latest my-app` 命令。其实 `create-hono` 提供了很多实用的参数,可以帮助你自动化并自定义项目创建过程(选择模板、跳过交互式提示、指定包管理器、使用本地缓存等)。
## 传递参数
使用 `npm create`(或 `npx`)时,传给初始化脚本的参数必须放在 `--` 之后。`--` 后面的所有内容都会转发给初始化器。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
# 将参数转发给 create-hono(npm 必须使用 `--`)
npm create hono@latest my-app -- --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [yarn]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
yarn create hono my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [pnpm]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
pnpm create hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [bun]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
bun create hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [deno]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
deno init --npm hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
:::
## 常用参数
| 参数 | 说明 | 示例 |
| :---------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | :----------------------------- |
| `--template ` | 选择一个起始模板,并跳过交互式模板提示。模板名称可能包括 `bun`、`cloudflare-workers`、`vercel` 等 | `--template cloudflare-workers` |
| `--install` | 模板创建完毕后自动安装依赖。 | `--install` |
| `--pm ` | 指定安装依赖时使用的包管理器。常见值:`npm`、`pnpm`、`yarn`。 | `--pm pnpm` |
| `--offline` | 使用本地缓存/模板,而不是获取最新的远程模板。适合离线环境或希望固定模板版本的场景。 | `--offline` |
> [!NOTE]
> 模板列表与可用选项由 `create-hono` 项目维护。本文仅汇总了最常用的参数——完整且权威的参考请查看下方仓库链接。
## 示例流程
### 最小化、交互式
```bash
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
命令会提示你选择模板和其他选项。
### 非交互式:指定模板与包管理器
```bash
npm create hono@latest my-app -- --template vercel --pm npm --install
```
该命令会基于 `vercel` 模板创建 `my-app`,使用 `npm` 安装依赖,并跳过所有交互式提问。
### 使用离线缓存(无网络)
```bash
pnpm create hono@latest my-app --template deno --offline
```
## 故障排查与提示
- 如果某个参数似乎没有生效,请确认在使用 `npm create`/`npx` 时是否加上了 `--` 进行转发。
- 想查看最新的模板与参数列表,可以直接查阅 `create-hono` 仓库,或者本地运行初始化工具并查看其帮助信息。
## 相关链接
- `create-hono` 仓库:[create-hono](https://github.com/honojs/create-hono)
# 示例
请参阅[示例章节](/examples/)。
# 常见问题
本指南整理了关于 Hono 的常见疑问及解决方式。
## Hono 是否提供官方的 Renovate 配置?
目前 Hono 团队没有维护 [Renovate](https://github.com/renovatebot/renovate) 的官方配置。
因此,请参考以下方式使用第三方的 renovate-config。
在你的 `renovate.json` 中写入:
```json
// renovate.json
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"github>shinGangan/renovate-config-hono" // [!code ++]
]
}
```
更多详情请参阅 [renovate-config-hono](https://github.com/shinGangan/renovate-config-hono) 仓库。
# 助手
助手(Helper)可以在开发应用时提供支持。与中间件不同,它们不会作为处理函数运行,而是提供便捷的实用功能。
例如,[Cookie 助手](/docs/helpers/cookie) 的使用方式如下:
```ts
import { getCookie, setCookie } from 'hono/cookie'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/cookie', (c) => {
const yummyCookie = getCookie(c, 'yummy_cookie')
// ...
setCookie(c, 'delicious_cookie', 'macha')
//
})
```
## 可用的助手
- [Accepts](/docs/helpers/accepts)
- [Adapter](/docs/helpers/adapter)
- [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
- [css](/docs/helpers/css)
- [Dev](/docs/helpers/dev)
- [Factory](/docs/helpers/factory)
- [html](/docs/helpers/html)
- [JWT](/docs/helpers/jwt)
- [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
- [Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
- [Testing](/docs/helpers/testing)
- [WebSocket](/docs/helpers/websocket)
# 客户端组件
`hono/jsx` 不仅支持服务端渲染,也支持在客户端运行。这意味着你可以在浏览器里构建交互式界面,我们把它称作客户端组件,或 `hono/jsx/dom`。
它既快又小。`hono/jsx/dom` 的计数器示例在 Brotli 压缩后只有 2.8KB,而 React 的同类示例则有 47.8KB。
本章介绍客户端组件特有的功能。
## 计数器示例
下面是一个简单的计数器示例,代码与 React 中的写法相同。
```tsx
import { useState } from 'hono/jsx'
import { render } from 'hono/jsx/dom'
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
Count: {count}
)
}
function App() {
return (
)
}
const root = document.getElementById('root')
render(, root)
```
## `render()`
你可以使用 `render()` 将 JSX 组件插入到指定的 HTML 元素中。
```tsx
render(, container)
```
## 与 React 兼容的 Hook
`hono/jsx/dom` 提供了与 React 兼容或部分兼容的 Hook。具体 API 可以参考 [React 文档](https://react.dev/reference/react/hooks)。
- `useState()`
- `useEffect()`
- `useRef()`
- `useCallback()`
- `use()`
- `startTransition()`
- `useTransition()`
- `useDeferredValue()`
- `useMemo()`
- `useLayoutEffect()`
- `useReducer()`
- `useDebugValue()`
- `createElement()`
- `memo()`
- `isValidElement()`
- `useId()`
- `createRef()`
- `forwardRef()`
- `useImperativeHandle()`
- `useSyncExternalStore()`
- `useInsertionEffect()`
- `useFormStatus()`
- `useActionState()`
- `useOptimistic()`
## `startViewTransition()` 系列
`startViewTransition()` 系列提供了原生的 Hook 与函数,帮助你更轻松地使用 [View Transitions API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/View_Transitions_API)。下面展示几种典型写法。
### 1. 最简单的示例
借助 `startViewTransition()`,可以非常简洁地调用 `document.startViewTransition` 来实现过渡效果。
```tsx
import { useState, startViewTransition } from 'hono/jsx'
import { css, Style } from 'hono/css'
export default function App() {
const [showLargeImage, setShowLargeImage] = useState(false)
return (
<>
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
Hello Hono!
{props.messages.map((message) => {
return - {message}!!
})}
)
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
const messages = ['Good Morning', 'Good Evening', 'Good Night']
return c.html()
})
export default app
```
## 元数据提升
你可以在组件中直接书写 ``、`<link>`、`<meta>` 等文档元数据标签。框架会自动将这些标签提升到文档的 `<head>` 区域。对于 `<head>` 元素距离实际决定元数据的组件较远的情况,这一点尤为便利。
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content) => {
return c.html(
<html>
<head></head>
<body>{content}</body>
</html>
)
})
await next()
})
app.get('/about', (c) => {
return c.render(
<>
<title>About Page
about page content
)
})
export default app
```
## Fragment
使用 Fragment 可以在不增加额外节点的情况下包裹多个元素:
```tsx
import { Fragment } from 'hono/jsx'
const List = () => (
first child
second child
third child
)
```
如果配置正确,也可以写成 `<>`。
```tsx
const List = () => (
<>
first child
second child
third child
)
```
## `PropsWithChildren`
使用 `PropsWithChildren` 可以在函数组件中正确推断子元素类型。
```tsx
import { PropsWithChildren } from 'hono/jsx'
type Post = {
id: number
title: string
}
function Component({ title, children }: PropsWithChildren) {
return (
{title}
{children}
)
}
```
## 插入原始 HTML
如果需要直接插入 HTML,可以使用 `dangerouslySetInnerHTML`:
```tsx
app.get('/foo', (c) => {
const inner = { __html: 'JSX · SSR' }
const Div =
})
```
## 记忆化
通过 `memo` 记忆化生成的字符串,可以优化组件性能:
```tsx
import { memo } from 'hono/jsx'
const Header = memo(() => )
const Footer = memo(() => )
const Layout = (
)
```
## Context
使用 `useContext` 可以在组件树的任意层级共享数据,无需逐层传递 props。
```tsx
import type { FC } from 'hono/jsx'
import { createContext, useContext } from 'hono/jsx'
const themes = {
light: {
color: '#000000',
background: '#eeeeee',
},
dark: {
color: '#ffffff',
background: '#222222',
},
}
const ThemeContext = createContext(themes.light)
const Button: FC = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext)
return
}
const Toolbar: FC = () => {
return (
)
}
// ...
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## 异步组件
`hono/jsx` 支持异步组件,因此可以在组件中使用 `async`/`await`。当你使用 `c.html()` 渲染时,会自动等待异步结果。
```tsx
const AsyncComponent = async () => {
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 1000)) // 延迟 1 秒
return Done!
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## Suspense
提供了类似 React 的 `Suspense` 功能。
将异步组件包裹在 `Suspense` 中时,会先渲染备用内容(fallback),待 Promise 解析后再显示真实内容。你可以结合 `renderToReadableStream()` 使用。
```tsx
import { renderToReadableStream, Suspense } from 'hono/jsx/streaming'
//...
app.get('/', (c) => {
const stream = renderToReadableStream(
loading...}>
)
return c.body(stream, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=UTF-8',
'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked',
},
})
})
```
## ErrorBoundary
使用 `ErrorBoundary` 可以捕获子组件中的错误。
在下例中,如果抛出错误,就会展示 `fallback` 指定的内容。
```tsx
function SyncComponent() {
throw new Error('Error')
return Hello
}
app.get('/sync', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
)
})
```
`ErrorBoundary` 也可以与异步组件及 `Suspense` 搭配使用。
```tsx
async function AsyncComponent() {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000))
throw new Error('Error')
return Hello
}
app.get('/with-suspense', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
Loading...}>
)
})
```
## StreamingContext
`StreamingContext` 可用于为 `Suspense`、`ErrorBoundary` 等流式组件提供配置。例如在生成的 `
) : (
)}
Hello
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}