This is the full developer documentation for Hono.
# Start of Hono documentation
# Hono
Hono —— _**在日语中意为火焰🔥**_ —— 是一个基于 Web 标准构建的小巧、简单且极速的 Web 应用框架。
它能够运行在任意 JavaScript 运行时:Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、Vercel、Netlify、AWS Lambda、Lambda@Edge,以及 Node.js。
快,而且不止于快。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hono!'))
export default app
```
## 快速上手
只需运行下列命令之一:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono@latest
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono@latest
```
:::
## 核心特性
- **极速性能** 🚀 —— `RegExpRouter` 路由器拥有极致性能,没有线性循环,真正的快。
- **轻量体积** 🪶 —— `hono/tiny` 预设压缩后小于 14kB。Hono 没有任何依赖,只使用 Web 标准。
- **多运行时** 🌍 —— 兼容 Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、AWS Lambda 与 Node.js,同一份代码跑遍所有平台。
- **电池全配** 🔋 —— 内置中间件、可自定义中间件、第三方中间件与助手函数,开箱即用。
- **愉悦的开发体验** 😃 —— API 简洁清晰,对 TypeScript 提供一流支持,如今还拥抱了完备的类型系统。
## 适用场景
Hono 是一个类似 Express 的纯后端 Web 应用框架,没有前端层。
它可以在 CDN 边缘运行,与中间件组合即可搭建更大的应用。
以下是几个典型案例:
- 构建 Web API
- 作为后端服务器的代理
- CDN 边缘的入口层
- 边缘计算应用
- 库或框架的基础服务器
- 全栈应用
## 谁在使用 Hono?
| 项目 | 平台 | 用途 |
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com) | Cloudflare Workers | 免费开源的 CDN 服务,_Hono 被用于提供 API 服务_。 |
| [Cloudflare D1](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/d1/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器 SQL 数据库,_Hono 被用于内部 API 服务_。 |
| [Cloudflare Workers KV](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/workers-kv/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器键值数据库,_Hono 被用于内部 API 服务_。 |
| [BaseAI](https://baseai.dev) | 本地 AI 服务器 | 带有记忆功能的无服务器 AI Agent 流水线开源框架,_使用 Hono 搭建 API 服务器_。 |
| [Unkey](https://unkey.dev) | Cloudflare Workers | 开源的 API 鉴权与授权平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
| [OpenStatus](https://openstatus.dev) | Bun | 开源的网站与 API 监控平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
| [Deno Benchmarks](https://deno.com/benchmarks) | Deno | 基于 V8 的安全 TypeScript 运行时,_Hono 用于基准测试_。 |
| [Clerk](https://clerk.com) | Cloudflare Workers | 开源的用户管理平台,_Hono 被用于 API 服务器_。 |
还有以下团队也在生产环境中使用 Hono:
- [Drivly](https://driv.ly/) - Cloudflare Workers
- [repeat.dev](https://repeat.dev/) - Cloudflare Workers
想了解更多?请访问 [Who is using Hono in production?](https://github.com/orgs/honojs/discussions/1510)。
## 一分钟体验 Hono
以下演示展示了如何使用 Hono 在 Cloudflare Workers 上创建应用。

## 极速表现
**在 Cloudflare Workers 的各类路由器中,Hono 是最快的。**
```
Hono x 402,820 ops/sec ±4.78% (80 runs sampled)
itty-router x 212,598 ops/sec ±3.11% (87 runs sampled)
sunder x 297,036 ops/sec ±4.76% (77 runs sampled)
worktop x 197,345 ops/sec ±2.40% (88 runs sampled)
Fastest is Hono
✨ Done in 28.06s.
```
查看 [更多基准测试](/docs/concepts/benchmarks)。
## 轻量体积
**Hono 非常小。**在使用 `hono/tiny` 预设并压缩后,体积 **低于 14KB**。
拥有众多中间件和适配器,但只会在使用时才打包。作为对比,Express 的体积为 572KB。
```
$ npx wrangler dev --minify ./src/index.ts
⛅️ wrangler 2.20.0
--------------------
⬣ Listening at http://0.0.0.0:8787
- http://127.0.0.1:8787
- http://192.168.128.165:8787
Total Upload: 11.47 KiB / gzip: 4.34 KiB
```
## 多款路由器
**Hono 提供多种路由器实现。**
**RegExpRouter** 是 JavaScript 世界中最快的路由器。它在派发前先构建一个巨大的正则表达式,用以匹配路由。配合 **SmartRouter**,即可支持所有路由模式。
**LinearRouter** 能够极快地注册路由,适用于每次请求都会初始化应用的运行时。**PatternRouter** 则以简单的方式添加并匹配路由模式,让体积更小。
查看 [更多关于路由的信息](/docs/concepts/routers)。
## Web 标准
得益于 **Web 标准**,Hono 可以运行在众多平台上。
- Cloudflare Workers
- Cloudflare Pages
- Fastly Compute
- Deno
- Bun
- Vercel
- AWS Lambda
- Lambda@Edge
- 以及更多
通过使用 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server),Hono 也能在 Node.js 上运行。
查看 [更多关于 Web 标准的信息](/docs/concepts/web-standard)。
## 中间件与助手
**Hono 拥有大量中间件与助手函数**,真正实现“写得更少,做得更多”。
开箱即用的中间件与助手包括:
- [Basic Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)
- [Bearer Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/bearer-auth)
- [Body Limit](/docs/middleware/builtin/body-limit)
- [Cache](/docs/middleware/builtin/cache)
- [Compress](/docs/middleware/builtin/compress)
- [Context Storage](/docs/middleware/builtin/context-storage)
- [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
- [CORS](/docs/middleware/builtin/cors)
- [ETag](/docs/middleware/builtin/etag)
- [html](/docs/helpers/html)
- [JSX](/docs/guides/jsx)
- [JWT Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/jwt)
- [Logger](/docs/middleware/builtin/logger)
- [Language](/docs/middleware/builtin/language)
- [Pretty JSON](/docs/middleware/builtin/pretty-json)
- [Secure Headers](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers)
- [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
- [Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
- [GraphQL Server](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/graphql-server)
- [Firebase Authentication](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/firebase-auth)
- [Sentry](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/sentry)
- 以及更多!
例如,在 Hono 中仅需几行代码就能加入 ETag 与请求日志:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { etag } from 'hono/etag'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(etag(), logger())
```
查看 [更多关于中间件的信息](/docs/concepts/middleware)。
## 开发者体验
Hono 带来令人愉悦的“**开发者体验**”。
得益于 `Context` 对象,可以轻松获取 Request/Response。
此外,Hono 采用 TypeScript 编写,自带“**类型**”。
例如,路径参数会被推断为字面量类型。
借助 Validator 与 Hono Client `hc`,可以启用 RPC 模式。
在该模式下,你可以继续使用自己喜爱的校验器(如 Zod),轻松在服务端与客户端之间共享 API 规范,从而构建类型安全的应用。
查看 [Hono Stacks](/docs/concepts/stacks)。
# 第三方中间件
“第三方中间件”指的是那些未随 Hono 主包一同发布的中间件。
这些中间件大多基于外部库实现。
### 认证
- [Auth.js(Next Auth)](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/auth-js)
- [Clerk Auth](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/clerk-auth)
- [OAuth Providers](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/oauth-providers)
- [OIDC Auth](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/oidc-auth)
- [Firebase Auth](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/firebase-auth)
- [Verify RSA JWT(JWKS)](https://github.com/wataruoguchi/verify-rsa-jwt-cloudflare-worker)
- [Stytch Auth](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/stytch-auth)
### 校验器
- [ArkType 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/arktype-validator)
- [Effect Schema 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/effect-validator)
- [Standard Schema 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/standard-validator)
- [TypeBox 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/typebox-validator)
- [Typia 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/typia-validator)
- [unknownutil 校验器](https://github.com/ryoppippi/hono-unknownutil-validator)
- [Valibot 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/valibot-validator)
- [Zod 校验器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator)
### OpenAPI
- [Zod OpenAPI](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-openapi)
- [Scalar](https://github.com/scalar/scalar/tree/main/integrations/hono)
- [Swagger UI](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/swagger-ui)
- [Hono OpenAPI](https://github.com/rhinobase/hono-openapi)
### 其他
- [Bun Transpiler](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/bun-transpiler)
- [esbuild Transpiler](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/esbuild-transpiler)
- [Event Emitter](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/event-emitter)
- [GraphQL Server](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/graphql-server)
- [Hono Rate Limiter](https://github.com/rhinobase/hono-rate-limiter)
- [Node WebSocket Helper](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/node-ws)
- [Prometheus Metrics](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/prometheus)
- [OpenTelemetry](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/otel)
- [Qwik City](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/qwik-city)
- [React Compatibility](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/react-compat)
- [React Renderer](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/react-renderer)
- [RONIN(数据库)](https://github.com/ronin-co/hono-client)
- [Sentry](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/sentry)
- [tRPC Server](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/trpc-server)
- [Geo](https://github.com/ktkongtong/hono-geo-middleware/tree/main/packages/middleware)
- [Hono Simple DI](https://github.com/maou-shonen/hono-simple-DI)
- [Highlight.io](https://www.highlight.io/docs/getting-started/backend-sdk/js/hono)
- [Apitally(API 监控与分析)](https://docs.apitally.io/frameworks/hono)
- [Cap Checkpoint](https://capjs.js.org/guide/middleware/hono.html)
# Basic Auth 中间件
这个中间件可以为指定路径启用 Basic 认证。
在 Cloudflare Workers 或其他平台上自己实现 Basic 认证往往比想象中复杂,但借助该中间件就能轻松搞定。
想了解 Basic 认证方案在幕后是如何运作的,请查阅 [MDN 文档](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication#basic_authentication_scheme)。
## Import
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
return c.text('You are authorized')
})
```
若要将认证限定在特定的路由与方法组合:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
return c.text('Viewing page')
})
app.delete(
'/auth/page',
basicAuth({ username: 'hono', password: 'acoolproject' }),
(c) => {
return c.text('Page deleted')
}
)
```
如果你希望自行验证用户,可以指定 `verifyUser` 选项;返回 `true` 表示通过认证。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
basicAuth({
verifyUser: (username, password, c) => {
return (
username === 'dynamic-user' && password === 'hono-password'
)
},
})
)
```
## 选项
### username:`string`
进行认证的用户名。
### password:`string`
与给定用户名匹配的密码。
### realm:`string`
作为 WWW-Authenticate 挑战头一部分返回的领域(Realm)名称,默认值为 `"Secure Area"`。
详情可参阅:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/WWW-Authenticate#directives
### hashFunction:`Function`
用于处理哈希并安全比较密码的函数。
### verifyUser:`(username: string, password: string, c: Context) => boolean | Promise`
自定义的用户验证函数。
### invalidUserMessage:`string | object | MessageFunction`
`MessageFunction` 的签名为 `(c: Context) => string | object | Promise`,用于在用户无效时返回自定义消息。
## 更多选项
### ...users:`{ username: string, password: string }[]`
## 使用示例
### 定义多个用户
该中间件也允许传入额外参数,以对象形式定义更多 `username` 与 `password` 组合。
```ts
app.use(
'/auth/*',
basicAuth(
{
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
// Define other params in the first object
realm: 'www.example.com',
},
{
username: 'hono-admin',
password: 'super-secure',
// Cannot redefine other params here
},
{
username: 'hono-user-1',
password: 'a-secret',
// Or here
}
)
)
```
或者减少硬编码:
```ts
import { users } from '../config/users'
app.use(
'/auth/*',
basicAuth(
{
realm: 'www.example.com',
...users[0],
},
...users.slice(1)
)
)
```
# Bearer Auth 中间件
Bearer Auth 中间件会通过校验请求头中的 API 令牌来提供身份验证功能。
访问端点的 HTTP 客户端需要添加 `Authorization` 请求头,并设置为 `Bearer {token}`。
在终端中使用 `curl` 时类似如下:
```sh
curl -H 'Authorization: Bearer honoiscool' http://localhost:8787/auth/page
```
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { bearerAuth } from 'hono/bearer-auth'
```
## 用法
> [!NOTE]
> 令牌必须匹配正则 `/[A-Za-z0-9._~+/-]+=*/`,否则会返回 400 错误。该正则既兼容 URL 安全的 Base64,也兼容标准 Base64 编码的 JWT。中间件并不要求 Bearer 令牌一定是 JWT,只需符合上述正则即可。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const token = 'honoiscool'
app.use('/api/*', bearerAuth({ token }))
app.get('/api/page', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'You are authorized' })
})
```
若要将认证限定在特定的路由与方法组合:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const token = 'honoiscool'
app.get('/api/page', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'Read posts' })
})
app.post('/api/page', bearerAuth({ token }), (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'Created post!' }, 201)
})
```
如果要实现多种令牌(例如:任意有效令牌可读取,但创建/更新/删除需特权令牌):
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const readToken = 'read'
const privilegedToken = 'read+write'
const privilegedMethods = ['POST', 'PUT', 'PATCH', 'DELETE']
app.on('GET', '/api/page/*', async (c, next) => {
// 有效令牌列表
const bearer = bearerAuth({ token: [readToken, privilegedToken] })
return bearer(c, next)
})
app.on(privilegedMethods, '/api/page/*', async (c, next) => {
// 单个特权令牌
const bearer = bearerAuth({ token: privilegedToken })
return bearer(c, next)
})
// 定义 GET、POST 等处理器
```
若想自行验证令牌值,可以指定 `verifyToken` 选项;返回 `true` 即表示通过。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth-verify-token/*',
bearerAuth({
verifyToken: async (token, c) => {
return token === 'dynamic-token'
},
})
)
```
## 选项
### token:`string` | `string[]`
用于校验传入 Bearer 令牌的字符串。
### realm:`string`
作为 WWW-Authenticate 挑战头一部分返回的领域名称,默认值为 `""`。
更多信息:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/WWW-Authenticate#directives
### prefix:`string`
Authorization 头部值的前缀(也称为 schema),默认值为 `"Bearer"`。
### headerName:`string`
要检查的请求头名称,默认是 `Authorization`。
### hashFunction:`Function`
用于处理哈希并安全比较认证令牌的函数。
### verifyToken:`(token: string, c: Context) => boolean | Promise`
自定义的令牌验证函数。
### noAuthenticationHeaderMessage:`string | object | MessageFunction`
`MessageFunction` 的签名为 `(c: Context) => string | object | Promise`,在请求未携带认证头时返回自定义消息。
### invalidAuthenticationHeaderMessage:`string | object | MessageFunction`
当认证头无效时返回的自定义消息。
### invalidTokenMessage:`string | object | MessageFunction`
当令牌无效时返回的自定义消息。
# Body Limit 中间件
Body Limit 中间件可以限制请求正文(Body)的大小。
该中间件会优先读取请求中的 `Content-Length` 头部(若存在)。
如果未设置,则会以流方式读取正文,一旦超过设定的大小,就会执行错误处理函数。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { bodyLimit } from 'hono/body-limit'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.post(
'/upload',
bodyLimit({
maxSize: 50 * 1024, // 50kb
onError: (c) => {
return c.text('overflow :(', 413)
},
}),
async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.parseBody()
if (body['file'] instanceof File) {
console.log(`Got file sized: ${body['file'].size}`)
}
return c.text('pass :)')
}
)
```
## 选项
### maxSize:`number`
要限制的最大文件大小。默认值为 `100 * 1024`(100kb)。
### onError:`OnError`
当正文超过限制时触发的错误处理函数。
## 在 Bun 中处理大请求
如果你使用 Body Limit 中间件来允许超过默认大小的请求体,可能还需要调整 `Bun.serve` 的配置。[在撰写本文时](https://github.com/oven-sh/bun/blob/f2cfa15e4ef9d730fc6842ad8b79fb7ab4c71cb9/packages/bun-types/bun.d.ts#L2191),`Bun.serve` 的默认请求体限制为 128MiB。即便你在 Hono 的 Body Limit 中间件中设置了更大的值,请求仍会失败,并且中间件中的 `onError` 处理器不会被调用。原因是 `Bun.serve()` 会在将请求交给 Hono 前就把状态码设为 `413` 并终止连接。
因此,如果你希望在 Hono + Bun 中接受超过 128MiB 的请求,需要同时为 Bun 设置更大的限制:
```ts
export default {
port: process.env['PORT'] || 3000,
fetch: app.fetch,
maxRequestBodySize: 1024 * 1024 * 200, // 在此填入你的值
}
```
或者根据你的项目结构:
```ts
Bun.serve({
fetch(req, server) {
return app.fetch(req, { ip: server.requestIP(req) })
},
maxRequestBodySize: 1024 * 1024 * 200, // 在此填入你的值
})
```
# Cache 中间件
Cache 中间件使用 Web 标准中的 [Cache API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Cache)。
目前该中间件支持使用自定义域名的 Cloudflare Workers 项目,以及运行在 [Deno 1.26+](https://github.com/denoland/deno/releases/tag/v1.26.0) 的 Deno 项目,同时也可用于 Deno Deploy。
在 Cloudflare Workers 中,平台会遵循 `Cache-Control` 头并返回缓存的响应。详情可参阅 [Cloudflare 缓存文档](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/cache/)。Deno 不会根据头部自动刷新缓存,因此如果需要更新缓存,需要自行实现机制。
不同平台的使用方式见下文的 [用法](#usage)。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { cache } from 'hono/cache'
```
## 用法
::: code-group
```ts [Cloudflare Workers]
app.get(
'*',
cache({
cacheName: 'my-app',
cacheControl: 'max-age=3600',
})
)
```
```ts [Deno]
// 在 Deno 运行时时必须使用 `wait: true`
app.get(
'*',
cache({
cacheName: 'my-app',
cacheControl: 'max-age=3600',
wait: true,
})
)
```
:::
## 选项
### cacheName:`string` | `(c: Context) => string` | `Promise`
缓存名称,可用来区分存储在不同标识下的缓存。
### wait:`boolean`
指示 Hono 是否需要等待 `cache.put` 返回的 Promise 解析后再继续处理请求。在 Deno 环境中**必须**设置为 `true`。默认值为 `false`。
### cacheControl:`string`
`Cache-Control` 头部的指令字符串。更多信息参考 [MDN 文档](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cache-Control)。未提供该选项时,请求中不会自动添加 `Cache-Control` 头。
### vary:`string` | `string[]`
设置响应中的 `Vary` 头。如果原始响应已经包含 `Vary`,则会合并并去重所有值。若设置为 `*` 则会报错。关于 Vary 头及其对缓存策略的影响,可参阅 [MDN 文档](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Vary)。
### keyGenerator:`(c: Context) => string | Promise`
为 `cacheName` 对应的每个请求生成键,可用于基于请求参数或上下文参数缓存数据。默认值为 `c.req.url`。
### cacheableStatusCodes:`number[]`
需要缓存的状态码数组。默认值为 `[200]`。可以通过该选项缓存特定状态码的响应。
```ts
app.get(
'*',
cache({
cacheName: 'my-app',
cacheControl: 'max-age=3600',
cacheableStatusCodes: [200, 404, 412],
})
)
```
# Combine 中间件
Combine 中间件可以把多个中间件函数组合成一个中间件,提供以下三个工具函数:
- `some`:只要其中一个中间件成功运行即可。
- `every`:依次执行所有中间件。
- `except`:在条件不成立时执行所有中间件。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { some, every, except } from 'hono/combine'
```
## 用法
下面示例展示了如何用 Combine 中间件构建复杂的访问控制规则。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { bearerAuth } from 'hono/bearer-auth'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/cloudflare-workers'
import { every, some } from 'hono/combine'
import { ipRestriction } from 'hono/ip-restriction'
import { rateLimit } from '@/my-rate-limit'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
some(
every(
ipRestriction(getConnInfo, { allowList: ['192.168.0.2'] }),
bearerAuth({ token })
),
// 如果两个条件都满足,则不会执行 rateLimit。
rateLimit()
)
)
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono!'))
```
### some
执行第一个返回成功的中间件。中间件按顺序应用,只要某个中间件成功结束,后续中间件就不会再执行。
```ts
import { some } from 'hono/combine'
import { bearerAuth } from 'hono/bearer-auth'
import { myRateLimit } from '@/rate-limit'
// 如果客户端拥有有效令牌,则跳过限流。
// 否则执行限流。
app.use(
'/api/*',
some(bearerAuth({ token }), myRateLimit({ limit: 100 }))
)
```
### every
依次执行所有中间件,只要有一个失败就会停止。中间件按顺序应用,如果任何一个抛出错误,后续中间件将不会执行。
```ts
import { some, every } from 'hono/combine'
import { bearerAuth } from 'hono/bearer-auth'
import { myCheckLocalNetwork } from '@/check-local-network'
import { myRateLimit } from '@/rate-limit'
// 如果客户端位于本地网络,则跳过认证和限流。
// 否则同时应用认证与限流。
app.use(
'/api/*',
some(
myCheckLocalNetwork(),
every(bearerAuth({ token }), myRateLimit({ limit: 100 }))
)
)
```
### except
当条件满足时跳过执行,其余情况会运行所有中间件。条件可以是字符串或函数,若需要匹配多个目标可传入数组。
```ts
import { except } from 'hono/combine'
import { bearerAuth } from 'hono/bearer-auth'
// 如果访问公共 API,则跳过认证。
// 否则需要有效令牌。
app.use('/api/*', except('/api/public/*', bearerAuth({ token })))
```
# Compress 中间件
该中间件会根据请求头 `Accept-Encoding` 压缩响应正文。
::: info
**注意**:在 Cloudflare Workers 与 Deno Deploy 上,响应正文会自动压缩,因此无需使用此中间件。
**Bun**:该中间件依赖 `CompressionStream`,而 bun 目前尚未支持。
:::
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { compress } from 'hono/compress'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(compress())
```
## 选项
### encoding:`'gzip'` | `'deflate'`
指定可用于压缩响应的算法,可选择 `gzip` 或 `deflate`。若未设置,则默认同时支持两者,并根据 `Accept-Encoding` 自动选择。当客户端在 `Accept-Encoding` 中同时声明两者时,若未提供该选项,将优先使用 `gzip`。
### threshold:`number`
触发压缩的最小字节数,默认值为 1024 字节。
# Context Storage 中间件
Context Storage 中间件会将 Hono 的 `Context` 存入 `AsyncLocalStorage`,以便在全局范围访问。
::: info
**注意**:该中间件依赖 `AsyncLocalStorage`,需要运行环境提供支持。
**Cloudflare Workers**:如需启用 `AsyncLocalStorage`,请在 `wrangler.toml` 中添加 [`nodejs_compat` 或 `nodejs_als` 标志](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/compatibility-dates/#nodejs-compatibility-flag)。
:::
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { contextStorage, getContext } from 'hono/context-storage'
```
## 用法
在应用了 `contextStorage()` 中间件后,可通过 `getContext()` 取得当前的 Context 对象。
```ts
type Env = {
Variables: {
message: string
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.use(contextStorage())
app.use(async (c, next) => {
c.set('message', 'Hello!')
await next()
})
// 可以在处理器之外访问变量。
const getMessage = () => {
return getContext().var.message
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text(getMessage())
})
```
在 Cloudflare Workers 中,还可以在处理器外部访问绑定(bindings)。
```ts
type Env = {
Bindings: {
KV: KVNamespace
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.use(contextStorage())
const setKV = (value: string) => {
return getContext().env.KV.put('key', value)
}
```
# CORS 中间件
Cloudflare Workers 常被用来提供 Web API,并由外部前端调用。
这类场景需要实现 CORS,我们同样可以通过中间件来完成。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { cors } from 'hono/cors'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
// CORS 中间件需在路由之前调用
app.use('/api/*', cors())
app.use(
'/api2/*',
cors({
origin: 'http://example.com',
allowHeaders: ['X-Custom-Header', 'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests'],
allowMethods: ['POST', 'GET', 'OPTIONS'],
exposeHeaders: ['Content-Length', 'X-Kuma-Revision'],
maxAge: 600,
credentials: true,
})
)
app.all('/api/abc', (c) => {
return c.json({ success: true })
})
app.all('/api2/abc', (c) => {
return c.json({ success: true })
})
```
多个允许来源:
```ts
app.use(
'/api3/*',
cors({
origin: ['https://example.com', 'https://example.org'],
})
)
// 也可以传入函数
app.use(
'/api4/*',
cors({
// `c` 为 `Context` 对象
origin: (origin, c) => {
return origin.endsWith('.example.com')
? origin
: 'http://example.com'
},
})
)
```
基于来源动态决定允许的方法:
```ts
app.use(
'/api5/*',
cors({
origin: (origin) =>
origin === 'https://example.com' ? origin : '*',
// `c` 为 `Context` 对象
allowMethods: (origin, c) =>
origin === 'https://example.com'
? ['GET', 'HEAD', 'POST', 'PATCH', 'DELETE']
: ['GET', 'HEAD'],
})
)
```
## 选项
### origin:`string` | `string[]` | `(origin: string, c: Context) => string`
对应 CORS 头 `_Access-Control-Allow-Origin_` 的值。也可以传入回调函数,例如 `origin: (origin) => (origin.endsWith('.example.com') ? origin : 'http://example.com')`。默认值为 `*`。
### allowMethods:`string[]` | `(origin: string, c: Context) => string[]`
对应 `_Access-Control-Allow-Methods_` 头的值。也可以传入回调函数,根据来源动态决定允许的方法。默认值为 `['GET', 'HEAD', 'PUT', 'POST', 'DELETE', 'PATCH']`。
### allowHeaders:`string[]`
对应 `_Access-Control-Allow-Headers_` 头的值。默认值为 `[]`。
### maxAge:`number`
对应 `_Access-Control-Max-Age_` 头的值。
### credentials:`boolean`
对应 `_Access-Control-Allow-Credentials_` 头的值。
### exposeHeaders:`string[]`
对应 `_Access-Control-Expose-Headers_` 头的值。默认值为 `[]`。
## 根据环境配置 CORS
若希望根据运行环境(如开发/生产)调整 CORS 配置,注入环境变量是一种方便方式,可避免让应用自行判断运行环境。示例如下:
```ts
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
const corsMiddlewareHandler = cors({
origin: c.env.CORS_ORIGIN,
})
return corsMiddlewareHandler(c, next)
})
```
## 搭配 Vite 使用
如果在 Vite 中使用 Hono,需要在 `vite.config.ts` 中将 `server.cors` 设为 `false`,以禁用 Vite 自带的 CORS 功能,从而避免与 Hono 的 CORS 中间件冲突。
```ts
// vite.config.ts
import { cloudflare } from '@cloudflare/vite-plugin'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig({
server: {
cors: false, // 禁用 Vite 内建的 CORS 设置
},
plugins: [cloudflare()],
})
```
# CSRF 防护
该中间件通过校验 `Origin` 与 `Sec-Fetch-Site` 请求头来抵御 CSRF 攻击,只要其中任一校验通过即可放行。
中间件仅会对以下请求进行校验:
- 使用不安全 HTTP 方法(非 GET、HEAD、OPTIONS)
- Content-Type 为 HTML 表单可发送的类型(`application/x-www-form-urlencoded`、`multipart/form-data` 或 `text/plain`)
旧版浏览器可能不会发送 `Origin` 头,或运行在移除了这些头部的反向代理环境中,此时该中间件效果会受限,建议改用其他基于 CSRF Token 的方案。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { csrf } from 'hono/csrf'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
// 默认同时验证 origin 与 sec-fetch-site
app.use(csrf())
// 允许特定来源
app.use(csrf({ origin: 'https://myapp.example.com' }))
// 允许多个来源
app.use(
csrf({
origin: [
'https://myapp.example.com',
'https://development.myapp.example.com',
],
})
)
// 允许指定的 sec-fetch-site 值
app.use(csrf({ secFetchSite: 'same-origin' }))
app.use(csrf({ secFetchSite: ['same-origin', 'none'] }))
// 动态校验来源
// 强烈建议验证协议并确保以 `$` 结尾匹配。
// 切勿使用前缀匹配。
app.use(
'*',
csrf({
origin: (origin) =>
/https:\/\/(\w+\.)?myapp\.example\.com$/.test(origin),
})
)
// 动态校验 sec-fetch-site
app.use(
csrf({
secFetchSite: (secFetchSite, c) => {
// 始终允许同源请求
if (secFetchSite === 'same-origin') return true
// 为 webhook 端点允许跨站请求
if (
secFetchSite === 'cross-site' &&
c.req.path.startsWith('/webhook/')
) {
return true
}
return false
},
})
)
```
## 选项
### origin:`string` | `string[]` | `Function`
指定允许通过 CSRF 校验的来源:
- **`string`**:单个允许来源(例如 `'https://example.com'`)
- **`string[]`**:允许来源组成的数组
- **`Function`**:自定义处理函数 `(origin: string, context: Context) => boolean`,可灵活编写校验或放行逻辑
**默认值**:仅允许与请求 URL 同源。
函数会收到请求头中的 `Origin` 值与当前请求的上下文,可基于路径、请求头或其他上下文信息进行动态判断。
### secFetchSite:`string` | `string[]` | `Function`
利用 [Fetch Metadata](https://web.dev/articles/fetch-metadata) 机制,指定允许通过 CSRF 校验的 `Sec-Fetch-Site` 请求头:
- **`string`**:单个允许值(例如 `'same-origin'`)
- **`string[]`**:允许值数组(例如 `['same-origin', 'none']`)
- **`Function`**:自定义处理函数 `(secFetchSite: string, context: Context) => boolean`
**默认值**:仅允许 `'same-origin'`。
常见的 `Sec-Fetch-Site` 取值:
- `same-origin`:来自同源的请求
- `same-site`:来自同站点(不同子域)的请求
- `cross-site`:来自不同站点的请求
- `none`:非网页发起的请求(例如地址栏或书签)
该函数会收到请求头中的 `Sec-Fetch-Site` 值及上下文,可据此动态判断是否允许。
# ETag 中间件
使用该中间件即可轻松为响应添加 ETag 头。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { etag } from 'hono/etag'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use('/etag/*', etag())
app.get('/etag/abc', (c) => {
return c.text('Hono is cool')
})
```
## 保留的响应头
304 响应必须包含与等效的 200 OK 响应相同的头部。默认保留的头包括:Cache-Control、Content-Location、Date、ETag、Expires 与 Vary。
若希望追加更多头部,可使用 `retainedHeaders` 选项,并借助包含默认值的 `RETAINED_304_HEADERS` 数组常量:
```ts
import { etag, RETAINED_304_HEADERS } from 'hono/etag'
// ...
app.use(
'/etag/*',
etag({
retainedHeaders: ['x-message', ...RETAINED_304_HEADERS],
})
)
```
## 选项
### weak:`boolean`
是否使用[弱验证](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Conditional_requests#weak_validation)。若设置为 `true`,会在值前添加 `w/` 前缀。默认值为 `false`。
### retainedHeaders:`string[]`
在 304 响应中需要保留的头部列表。
### generateDigest:`(body: Uint8Array) => ArrayBuffer | Promise`
自定义的摘要生成函数。默认使用 `SHA-1`。该函数会收到响应体的 `Uint8Array`,需要返回 `ArrayBuffer` 或 Promise 的哈希值。
# IP Restriction 中间件
IP Restriction 中间件可基于访问者的 IP 地址限制资源访问。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { ipRestriction } from 'hono/ip-restriction'
```
## 用法
以下示例适用于运行在 Bun 上的应用,仅允许本地访问。将要拒绝的规则写在 `denyList` 中,要允许的规则写在 `allowList` 中。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/bun'
import { ipRestriction } from 'hono/ip-restriction'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
ipRestriction(getConnInfo, {
denyList: [],
allowList: ['127.0.0.1', '::1'],
})
)
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono!'))
```
请将适用于你环境的 [ConnInfo 助手](/docs/helpers/conninfo) 所提供的 `getConnInfo` 作为 `ipRestriction` 的第一个参数。例如在 Deno 中可以这样写:
```ts
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/deno'
import { ipRestriction } from 'hono/ip-restriction'
// ...
app.use(
'*',
ipRestriction(getConnInfo, {
// ...
})
)
```
## 规则
编写规则时可遵循以下格式。
### IPv4
- `192.168.2.0` - 固定 IP 地址
- `192.168.2.0/24` - CIDR 表示法
- `*` - 全部地址
### IPv6
- `::1` - 固定 IP 地址
- `::1/10` - CIDR 表示法
- `*` - 全部地址
## 错误处理
若要自定义错误响应,可通过第三个参数返回一个 `Response`。
```ts
app.use(
'*',
ipRestriction(
getConnInfo,
{
denyList: ['192.168.2.0/24'],
},
async (remote, c) => {
return c.text(`Blocking access from ${remote.addr}`, 403)
}
)
)
```
# JSX Renderer 中间件
JSX Renderer 中间件允许你在渲染 JSX 时,通过 `c.render()` 设置页面布局,而无需调用 `c.setRenderer()`。同时,可在组件中使用 `useRequestContext()` 访问 Context 实例。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { jsxRenderer, useRequestContext } from 'hono/jsx-renderer'
```
## 用法
```jsx
const app = new Hono()
app.get(
'/page/*',
jsxRenderer(({ children }) => {
return (
{children}
)
})
)
app.get('/page/about', (c) => {
return c.render(About me!
)
})
```
## 选项
### docType:`boolean` | `string`
如不希望在 HTML 开头添加 DOCTYPE,可将 `docType` 设为 `false`。
```tsx
app.use(
'*',
jsxRenderer(
({ children }) => {
return (
{children}
)
},
{ docType: false }
)
)
```
你也可以自定义 DOCTYPE:
```tsx
app.use(
'*',
jsxRenderer(
({ children }) => {
return (
{children}
)
},
{
docType:
'',
}
)
)
```
### stream:`boolean` | `Record`
当设置为 `true` 或传入一个对象时,会以流式响应的方式渲染。
```tsx
const AsyncComponent = async () => {
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 1000)) // 延迟 1 秒
return Hi!
}
app.get(
'*',
jsxRenderer(
({ children }) => {
return (
SSR Streaming
{children}
)
},
{ stream: true }
)
)
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.render(
loading...}>
)
})
```
当设置为 `true` 时,会自动添加如下响应头:
```ts
{
'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked',
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=UTF-8',
'Content-Encoding': 'Identity'
}
```
传入对象时,可自定义这些头部的具体取值。
## 嵌套布局
通过 `Layout` 组件可以实现布局嵌套。
```tsx
app.use(
jsxRenderer(({ children }) => {
return (
{children}
)
})
)
const blog = new Hono()
blog.use(
jsxRenderer(({ children, Layout }) => {
return (
{children}
)
})
)
app.route('/blog', blog)
```
## `useRequestContext()`
`useRequestContext()` 会返回当前请求的 Context 实例。
```tsx
import { useRequestContext, jsxRenderer } from 'hono/jsx-renderer'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(jsxRenderer())
const RequestUrlBadge: FC = () => {
const c = useRequestContext()
return {c.req.url}
}
app.get('/page/info', (c) => {
return c.render(
You are accessing:
)
})
```
::: warning
在 Deno 中若启用 JSX 的 `precompile` 选项,将无法使用 `useRequestContext()`。请改用 `react-jsx`:
```json
"compilerOptions": {
"jsx": "precompile", // [!code --]
"jsx": "react-jsx", // [!code ++]
"jsxImportSource": "hono/jsx"
}
}
```
:::
## 扩展 `ContextRenderer`
通过如下方式扩展 `ContextRenderer`,即可向渲染器传入额外数据。例如针对不同页面修改 `` 中的内容。
```tsx
declare module 'hono' {
interface ContextRenderer {
(
content: string | Promise,
props: { title: string }
): Response
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.get(
'/page/*',
jsxRenderer(({ children, title }) => {
return (
{title}
{children}
)
})
)
app.get('/page/favorites', (c) => {
return c.render(
- Eating sushi
- Watching baseball games
,
{
title: 'My favorites',
}
)
})
```
# JWK Auth 中间件
JWK Auth 中间件会使用 JWK(JSON Web Key)验证令牌来为请求进行身份认证。它会检查 `Authorization` 请求头及其他配置来源(如设置了 `cookie` 选项时的 Cookie)。中间件会使用提供的 `keys` 验证令牌,或在指定 `jwks_uri` 时从该地址拉取公钥;如果设置了 `cookie` 选项,还会从 Cookie 中提取令牌。
:::info
客户端发送的 Authorization 头必须携带身份验证方案。
例如:`Bearer my.token.value` 或 `Basic my.token.value`
:::
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { jwk } from 'hono/jwk'
import { verifyWithJwks } from 'hono/jwt'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwk({
jwks_uri: `https://${backendServer}/.well-known/jwks.json`,
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
return c.text('You are authorized')
})
```
获取 payload:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwk({
jwks_uri: `https://${backendServer}/.well-known/jwks.json`,
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
const payload = c.get('jwtPayload')
return c.json(payload) // 例如:{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "iat": 1516239022 }
})
```
允许匿名访问:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwk({
jwks_uri: (c) =>
`https://${c.env.authServer}/.well-known/jwks.json`,
allow_anon: true,
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
const payload = c.get('jwtPayload')
return c.json(payload ?? { message: 'hello anon' })
})
```
## 在中间件外使用 `verifyWithJwks`
`verifyWithJwks` 工具函数可以在 Hono 中间件之外校验 JWT,例如在 SvelteKit 的 SSR 页面或其他服务端环境中:
```ts
const id_payload = await verifyWithJwks(
id_token,
{
jwks_uri: 'https://your-auth-server/.well-known/jwks.json',
},
{
cf: { cacheEverything: true, cacheTtl: 3600 },
}
)
```
## 选项
### keys:`HonoJsonWebKey[] | (c: Context) => Promise`
公钥数组,或返回公钥数组的函数。若传入函数,将收到 Context 作为参数。
### jwks_uri:`string` | `(c: Context) => Promise`
若设置该值,将会从对应 URI 拉取 JWK 列表(JSON 中的 `keys` 字段),并与 `keys` 选项中提供的公钥合并。也可以传入回调函数,根据 Context 动态生成 URI。
### allow_anon:`boolean`
设为 `true` 时,即使请求未携带有效令牌也允许通过。可通过 `c.get('jwtPayload')` 判断请求是否已认证。默认值为 `false`。
### cookie:`string`
若设置该值,将使用该键名从 Cookie 头中提取令牌并进行验证。
### headerName:`string`
要读取 JWT 的请求头名称,默认为 `Authorization`。
# JWT Auth 中间件
JWT Auth 中间件会通过验证 JWT 令牌为请求提供身份认证。
若未设置 `cookie` 选项,中间件会检查 `Authorization` 请求头;可以通过 `headerName` 自定义要检查的头名。
:::info
客户端发送的 Authorization 头必须包含身份验证方案。
例如:`Bearer my.token.value` 或 `Basic my.token.value`
:::
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { jwt } from 'hono/jwt'
import type { JwtVariables } from 'hono/jwt'
```
## 用法
```ts
// 指定变量类型,以便推断 `c.get('jwtPayload')`:
type Variables = JwtVariables
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: Variables }>()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwt({
secret: 'it-is-very-secret',
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
return c.text('You are authorized')
})
```
获取 payload:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwt({
secret: 'it-is-very-secret',
issuer: 'my-trusted-issuer',
})
)
app.get('/auth/page', (c) => {
const payload = c.get('jwtPayload')
return c.json(payload) // 例如:{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "iat": 1516239022, "iss": "my-trusted-issuer" }
})
```
::: tip
`jwt()` 只是一个中间件函数。如果需要使用环境变量(例如 `c.env.JWT_SECRET`),可以这样写:
```js
app.use('/auth/*', (c, next) => {
const jwtMiddleware = jwt({
secret: c.env.JWT_SECRET,
})
return jwtMiddleware(c, next)
})
```
:::
## 选项
### secret:`string`
用于签名的密钥。
### cookie:`string`
若设置该值,将使用对应键名从 Cookie 头中提取令牌并进行验证。
### alg:`string`
用于验证的算法类型,默认值为 `HS256`。
可用算法包括:`HS256` | `HS384` | `HS512` | `RS256` | `RS384` | `RS512` | `PS256` | `PS384` | `PS512` | `ES256` | `ES384` | `ES512` | `EdDSA`。
### headerName:`string`
要读取 JWT 的请求头名称,默认是 `Authorization`。
```ts
app.use(
'/auth/*',
jwt({
secret: 'it-is-very-secret',
headerName: 'x-custom-auth-header',
})
)
```
### verifyOptions:`VerifyOptions`
用于控制令牌验证的选项。
#### verifyOptions.iss:`string | RegExp`
期望的发行者(issuer)。若未设置,则不会校验 `iss` 声明。
#### verifyOptions.nbf:`boolean`
当设置为 `true` 时,如果令牌包含 `nbf`(not before)声明,将进行校验。默认值为 `true`。
#### verifyOptions.iat:`boolean`
当设置为 `true` 时,如果令牌包含 `iat`(issued at)声明,将进行校验。默认值为 `true`。
#### verifyOptions.exp:`boolean`
当设置为 `true` 时,如果令牌包含 `exp`(expiration)声明,将进行校验。默认值为 `true`。
# Language 中间件
Language Detector 中间件会自动识别用户首选语言(Locale),并通过 `c.get('language')` 提供结果。它支持从查询参数、Cookie、请求头以及 URL 路径等多种来源检测语言,非常适合用在国际化(i18n)与按地区定制内容的场景。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { languageDetector } from 'hono/language'
```
## 基础用法
以下示例会按照默认顺序(查询参数 → Cookie → 请求头)检测语言,并在无法识别时回退到英文:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
languageDetector({
supportedLanguages: ['en', 'ar', 'ja'], // 必须包含回退语言
fallbackLanguage: 'en', // 必填
})
)
app.get('/', (c) => {
const lang = c.get('language')
return c.text(`Hello! Your language is ${lang}`)
})
```
### 客户端示例
```sh
# 通过路径
curl http://localhost:8787/ar/home
# 通过查询参数
curl http://localhost:8787/?lang=ar
# 通过 Cookie
curl -H 'Cookie: language=ja' http://localhost:8787/
# 通过请求头
curl -H 'Accept-Language: ar,en;q=0.9' http://localhost:8787/
```
## 默认配置
```ts
export const DEFAULT_OPTIONS: DetectorOptions = {
order: ['querystring', 'cookie', 'header'],
lookupQueryString: 'lang',
lookupCookie: 'language',
lookupFromHeaderKey: 'accept-language',
lookupFromPathIndex: 0,
caches: ['cookie'],
ignoreCase: true,
fallbackLanguage: 'en',
supportedLanguages: ['en'],
cookieOptions: {
sameSite: 'Strict',
secure: true,
maxAge: 365 * 24 * 60 * 60,
httpOnly: true,
},
debug: false,
}
```
## 关键行为
### 检测流程
1. **顺序**:默认按以下顺序检查来源:
- 查询参数(?lang=ar)
- Cookie(language=ar)
- `Accept-Language` 请求头
2. **缓存**:会将检测到的语言写入 Cookie(默认 1 年)
3. **回退**:若未能检测到有效语言,则使用 `fallbackLanguage`(该值必须存在于 `supportedLanguages`)
## 高级配置
### 自定义检测顺序
优先从路径(如 `/en/about`)检测:
```ts
app.use(
languageDetector({
order: ['path', 'cookie', 'querystring', 'header'],
lookupFromPathIndex: 0, // /en/profile → 索引 0 对应 'en'
supportedLanguages: ['en', 'ar'],
fallbackLanguage: 'en',
})
)
```
### 转换语言代码
对复杂的语言代码进行归一化(例如 `en-US` → `en`):
```ts
app.use(
languageDetector({
convertDetectedLanguage: (lang) => lang.split('-')[0],
supportedLanguages: ['en', 'ja'],
fallbackLanguage: 'en',
})
)
```
### 配置 Cookie
```ts
app.use(
languageDetector({
lookupCookie: 'app_lang',
caches: ['cookie'],
cookieOptions: {
path: '/', // Cookie 路径
sameSite: 'Lax', // SameSite 策略
secure: true, // 仅通过 HTTPS 发送
maxAge: 86400 * 365, // 有效期 1 年
httpOnly: true, // 前端 JS 不可访问
domain: '.example.com', // 可选:指定域名
},
})
)
```
若需禁用 Cookie 缓存:
```ts
languageDetector({
caches: false,
})
```
### 调试
打印检测日志:
```ts
languageDetector({
debug: true, // 输出示例:“Detected from querystring: ar”
})
```
## 选项参考
### 基础选项
| 选项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 必填 | 说明 |
| :------------------- | :--------------- | :------------------------------------ | :------- | :--------------------- |
| `supportedLanguages` | `string[]` | `['en']` | 是 | 允许的语言代码 |
| `fallbackLanguage` | `string` | `'en'` | 是 | 默认语言 |
| `order` | `DetectorType[]` | `['querystring', 'cookie', 'header']` | 否 | 检测顺序 |
| `debug` | `boolean` | `false` | 否 | 是否输出日志 |
### 检测相关选项
| 选项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| :-------------------- | :------- | :------------------ | :------------------- |
| `lookupQueryString` | `string` | `'lang'` | 查询参数名 |
| `lookupCookie` | `string` | `'language'` | Cookie 名称 |
| `lookupFromHeaderKey` | `string` | `'accept-language'` | 请求头名称 |
| `lookupFromPathIndex` | `number` | `0` | 路径分段索引 |
### Cookie 相关选项
| 选项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| :----------------------- | :---------------------------- | :----------- | :------------------- |
| `caches` | `CacheType[] \| false` | `['cookie']` | 缓存策略 |
| `cookieOptions.path` | `string` | `'/'` | Cookie 路径 |
| `cookieOptions.sameSite` | `'Strict' \| 'Lax' \| 'None'` | `'Strict'` | SameSite 策略 |
| `cookieOptions.secure` | `boolean` | `true` | 是否仅通过 HTTPS 发送 |
| `cookieOptions.maxAge` | `number` | `31536000` | 过期时间(秒) |
| `cookieOptions.httpOnly` | `boolean` | `true` | 是否禁止 JS 访问 |
| `cookieOptions.domain` | `string` | `undefined` | Cookie 域名 |
### 高级选项
| 选项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| :------------------------ | :------------------------- | :---------- | :------------------------ |
| `ignoreCase` | `boolean` | `true` | 是否忽略大小写 |
| `convertDetectedLanguage` | `(lang: string) => string` | `undefined` | 自定义语言代码转换 |
## 校验与错误处理
- `fallbackLanguage` 必须出现在 `supportedLanguages` 中(否则初始化时会抛错)
- `lookupFromPathIndex` 必须大于等于 0
- 配置无效时会在中间件初始化阶段抛出错误
- 检测失败会静默使用 `fallbackLanguage`
## 常见示例
### 基于路径的路由
```ts
app.get('/:lang/home', (c) => {
const lang = c.get('language') // 'en'、'ar' 等
return c.json({ message: getLocalizedContent(lang) })
})
```
### 支持多种语言代码
```ts
languageDetector({
supportedLanguages: ['en', 'en-GB', 'ar', 'ar-EG'],
convertDetectedLanguage: (lang) => lang.replace('_', '-'), // 统一格式
})
```
# Logger 中间件
简单易用的日志中间件。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(logger())
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono!'))
```
## 日志内容
Logger 中间件会为每个请求记录以下信息:
- **入站请求**:记录 HTTP 方法、请求路径以及请求内容。
- **出站响应**:记录 HTTP 方法、请求路径、响应状态码以及请求/响应耗时。
- **状态码着色**:不同范围的状态码会使用不同颜色,方便快速识别。
- **耗时显示**:请求-响应的耗时以可读的格式输出(毫秒或秒)。
借助 Logger 中间件,你可以更轻松地监控 Hono 应用的请求/响应流,并快速定位问题或性能瓶颈。
你还可以传入自定义的 `PrintFunc` 来扩展日志输出方式。
## PrintFunc
Logger 中间件可以接收一个可选的 `PrintFunc` 参数,用于自定义日志行为或追加额外信息。
## 选项
### fn:`PrintFunc(str: string, ...rest: string[])`
- `str`:由 Logger 中间件传入的主消息。
- `...rest`:需要一并输出到控制台的其他字符串。
### 示例
为 Logger 中间件提供自定义 `PrintFunc`:
```ts
export const customLogger = (message: string, ...rest: string[]) => {
console.log(message, ...rest)
}
app.use(logger(customLogger))
```
在路由中使用自定义日志:
```ts
app.post('/blog', (c) => {
// 路由逻辑
customLogger('Blog saved:', `Path: ${blog.url},`, `ID: ${blog.id}`)
// 输出示例:
// <-- POST /blog
// Blog saved: Path: /blog/example, ID: 1
// --> POST /blog 201 93ms
// 返回 Context
})
```
# Method Override 中间件
该中间件会根据表单、请求头或查询参数中的配置,将请求转交给与原始方法不同的处理器并返回其响应。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { methodOverride } from 'hono/method-override'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
// 未传入选项时,会读取表单中的 `_method` 字段,例如 DELETE,作为要执行的请求方法。
app.use('/posts', methodOverride({ app }))
app.delete('/posts', (c) => {
// ....
})
```
## 示例
由于 HTML 表单无法直接发送 DELETE 方法,可将 `_method` 字段设为 `DELETE` 再提交,请求就会执行 `app.delete()` 对应的处理器。
HTML 表单:
```html
```
应用逻辑:
```ts
import { methodOverride } from 'hono/method-override'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('/posts', methodOverride({ app }))
app.delete('/posts', () => {
// ...
})
```
你也可以调整默认字段,或改为使用请求头、查询参数:
```ts
app.use('/posts', methodOverride({ app, form: '_custom_name' }))
app.use(
'/posts',
methodOverride({ app, header: 'X-METHOD-OVERRIDE' })
)
app.use('/posts', methodOverride({ app, query: '_method' }))
```
## 选项
### app:`Hono`
应用中使用的 `Hono` 实例。
### form:`string`
包含方法名的表单字段名称,默认值为 `_method`。
### header:`boolean`
包含方法名的请求头名称。
### query:`boolean`
包含方法名的查询参数名称。
# Pretty JSON 中间件
Pretty JSON 中间件可以为 JSON 响应正文启用“美化打印”。
只需在 URL 查询参数中添加 `?pretty`,JSON 字符串就会以缩进形式返回。
```js
// GET /
{"project":{"name":"Hono","repository":"https://github.com/honojs/hono"}}
```
将变为:
```js
// GET /?pretty
{
"project": {
"name": "Hono",
"repository": "https://github.com/honojs/hono"
}
}
```
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { prettyJSON } from 'hono/pretty-json'
```
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(prettyJSON()) // 若需配置可用 prettyJSON({ space: 4 })
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'Hono!' })
})
```
## 选项
### space:`number`
缩进所使用的空格数量,默认值为 `2`。
### query:`string`
触发美化的查询参数名称,默认值为 `pretty`。
# Request ID 中间件
Request ID 中间件会为每个请求生成唯一 ID,便于在处理器中使用。
::: info
**Node.js**:该中间件使用 `crypto.randomUUID()` 生成 ID。全局 `crypto` 自 Node.js 20 起才默认提供,因此更早版本可能会报错,此时可通过 `generator` 选项自定义生成方式。不过若使用 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server),它会自动在全局注入 `crypto`,无需额外配置。
:::
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { requestId } from 'hono/request-id'
```
## 用法
只要应用了 Request ID 中间件,就能在处理器或后续中间件中通过 `requestId` 变量访问该 ID。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use('*', requestId())
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text(`Your request id is ${c.get('requestId')}`)
})
```
如果希望显式指定类型,可导入 `RequestIdVariables` 并在 `new Hono()` 的泛型参数中传入:
```ts
import type { RequestIdVariables } from 'hono/request-id'
const app = new Hono<{
Variables: RequestIdVariables
}>()
```
### 自定义 Request ID
当请求头中包含自定义 ID(默认读取 `X-Request-Id`)时,中间件会直接使用该值而不再生成新的 ID:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use('*', requestId())
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text(`${c.get('requestId')}`)
})
const res = await app.request('/', {
headers: {
'X-Request-Id': 'your-custom-id',
},
})
console.log(await res.text()) // your-custom-id
```
若要禁用该行为,可将 [`headerName` 选项](#headername-string) 设为空字符串。
## 选项
### limitLength:`number`
请求 ID 的最大长度,默认值为 `255`。
### headerName:`string`
用于读取请求 ID 的请求头名称,默认值为 `X-Request-Id`。
### generator:`(c: Context) => string`
自定义的请求 ID 生成函数,默认使用 `crypto.randomUUID()`。
# Secure Headers 中间件
Secure Headers 中间件可简化安全响应头的配置。它借鉴了 Helmet 的能力,允许你按需启用或禁用特定的安全头。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { secureHeaders } from 'hono/secure-headers'
```
## 用法
默认情况下即可使用推荐设置:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(secureHeaders())
```
如需关闭某些头部,可将对应选项设为 `false`:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
secureHeaders({
xFrameOptions: false,
xXssProtection: false,
})
)
```
也可以通过字符串覆盖默认值:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
secureHeaders({
strictTransportSecurity:
'max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload',
xFrameOptions: 'DENY',
xXssProtection: '1',
})
)
```
## 支持的选项
每个选项都会映射到对应的响应头键值对。
| 选项 | 响应头 | 值 | 默认值 |
| ------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------- |
| - | X-Powered-By | (删除该头) | True |
| contentSecurityPolicy | [Content-Security-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP) | 用法:见[配置 Content-Security-Policy](#setting-content-security-policy) | No Setting |
| contentSecurityPolicyReportOnly | [Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only) | 用法:见[配置 Content-Security-Policy](#setting-content-security-policy) | No Setting |
| crossOriginEmbedderPolicy | [Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy) | require-corp | **False** |
| crossOriginResourcePolicy | [Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy) | same-origin | True |
| crossOriginOpenerPolicy | [Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy) | same-origin | True |
| originAgentCluster | [Origin-Agent-Cluster](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Origin-Agent-Cluster) | ?1 | True |
| referrerPolicy | [Referrer-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Referrer-Policy) | no-referrer | True |
| reportingEndpoints | [Reporting-Endpoints](https://www.w3.org/TR/reporting-1/#header) | 用法:见[配置 Content-Security-Policy](#setting-content-security-policy) | No Setting |
| reportTo | [Report-To](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Content-Security-Policy/report-to) | 用法:见[配置 Content-Security-Policy](#setting-content-security-policy) | No Setting |
| strictTransportSecurity | [Strict-Transport-Security](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Strict-Transport-Security) | max-age=15552000; includeSubDomains | True |
| xContentTypeOptions | [X-Content-Type-Options](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Content-Type-Options) | nosniff | True |
| xDnsPrefetchControl | [X-DNS-Prefetch-Control](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-DNS-Prefetch-Control) | off | True |
| xDownloadOptions | [X-Download-Options](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/blogs/ie/ie8-security-part-v-comprehensive-protection#mime-handling-force-save) | noopen | True |
| xFrameOptions | [X-Frame-Options](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Frame-Options) | SAMEORIGIN | True |
| xPermittedCrossDomainPolicies | [X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies) | none | True |
| xXssProtection | [X-XSS-Protection](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-XSS-Protection) | 0 | True |
| permissionPolicy | [Permissions-Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Permissions-Policy) | 用法:见[配置 Permission-Policy](#setting-permission-policy) | No Setting |
## 中间件冲突
如果多个中间件会修改同一个头部,需要注意执行顺序。
如下所示,Secure Headers 先执行,会移除 `x-powered-by`:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(secureHeaders())
app.use(poweredBy())
```
而以下顺序会先执行 Powered-By,再由 Secure Headers 保留其结果:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(poweredBy())
app.use(secureHeaders())
```
## 配置 Content-Security-Policy
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'/test',
secureHeaders({
reportingEndpoints: [
{
name: 'endpoint-1',
url: 'https://example.com/reports',
},
],
// 或者使用 reportTo
// reportTo: [
// {
// group: 'endpoint-1',
// max_age: 10886400,
// endpoints: [{ url: 'https://example.com/reports' }],
// },
// ],
contentSecurityPolicy: {
defaultSrc: ["'self'"],
baseUri: ["'self'"],
childSrc: ["'self'"],
connectSrc: ["'self'"],
fontSrc: ["'self'", 'https:', 'data:'],
formAction: ["'self'"],
frameAncestors: ["'self'"],
frameSrc: ["'self'"],
imgSrc: ["'self'", 'data:'],
manifestSrc: ["'self'"],
mediaSrc: ["'self'"],
objectSrc: ["'none'"],
reportTo: 'endpoint-1',
sandbox: ['allow-same-origin', 'allow-scripts'],
scriptSrc: ["'self'"],
scriptSrcAttr: ["'none'"],
scriptSrcElem: ["'self'"],
styleSrc: ["'self'", 'https:', "'unsafe-inline'"],
styleSrcAttr: ['none'],
styleSrcElem: ["'self'", 'https:', "'unsafe-inline'"],
upgradeInsecureRequests: [],
workerSrc: ["'self'"],
},
})
)
```
### `nonce` 属性
可通过从 `hono/secure-headers` 导入的 `NONCE` 常量,在 `scriptSrc` 或 `styleSrc` 中添加 [`nonce` 属性](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Global_attributes/nonce):
```tsx
import { secureHeaders, NONCE } from 'hono/secure-headers'
import type { SecureHeadersVariables } from 'hono/secure-headers'
// 指定变量类型,以便推断 `c.get('secureHeadersNonce')`
type Variables = SecureHeadersVariables
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: Variables }>()
// 为 scriptSrc 设置预定义的 nonce 值:
app.get(
'*',
secureHeaders({
contentSecurityPolicy: {
scriptSrc: [NONCE, 'https://allowed1.example.com'],
},
})
)
// 在处理器中读取 `c.get('secureHeadersNonce')`:
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
{/** contents */}
)
})
```
若希望自行生成 nonce,可传入函数:
```tsx
const app = new Hono<{
Variables: { myNonce: string }
}>()
const myNonceGenerator: ContentSecurityPolicyOptionHandler = (c) => {
// 每次请求都会调用此函数
const nonce = Math.random().toString(36).slice(2)
c.set('myNonce', nonce)
return `'nonce-${nonce}'`
}
app.get(
'*',
secureHeaders({
contentSecurityPolicy: {
scriptSrc: [myNonceGenerator, 'https://allowed1.example.com'],
},
})
)
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
{/** contents */}
)
})
```
## 配置 Permission-Policy
`Permission-Policy` 头可用来控制浏览器对特性与 API 的访问。示例如下:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
secureHeaders({
permissionsPolicy: {
fullscreen: ['self'], // fullscreen=(self)
bluetooth: ['none'], // bluetooth=(none)
payment: ['self', 'https://example.com'], // payment=(self "https://example.com")
syncXhr: [], // sync-xhr=()
camera: false, // camera=none
microphone: true, // microphone=*
geolocation: ['*'], // geolocation=*
usb: ['self', 'https://a.example.com', 'https://b.example.com'], // usb=(self "https://a.example.com" "https://b.example.com")
accelerometer: ['https://*.example.com'], // accelerometer=("https://*.example.com")
gyroscope: ['src'], // gyroscope=(src)
magnetometer: [
'https://a.example.com',
'https://b.example.com',
], // magnetometer=("https://a.example.com" "https://b.example.com")
},
})
)
```
# Timeout 中间件
Timeout 中间件可帮助你轻松管理请求超时,为请求设定最大执行时长,并在超时后返回自定义错误响应。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { timeout } from 'hono/timeout'
```
## 用法
以下示例展示了默认配置与自定义配置:
默认配置:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
// 为 /api 路径设置 5 秒超时
app.use('/api', timeout(5000))
// 路由处理
app.get('/api/data', async (c) => {
// 处理逻辑
return c.json({ data: 'Your data here' })
})
```
自定义配置:
```ts
import { HTTPException } from 'hono/http-exception'
// 自定义异常工厂函数
const customTimeoutException = (context) =>
new HTTPException(408, {
message: `Request timeout after waiting ${context.req.headers.get(
'Duration'
)} seconds. Please try again later.`,
})
// 若仅需固定消息
// const customTimeoutException = new HTTPException(408, {
// message: 'Operation timed out. Please try again later.'
// })
// 为 /api/long-process 设置 1 分钟超时并使用自定义异常
app.use('/api/long-process', timeout(60000, customTimeoutException))
app.get('/api/long-process', async (c) => {
// 模拟耗时操作
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 61000))
return c.json({ data: 'This usually takes longer' })
})
```
## 注意事项
- 超时时长使用毫秒,超时后中间件会拒绝 Promise,并可能抛出异常。
- Timeout 中间件无法直接用于流式响应。此类场景可配合 `stream.close` 与 `setTimeout` 一同使用。
```ts
app.get('/sse', async (c) => {
let id = 0
let running = true
let timer: number | undefined
return streamSSE(c, async (stream) => {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Stream timeout reached, closing stream')
stream.close()
}, 3000) as unknown as number
stream.onAbort(async () => {
console.log('Client closed connection')
running = false
clearTimeout(timer)
})
while (running) {
const message = `It is ${new Date().toISOString()}`
await stream.writeSSE({
data: message,
event: 'time-update',
id: String(id++),
})
await stream.sleep(1000)
}
})
})
```
## 中间件冲突
当使用其他错误处理或与时间相关的中间件时,请注意调用顺序,避免影响 Timeout 中间件的行为。
# Server-Timing 中间件
[Server-Timing](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Server-Timing) 中间件会在响应头中提供性能指标。
::: info
注意:在 Cloudflare Workers 上,定时器指标可能不够精确,因为[计时器仅记录最近一次 I/O 的耗时](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/learning/security-model/#step-1-disallow-timers-and-multi-threading)。
:::
## 导入
```ts [npm]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { timing, setMetric, startTime, endTime } from 'hono/timing'
import type { TimingVariables } from 'hono/timing'
```
## 用法
```js
// 指定变量类型,以推断 `c.get('metric')`
type Variables = TimingVariables
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: Variables }>()
// 在路由上应用中间件
app.use(timing());
app.get('/', async (c) => {
// 添加自定义指标
setMetric(c, 'region', 'europe-west3')
// 添加带计时的指标,单位必须为毫秒
setMetric(c, 'custom', 23.8, 'My custom Metric')
// 启动新的计时器
startTime(c, 'db');
const data = await db.findMany(...);
// 结束计时器
endTime(c, 'db');
return c.json({ response: data });
});
```
### 条件启用
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.use(
'*',
timing({
// c 为请求的 Context
enabled: (c) => c.req.method === 'POST',
})
)
```
## 效果
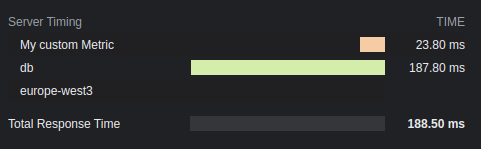
## 选项
### total:`boolean`
是否展示总响应时间。默认值为 `true`。
### enabled:`boolean` | `(c: Context) => boolean`
是否在响应头中添加计时信息。默认值为 `true`。
### totalDescription:`boolean`
总响应时间的描述信息,默认值为 `Total Response Time`。
### autoEnd:`boolean`
是否在请求结束时自动结束通过 `startTime()` 开启的计时器。若设置为 `false`,未手动结束的计时器不会出现在结果中。
### crossOrigin:`boolean` | `string` | `(c: Context) => boolean | string`
设置哪些来源可以读取该计时头:
- 设为 `false` 时,仅当前来源可读。
- 设为 `true` 时,所有来源可读。
- 若为字符串,可指定域名(多个域名用逗号分隔)。
默认值为 `false`。详情参阅[官方文档](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Timing-Allow-Origin)。
# Trailing Slash 中间件
该中间件用于在 GET 请求中处理 URL 末尾的斜杠。
如果资源未找到,`appendTrailingSlash` 会把 URL 重定向到带斜杠的版本;`trimTrailingSlash` 则会移除末尾斜杠。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import {
appendTrailingSlash,
trimTrailingSlash,
} from 'hono/trailing-slash'
```
## 用法
示例:将 `/about/me` 的 GET 请求重定向到 `/about/me/`。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { appendTrailingSlash } from 'hono/trailing-slash'
const app = new Hono({ strict: true })
app.use(appendTrailingSlash())
app.get('/about/me/', (c) => c.text('With Trailing Slash'))
```
示例:将 `/about/me/` 的 GET 请求重定向到 `/about/me`。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { trimTrailingSlash } from 'hono/trailing-slash'
const app = new Hono({ strict: true })
app.use(trimTrailingSlash())
app.get('/about/me', (c) => c.text('Without Trailing Slash'))
```
## 注意
仅在请求方法为 `GET` 且响应状态码为 `404` 时生效。
# Accepts 助手
Accepts 助手用于处理请求中的 Accept 系列请求头。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { accepts } from 'hono/accepts'
```
## `accepts()`
`accepts()` 函数会读取 Accept 请求头(例如 Accept-Encoding 与 Accept-Language),并返回最合适的取值。
```ts
import { accepts } from 'hono/accepts'
app.get('/', (c) => {
const accept = accepts(c, {
header: 'Accept-Language',
supports: ['en', 'ja', 'zh'],
default: 'en',
})
return c.json({ lang: accept })
})
```
### `AcceptHeader` 类型
`AcceptHeader` 类型的定义如下:
```ts
export type AcceptHeader =
| 'Accept'
| 'Accept-Charset'
| 'Accept-Encoding'
| 'Accept-Language'
| 'Accept-Patch'
| 'Accept-Post'
| 'Accept-Ranges'
```
## 配置项
### header: `AcceptHeader`
目标 Accept 请求头。
### supports: `string[]`
应用所支持的请求头取值。
### default: `string`
默认返回的值。
### match: `(accepts: Accept[], config: acceptsConfig) => string`
自定义匹配函数。
# Adapter 助手
Adapter 助手通过统一的接口,让你可以无缝访问不同平台。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { env, getRuntimeKey } from 'hono/adapter'
```
## `env()`
`env()` 函数用于在不同运行时中获取环境变量,适用范围不仅限于 Cloudflare Workers 的 Bindings。`env(c)` 返回的值会随着运行时而有所不同。
```ts
import { env } from 'hono/adapter'
app.get('/env', (c) => {
// 在 Node.js 或 Bun 中,NAME 对应 process.env.NAME
// 在 Cloudflare 中,NAME 来自 `wrangler.toml`
const { NAME } = env<{ NAME: string }>(c)
return c.text(NAME)
})
```
支持的运行时、无服务器平台与云服务:
- Cloudflare Workers
- `wrangler.toml`
- `wrangler.jsonc`
- Deno
- [`Deno.env`](https://docs.deno.com/runtime/manual/basics/env_variables)
- `.env` 文件
- Bun
- [`Bun.env`](https://bun.sh/guides/runtime/set-env)
- `process.env`
- Node.js
- `process.env`
- Vercel
- [Vercel 的环境变量](https://vercel.com/docs/projects/environment-variables)
- AWS Lambda
- [AWS Lambda 的环境变量](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/samples-blank.html#samples-blank-architecture)
- Lambda@Edge\
Lambda 不支持在 Lambda@Edge 中使用环境变量,你需要改用 [Lambda@Edge 事件](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide/lambda-event-structure.html)。
- Fastly Compute\
在 Fastly Compute 中,可以通过 ConfigStore 管理自定义数据。
- Netlify\
在 Netlify 中,可以使用 [Netlify Contexts](https://docs.netlify.com/site-deploys/overview/#deploy-contexts) 管理自定义数据。
### 指定运行时
你可以将运行时键作为第二个参数传入,以便从指定的运行时读取环境变量。
```ts
app.get('/env', (c) => {
const { NAME } = env<{ NAME: string }>(c, 'workerd')
return c.text(NAME)
})
```
## `getRuntimeKey()`
`getRuntimeKey()` 函数会返回当前运行时的标识符。
```ts
app.get('/', (c) => {
if (getRuntimeKey() === 'workerd') {
return c.text('You are on Cloudflare')
} else if (getRuntimeKey() === 'bun') {
return c.text('You are on Bun')
}
...
})
```
### 可用的运行时键
以下列出了可用的运行时键。尚未支持的运行时可能会被标记为 `other`,部分键名参考了 [WinterCG 的 Runtime Keys 提案](https://runtime-keys.proposal.wintercg.org/)。
- `workerd` - Cloudflare Workers
- `deno`
- `bun`
- `node`
- `edge-light` - Vercel Edge Functions
- `fastly` - Fastly Compute
- `other` - 其他未知运行时键
# ConnInfo 助手
ConnInfo 助手用于获取连接信息,例如客户端的远程地址等。
## 导入
::: code-group
```ts [Cloudflare Workers]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/cloudflare-workers'
```
```ts [Deno]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/deno'
```
```ts [Bun]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/bun'
```
```ts [Vercel]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/vercel'
```
```ts [Lambda@Edge]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
```
```ts [Node.js]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getConnInfo } from '@hono/node-server/conninfo'
```
:::
## 用法
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
const info = getConnInfo(c) // info 类型为 `ConnInfo`
return c.text(`Your remote address is ${info.remote.address}`)
})
```
## 类型定义
`getConnInfo()` 返回值的类型定义如下:
```ts
type AddressType = 'IPv6' | 'IPv4' | undefined
type NetAddrInfo = {
/**
* 传输协议类型
*/
transport?: 'tcp' | 'udp'
/**
* 传输端口号
*/
port?: number
address?: string
addressType?: AddressType
} & (
| {
/**
* 主机名(如 IP 地址)
*/
address: string
/**
* 主机名类型
*/
addressType: AddressType
}
| {}
)
/**
* HTTP 连接信息
*/
interface ConnInfo {
/**
* 远端信息
*/
remote: NetAddrInfo
}
```
# Cookie 助手
Cookie 助手提供简洁的接口来管理 Cookie,便于开发者设置、解析与删除 Cookie。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import {
deleteCookie,
getCookie,
getSignedCookie,
setCookie,
setSignedCookie,
generateCookie,
generateSignedCookie,
} from 'hono/cookie'
```
## 用法
### 普通 Cookie
```ts
app.get('/cookie', (c) => {
setCookie(c, 'cookie_name', 'cookie_value')
const yummyCookie = getCookie(c, 'cookie_name')
deleteCookie(c, 'cookie_name')
const allCookies = getCookie(c)
// ...
})
```
### 签名 Cookie
**注意**:由于 WebCrypto API 的异步特性(用于生成 HMAC SHA-256 签名),签名 Cookie 的设置与读取都返回 Promise。
```ts
app.get('/signed-cookie', async (c) => {
const secret = 'secret' // 确保密钥长度足够安全
await setSignedCookie(c, 'cookie_name0', 'cookie_value', secret)
const fortuneCookie = await getSignedCookie(
c,
secret,
'cookie_name0'
)
deleteCookie(c, 'cookie_name0')
// 如果签名被篡改或无效,`getSignedCookie` 会返回 `false`
const allSignedCookies = await getSignedCookie(c, secret)
// ...
})
```
### 生成 Cookie
`generateCookie` 与 `generateSignedCookie` 函数允许你直接生成 Cookie 字符串,而无需在响应头中设置。
#### `generateCookie`
```ts
// 基础用法
const cookie = generateCookie('delicious_cookie', 'macha')
// 返回:'delicious_cookie=macha; Path=/'
// 带配置项的 Cookie
const cookie = generateCookie('delicious_cookie', 'macha', {
path: '/',
secure: true,
httpOnly: true,
domain: 'example.com',
})
```
#### `generateSignedCookie`
```ts
// 基础的签名 Cookie 生成
const signedCookie = await generateSignedCookie(
'delicious_cookie',
'macha',
'secret chocolate chips'
)
// 带配置项的签名 Cookie
const signedCookie = await generateSignedCookie(
'delicious_cookie',
'macha',
'secret chocolate chips',
{
path: '/',
secure: true,
httpOnly: true,
}
)
```
**注意**:与 `setCookie` 和 `setSignedCookie` 不同,这两个函数只会返回生成好的 Cookie 字符串,如有需要需自行设置到响应头中。
## 配置项
### `setCookie` 与 `setSignedCookie`
- domain: `string`
- expires: `Date`
- httpOnly: `boolean`
- maxAge: `number`
- path: `string`
- secure: `boolean`
- sameSite: `'Strict'` | `'Lax'` | `'None'`
- priority: `'Low' | 'Medium' | 'High'`
- prefix: `secure` | `'host'`
- partitioned: `boolean`
示例:
```ts
// 普通 Cookie
setCookie(c, 'great_cookie', 'banana', {
path: '/',
secure: true,
domain: 'example.com',
httpOnly: true,
maxAge: 1000,
expires: new Date(Date.UTC(2000, 11, 24, 10, 30, 59, 900)),
sameSite: 'Strict',
})
// 签名 Cookie
await setSignedCookie(
c,
'fortune_cookie',
'lots-of-money',
'secret ingredient',
{
path: '/',
secure: true,
domain: 'example.com',
httpOnly: true,
maxAge: 1000,
expires: new Date(Date.UTC(2000, 11, 24, 10, 30, 59, 900)),
sameSite: 'Strict',
}
)
```
### `deleteCookie`
- path: `string`
- secure: `boolean`
- domain: `string`
示例:
```ts
deleteCookie(c, 'banana', {
path: '/',
secure: true,
domain: 'example.com',
})
```
`deleteCookie` 会返回被删除的值:
```ts
const deletedCookie = deleteCookie(c, 'delicious_cookie')
```
## `__Secure-` 与 `__Host-` 前缀
Cookie 助手支持在 Cookie 名称中使用 `__Secure-` 与 `__Host-` 前缀。
如果想确认 Cookie 名称是否携带前缀,可以通过 `prefix` 选项指定期望的前缀。
```ts
const securePrefixCookie = getCookie(c, 'yummy_cookie', 'secure')
const hostPrefixCookie = getCookie(c, 'yummy_cookie', 'host')
const securePrefixSignedCookie = await getSignedCookie(
c,
secret,
'fortune_cookie',
'secure'
)
const hostPrefixSignedCookie = await getSignedCookie(
c,
secret,
'fortune_cookie',
'host'
)
```
同样地,如果在设置 Cookie 时需要指定前缀,可以为 `prefix` 选项赋值。
```ts
setCookie(c, 'delicious_cookie', 'macha', {
prefix: 'secure', // 或 `host`
})
await setSignedCookie(
c,
'delicious_cookie',
'macha',
'secret choco chips',
{
prefix: 'secure', // 或 `host`
}
)
```
## 遵循最佳实践
最新的 Cookie RFC(又称 cookie-bis)与 CHIPS 规范提出了一系列 Cookie 设置最佳实践,开发者应遵循这些规则。
- [RFC6265bis-13](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-rfc6265bis-13)
- `Max-Age`/`Expires` 限制
- `__Host-`/`__Secure-` 前缀限制
- [CHIPS-01](https://www.ietf.org/archive/id/draft-cutler-httpbis-partitioned-cookies-01.html)
- `Partitioned` 限制
Hono 遵循上述最佳实践。当出现以下情况时,Cookie 助手会抛出 `Error`:
- Cookie 名称以 `__Secure-` 开头,但未设置 `secure` 选项。
- Cookie 名称以 `__Host-` 开头,但未设置 `secure` 选项。
- Cookie 名称以 `__Host-` 开头,但 `path` 不是 `/`。
- Cookie 名称以 `__Host-` 开头,但设置了 `domain`。
- `maxAge` 选项的值大于 400 天。
- `expires` 选项的值晚于当前时间 400 天。
# css 助手
css 助手(`hono/css`)是 Hono 内置的 CSS in JS(X) 工具。
你可以在命名为 `css` 的 JavaScript 模板字面量里编写 CSS。`css` 的返回值是类名,用于设置到元素的 `class` 属性上。`` 组件会渲染对应的 CSS 内容。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { css, cx, keyframes, Style } from 'hono/css'
```
## `css`
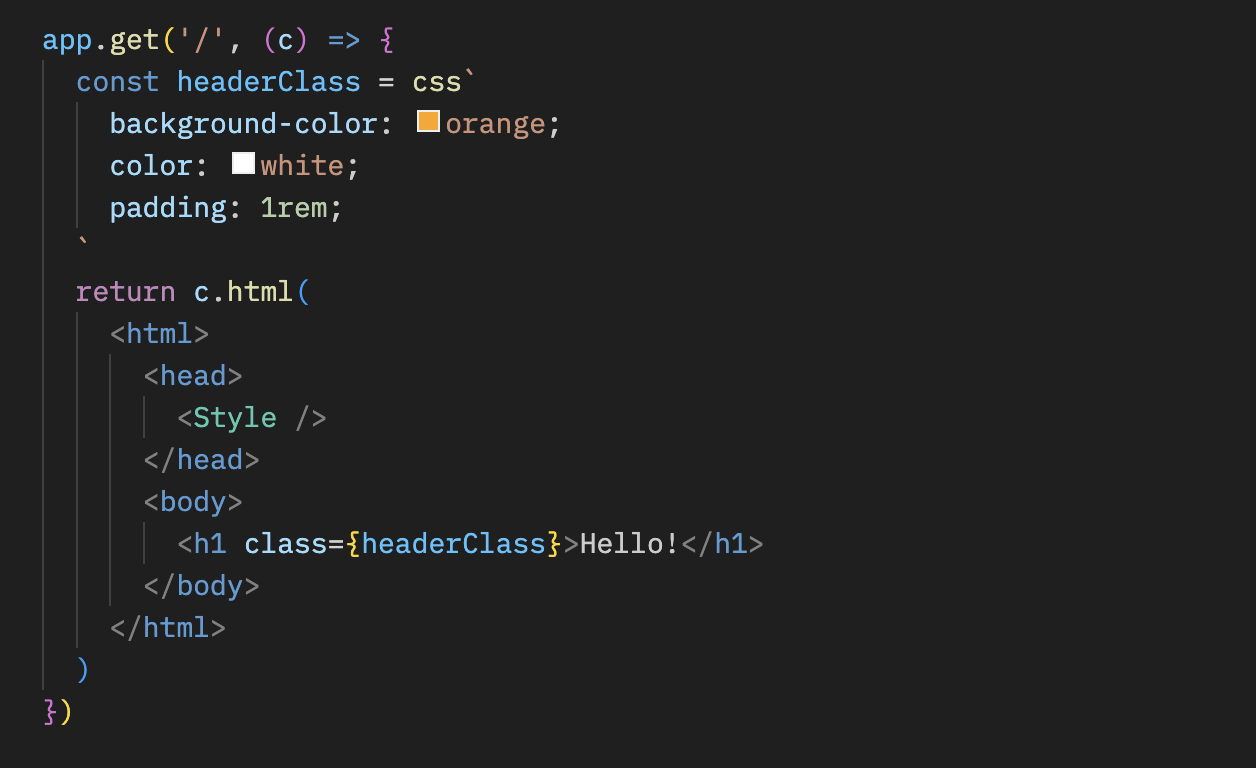
在 `css` 模板字面量中编写样式,并将返回值(这里是 `headerClass`)作为元素的 `class` 属性。别忘了引入 ``,它会输出 CSS 内容。
```ts{10,13}
app.get('/', (c) => {
const headerClass = css`
background-color: orange;
color: white;
padding: 1rem;
`
return c.html(
)
})
```
可通过 [嵌套选择器](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/Nesting_selector) `&` 定义伪类样式(例如 `:hover`)。
```ts
const buttonClass = css`
background-color: #fff;
&:hover {
background-color: red;
}
`
```
### 扩展
可以通过嵌入类名来扩展 CSS 定义。
```tsx
const baseClass = css`
color: white;
background-color: blue;
`
const header1Class = css`
${baseClass}
font-size: 3rem;
`
const header2Class = css`
${baseClass}
font-size: 2rem;
`
```
此外,`${baseClass} {}` 语法可以实现类的嵌套。
```tsx
const headerClass = css`
color: white;
background-color: blue;
`
const containerClass = css`
${headerClass} {
h1 {
font-size: 3rem;
}
}
`
return c.render(
)
```
### 全局样式
可以使用伪选择器 `:-hono-global` 定义全局样式。
```tsx
const globalClass = css`
:-hono-global {
html {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
}
`
return c.render(
Hello!
Today is a good day.
)
```
你也可以在 `` 组件中搭配 `css` 字面量书写样式。
```tsx
export const renderer = jsxRenderer(({ children, title }) => {
return (
{title}
{children}
)
})
```
## `keyframes`
使用 `keyframes` 可以编写 `@keyframes` 内容。在下例中,`fadeInAnimation` 即动画名称。
```tsx
const fadeInAnimation = keyframes`
from {
opacity: 0;
}
to {
opacity: 1;
}
`
const headerClass = css`
animation-name: ${fadeInAnimation};
animation-duration: 2s;
`
const Header = () =>
```
## `cx`
`cx` 用于组合多个类名。
```tsx
const buttonClass = css`
border-radius: 10px;
`
const primaryClass = css`
background: orange;
`
const Button = () => (
Click!
)
```
同时也支持组合普通字符串。
```tsx
const Header = () => Hi
```
## 与 [Secure Headers](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers) 中间件配合使用
若要与 [Secure Headers](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers) 中间件一同使用 css 助手,可在 `` 上设置 [`nonce` 属性](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Global_attributes/nonce),以避免因 CSS 助手引起的 Content-Security-Policy 限制。
```tsx{8,23}
import { secureHeaders, NONCE } from 'hono/secure-headers'
app.get(
'*',
secureHeaders({
contentSecurityPolicy: {
// 将预定义的 nonce 值传入 `styleSrc`
styleSrc: [NONCE],
},
})
)
app.get('/', (c) => {
const headerClass = css`
background-color: orange;
color: white;
padding: 1rem;
`
return c.html(
{/* 在 css 助手生成的 style/script 元素上添加 `nonce` 属性 */}
)
})
```
## 小贴士
如果使用 VS Code,可以安装 [vscode-styled-components](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=styled-components.vscode-styled-components) 扩展,为 css 标签模板提供语法高亮与智能提示。
# Dev 助手
Dev 助手提供了在开发阶段常用的辅助方法。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { getRouterName, showRoutes } from 'hono/dev'
```
## `getRouterName()`
使用 `getRouterName()` 可以获取当前使用的路由器名称。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
// ...
console.log(getRouterName(app))
```
## `showRoutes()`
`showRoutes()` 会在控制台打印已注册的路由。
假设你有如下应用:
```ts
const app = new Hono().basePath('/v1')
app.get('/posts', (c) => {
// ...
})
app.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
// ...
})
app.post('/posts', (c) => {
// ...
})
showRoutes(app, {
verbose: true,
})
```
当应用启动时,你会在控制台看到:
```txt
GET /v1/posts
GET /v1/posts/:id
POST /v1/posts
```
## 配置项
### verbose: `boolean`
设为 `true` 时输出更详细的信息。
### colorize: `boolean`
设为 `false` 时取消彩色输出。
# Factory 助手
Factory 助手提供了一些便捷函数,用于创建 Hono 的组件(例如中间件)。在某些场景下手动设置合适的 TypeScript 类型比较麻烦,该助手可以简化操作。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { createFactory, createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
```
## `createFactory()`
`createFactory()` 会创建一个 Factory 类的实例。
```ts
import { createFactory } from 'hono/factory'
const factory = createFactory()
```
你可以通过泛型参数传入自定义的 Env 类型:
```ts
type Env = {
Variables: {
foo: string
}
}
const factory = createFactory()
```
### 配置项
### defaultAppOptions: `HonoOptions`
`createApp()` 创建 Hono 应用时所使用的默认配置。
```ts
const factory = createFactory({
defaultAppOptions: { strict: false },
})
const app = factory.createApp() // 会应用 `strict: false`
```
## `createMiddleware()`
`createMiddleware()` 是 `factory.createMiddleware()` 的简化用法,用于创建自定义中间件。
```ts
const messageMiddleware = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.res.headers.set('X-Message', 'Good morning!')
})
```
提示:若需要传入类似 `message` 的参数,可以将其封装成函数。
```ts
const messageMiddleware = (message: string) => {
return createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.res.headers.set('X-Message', message)
})
}
app.use(messageMiddleware('Good evening!'))
```
## `factory.createHandlers()`
`createHandlers()` 可以让你在 `app.get('/')` 之外的地方定义处理函数。
```ts
import { createFactory } from 'hono/factory'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
// ...
const factory = createFactory()
const middleware = factory.createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.set('foo', 'bar')
await next()
})
const handlers = factory.createHandlers(logger(), middleware, (c) => {
return c.json(c.var.foo)
})
app.get('/api', ...handlers)
```
## `factory.createApp()`
`createApp()` 用于创建带有正确类型的 Hono 实例。如果你搭配 `createFactory()` 使用,可以避免重复声明 `Env` 类型。
如果直接编写如下代码,就需要在两个地方设置 `Env`:
```ts
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
type Env = {
Variables: {
myVar: string
}
}
// 1. 在 `new Hono()` 上设置 `Env`
const app = new Hono()
// 2. 在 `createMiddleware()` 上设置 `Env`
const mw = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
await next()
})
app.use(mw)
```
使用 `createFactory()` 与 `createApp()` 后,只需在一个位置指定 `Env`:
```ts
import { createFactory } from 'hono/factory'
// ...
// 将 `Env` 传入 `createFactory()`
const factory = createFactory()
const app = factory.createApp()
// factory 同时提供 `createMiddleware()`
const mw = factory.createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
await next()
})
```
`createFactory()` 还可以通过 `initApp` 选项对 `createApp()` 创建的实例进行初始化。以下示例展示了如何在应用中注入数据库实例。
```ts
// factory-with-db.ts
type Env = {
Bindings: {
MY_DB: D1Database
}
Variables: {
db: DrizzleD1Database
}
}
export default createFactory({
initApp: (app) => {
app.use(async (c, next) => {
const db = drizzle(c.env.MY_DB)
c.set('db', db)
await next()
})
},
})
```
```ts
// crud.ts
import factoryWithDB from './factory-with-db'
const app = factoryWithDB.createApp()
app.post('/posts', (c) => {
c.var.db.insert()
// ...
})
```
# html 助手
html 助手允许你在命名为 `html` 的 JavaScript 模板字面量中书写 HTML。通过 `raw()` 可以直接输出原始内容——但需要你自行确保字符串安全。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { html, raw } from 'hono/html'
```
## `html`
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/:username', (c) => {
const { username } = c.req.param()
return c.html(
html`
Hello! ${username}!
`
)
})
```
### 在 JSX 中插入片段
将内联脚本插入 JSX:
```tsx
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
Test Site
{html`
`}
Hello!
)
})
```
### 充当函数式组件
由于 `html` 返回 `HtmlEscapedString`,因此无需 JSX 也可以实现完整的函数式组件。
#### 使用 `html` 代替 `memo` 以简化流程
```typescript
const Footer = () => html`
`
```
### 接收 props 并嵌入值
```typescript
interface SiteData {
title: string
description: string
image: string
children?: any
}
const Layout = (props: SiteData) => html`
${props.title}
${props.children}
`
const Content = (props: { siteData: SiteData; name: string }) => (
Hello {props.name}
)
app.get('/', (c) => {
const props = {
name: 'World',
siteData: {
title: 'Hello <> World',
description: 'This is a description',
image: 'https://example.com/image.png',
},
}
return c.html()
})
```
## `raw()`
```ts
app.get('/', (c) => {
const name = 'John "Johnny" Smith'
return c.html(html`I'm ${raw(name)}.
`)
})
```
## 小贴士
借助以下工具,Visual Studio Code 与 vim 等编辑器可以把模板字面量识别为 HTML,从而启用语法高亮与格式化。
-
-
# JWT 身份验证助手
该助手提供一组函数用于编码、解码、签名与验证 JSON Web Token(JWT)。JWT 常用于 Web 应用中的身份验证与授权,本助手支持多种密码算法,提供完备的 JWT 能力。
## 导入
使用示例:
```ts
import { decode, sign, verify } from 'hono/jwt'
```
::: info
[JWT 中间件](/docs/middleware/builtin/jwt) 同样从 `hono/jwt` 中导入 `jwt` 函数。
:::
## `sign()`
该函数会对载荷进行编码,并使用指定算法与密钥生成 JWT。
```ts
sign(
payload: unknown,
secret: string,
alg?: 'HS256'
): Promise
```
### 示例
```ts
import { sign } from 'hono/jwt'
const payload = {
sub: 'user123',
role: 'admin',
exp: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + 60 * 5, // 5 分钟后过期
}
const secret = 'mySecretKey'
const token = await sign(payload, secret)
```
### 配置项
#### payload: `unknown`
要签名的 JWT 载荷。你可以参考 [Payload 校验](#payload-校验) 添加更多声明。
#### secret: `string`
用于签名或验证 JWT 的密钥。
#### alg: [AlgorithmTypes](#支持的-algorithmtypes)
JWT 的签名/验证算法,默认为 HS256。
## `verify()`
该函数会校验 JWT 的真实性与有效性,确保 Token 未被篡改;若你提供了 [Payload 校验](#payload-校验) 所需字段,也会同步检查这些约束。
```ts
verify(
token: string,
secret: string,
alg?: 'HS256'
issuer?: string | RegExp
): Promise
```
### 示例
```ts
import { verify } from 'hono/jwt'
const tokenToVerify = 'token'
const secretKey = 'mySecretKey'
const decodedPayload = await verify(tokenToVerify, secretKey)
console.log(decodedPayload)
```
### 配置项
#### token: `string`
待验证的 JWT。
#### secret: `string`
用于签名或验证 JWT 的密钥。
#### alg: [AlgorithmTypes](#支持的-algorithmtypes)
JWT 的签名/验证算法,默认为 HS256。
#### issuer: `string | RegExp`
期望的签发者,用于验证。
## `decode()`
该函数会在 **不** 验证签名的情况下解析 JWT,并返回其中的 header 与 payload。
```ts
decode(token: string): { header: any; payload: any }
```
### 示例
```ts
import { decode } from 'hono/jwt'
// 解码 JWT
const tokenToDecode =
'eyJhbGciOiAiSFMyNTYiLCAidHlwIjogIkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiAidXNlcjEyMyIsICJyb2xlIjogImFkbWluIn0.JxUwx6Ua1B0D1B0FtCrj72ok5cm1Pkmr_hL82sd7ELA'
const { header, payload } = decode(tokenToDecode)
console.log('Decoded Header:', header)
console.log('Decoded Payload:', payload)
```
### 配置项
#### token: `string`
需要解析的 JWT。
> `decode` 函数可以在 **不** 验证签名的情况下查看 JWT 的 header 与 payload,适合调试或提取信息。
## Payload 校验
在验证 JWT 时,会针对以下载荷字段执行检查:
- `exp`:确认 Token 是否已过期。
- `nbf`:确认 Token 是否在允许使用的时间之前被调用。
- `iat`:确认 Token 的签发时间不是未来。
- `iss`:确认 Token 是否由可信的签发者生成。
如果你希望在验证过程中启用这些检查,请确保 JWT 载荷中包含相应的字段。
## 自定义错误类型
模块定义了若干自定义错误,便于处理与 JWT 相关的问题。
- `JwtAlgorithmNotImplemented`:请求的 JWT 算法尚未实现。
- `JwtTokenInvalid`:JWT 无效。
- `JwtTokenNotBefore`:Token 在允许时间之前被使用。
- `JwtTokenExpired`:Token 已过期。
- `JwtTokenIssuedAt`:Token 的 `iat` 声明不正确。
- `JwtTokenIssuer`:Token 的 `iss` 声明不正确。
- `JwtTokenSignatureMismatched`:Token 签名不匹配。
## 支持的 AlgorithmTypes
当前支持以下 JWT 加密算法:
- `HS256`:基于 SHA-256 的 HMAC
- `HS384`:基于 SHA-384 的 HMAC
- `HS512`:基于 SHA-512 的 HMAC
- `RS256`:基于 SHA-256 的 RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5
- `RS384`:基于 SHA-384 的 RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5
- `RS512`:基于 SHA-512 的 RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5
- `PS256`:基于 SHA-256 与 MGF1(SHA-256) 的 RSASSA-PSS
- `PS384`:基于 SHA-384 与 MGF1(SHA-384) 的 RSASSA-PSS
- `PS512`:基于 SHA-512 与 MGF1(SHA-512) 的 RSASSA-PSS
- `ES256`:P-256 + SHA-256 的 ECDSA
- `ES384`:P-384 + SHA-384 的 ECDSA
- `ES512`:P-521 + SHA-512 的 ECDSA
- `EdDSA`:使用 Ed25519 的 EdDSA
# Proxy 助手
Proxy 助手提供了一些实用函数,帮助你将 Hono 应用用作(反向)代理。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { proxy } from 'hono/proxy'
```
## `proxy()`
`proxy()` 是一个封装 `fetch()` API 的代理函数。除了代理相关的额外选项外,其参数与返回值与 `fetch()` 相同。
该函数会用当前运行时支持的编码替换 `Accept-Encoding` 请求头,并清理不必要的响应头,最终返回一个可直接用于响应处理器的 `Response` 对象。
### 示例
基础用法:
```ts
app.get('/proxy/:path', (c) => {
return proxy(`http://${originServer}/${c.req.param('path')}`)
})
```
更复杂的示例:
```ts
app.get('/proxy/:path', async (c) => {
const res = await proxy(
`http://${originServer}/${c.req.param('path')}`,
{
headers: {
...c.req.header(), // 可选,只有在需要转发完整请求(包括凭证)时才指定
'X-Forwarded-For': '127.0.0.1',
'X-Forwarded-Host': c.req.header('host'),
Authorization: undefined, // 不转发 c.req.header('Authorization') 中的值
},
}
)
res.headers.delete('Set-Cookie')
return res
})
```
你也可以将 `c.req` 直接作为参数传入。
```ts
app.all('/proxy/:path', (c) => {
return proxy(`http://${originServer}/${c.req.param('path')}`, {
...c.req, // 可选,只有在需要转发完整请求(包括凭证)时才指定
headers: {
...c.req.header(),
'X-Forwarded-For': '127.0.0.1',
'X-Forwarded-Host': c.req.header('host'),
Authorization: undefined, // 不转发 c.req.header('Authorization') 中的值
},
})
})
```
通过 `customFetch` 选项可以覆盖默认的全局 `fetch` 函数:
```ts
app.get('/proxy', (c) => {
return proxy('https://example.com/', {
customFetch,
})
})
```
### `ProxyFetch`
`proxy()` 的类型定义为 `ProxyFetch`,如下所示:
```ts
interface ProxyRequestInit extends Omit {
raw?: Request
customFetch?: (request: Request) => Promise
headers?:
| HeadersInit
| [string, string][]
| Record
| Record
}
interface ProxyFetch {
(
input: string | URL | Request,
init?: ProxyRequestInit
): Promise
}
```
# Route 助手
Route 助手提供更丰富的路由信息,便于调试与中间件开发。它可以访问匹配到的路由列表以及当前正在处理的路由。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import {
matchedRoutes,
routePath,
baseRoutePath,
basePath,
} from 'hono/route'
```
## 用法
### 基本路由信息
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
const currentPath = routePath(c) // '/posts/:id'
const routes = matchedRoutes(c) // 匹配到的路由数组
return c.json({
path: currentPath,
totalRoutes: routes.length,
})
})
```
### 搭配子应用
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const apiApp = new Hono()
apiApp.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
return c.json({
routePath: routePath(c), // '/posts/:id'
baseRoutePath: baseRoutePath(c), // '/api'
basePath: basePath(c), // '/api'(包含实际参数)
})
})
app.route('/api', apiApp)
```
## `matchedRoutes()`
返回一个数组,其中包含当前请求匹配到的所有路由(包括中间件)。
```ts
app.all('/api/*', (c, next) => {
console.log('API middleware')
return next()
})
app.get('/api/users/:id', (c) => {
const routes = matchedRoutes(c)
// 返回:[
// { method: 'ALL', path: '/api/*', handler: [Function] },
// { method: 'GET', path: '/api/users/:id', handler: [Function] }
// ]
return c.json({ routes: routes.length })
})
```
## `routePath()`
返回当前处理器注册的路由路径模式。
```ts
app.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
console.log(routePath(c)) // '/posts/:id'
return c.text('Post details')
})
```
### 搭配索引参数
可以传入一个索引,获取指定位置的路由路径,行为类似 `Array.prototype.at()`。
```ts
app.all('/api/*', (c, next) => {
return next()
})
app.get('/api/users/:id', (c) => {
console.log(routePath(c, 0)) // '/api/*'(第一个匹配的路由)
console.log(routePath(c, -1)) // '/api/users/:id'(最后一个匹配的路由)
return c.text('User details')
})
```
## `baseRoutePath()`
返回路由定义时指定的基础路径模式。
```ts
const subApp = new Hono()
subApp.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
return c.text(baseRoutePath(c)) // '/:sub'
})
app.route('/:sub', subApp)
```
### 搭配索引参数
同样可以传入索引以获取特定位置的基础路由路径,行为类似 `Array.prototype.at()`。
```ts
app.all('/api/*', (c, next) => {
return next()
})
const subApp = new Hono()
subApp.get('/users/:id', (c) => {
console.log(baseRoutePath(c, 0)) // '/'(第一个匹配的路由)
console.log(baseRoutePath(c, -1)) // '/api'(最后一个匹配的路由)
return c.text('User details')
})
app.route('/api', subApp)
```
## `basePath()`
返回当前请求实际访问的基础路径(包含解析后的参数)。
```ts
const subApp = new Hono()
subApp.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
return c.text(basePath(c)) // '/api'(例如请求 '/api/posts/123')
})
app.route('/:sub', subApp)
```
# SSG 助手
SSG 助手可以从你的 Hono 应用生成静态站点。它会抓取已注册路由的内容,并保存为静态文件。
## 用法
### 手动生成
假设有如下简单的 Hono 应用:
```tsx
// index.tsx
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.html('Hello, World!'))
app.use('/about', async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content, head) => {
return c.html(
{head.title ?? ''}
{content}
)
})
await next()
})
app.get('/about', (c) => {
return c.render('Hello!', { title: 'Hono SSG Page' })
})
export default app
```
在 Node.js 中可以编写如下构建脚本:
```ts
// build.ts
import app from './index'
import { toSSG } from 'hono/ssg'
import fs from 'fs/promises'
toSSG(app, fs)
```
执行脚本后,将会生成如下文件:
```bash
ls ./static
about.html index.html
```
### 使用 Vite 插件
通过 `@hono/vite-ssg` 插件可以更轻松地完成以上流程。
详情请参阅:
https://github.com/honojs/vite-plugins/tree/main/packages/ssg
## toSSG
`toSSG` 是生成静态站点的核心函数,接收应用实例与文件系统模块作为参数,整体流程如下。
### 输入
toSSG 的参数定义在 `ToSSGInterface` 中:
```ts
export interface ToSSGInterface {
(
app: Hono,
fsModule: FileSystemModule,
options?: ToSSGOptions
): Promise
}
```
- `app`:传入注册好路由的 `new Hono()`。
- `fs`:传入如下对象,以下示例假设使用 `node:fs/promise`。
```ts
export interface FileSystemModule {
writeFile(path: string, data: string | Uint8Array): Promise
mkdir(
path: string,
options: { recursive: boolean }
): Promise
}
```
### 在 Deno 与 Bun 中使用适配器
如果想在 Deno 或 Bun 中使用 SSG,可通过对应的 `toSSG` 函数:
Deno:
```ts
import { toSSG } from 'hono/deno'
toSSG(app) // 第二个参数为可选项,类型为 `ToSSGOptions`。
```
Bun:
```ts
import { toSSG } from 'hono/bun'
toSSG(app) // 第二个参数为可选项,类型为 `ToSSGOptions`。
```
### 配置项
配置项定义在 `ToSSGOptions` 接口中:
```ts
export interface ToSSGOptions {
dir?: string
concurrency?: number
extensionMap?: Record
plugins?: SSGPlugin[]
}
```
- `dir`:静态文件输出目录,默认 `./static`。
- `concurrency`:并发生成的文件数量,默认 `2`。
- `extensionMap`:根据 `Content-Type` 决定输出文件的扩展名。
- `plugins`:SSG 插件数组,可扩展生成流程。
### 输出
`toSSG` 会返回如下结果类型:
```ts
export interface ToSSGResult {
success: boolean
files: string[]
error?: Error
}
```
## 生成文件
### 路由与文件名
默认的 `./static` 输出目录会遵循以下规则:
- `/` -> `./static/index.html`
- `/path` -> `./static/path.html`
- `/path/` -> `./static/path/index.html`
### 文件扩展名
文件扩展名取决于路由返回的 `Content-Type`。例如 `c.html` 的响应会保存为 `.html`。
如果需要自定义扩展名,可以设置 `extensionMap` 选项:
```ts
import { toSSG, defaultExtensionMap } from 'hono/ssg'
// 将 `application/x-html` 内容保存为 `.html`
toSSG(app, fs, {
extensionMap: {
'application/x-html': 'html',
...defaultExtensionMap,
},
})
```
注意:以 `/` 结尾的路径会被保存为 `index.ext`,与具体扩展名无关。
```ts
// 保存到 ./static/html/index.html
app.get('/html/', (c) => c.html('html'))
// 保存到 ./static/text/index.txt
app.get('/text/', (c) => c.text('text'))
```
## 中间件
Hono 提供了一些内置中间件来辅助 SSG。
### ssgParams
与 Next.js 的 `generateStaticParams` 类似,你可以按下列方式生成静态参数:
```ts
app.get(
'/shops/:id',
ssgParams(async () => {
const shops = await getShops()
return shops.map((shop) => ({ id: shop.id }))
}),
async (c) => {
const shop = await getShop(c.req.param('id'))
if (!shop) {
return c.notFound()
}
return c.render(
{shop.name}
)
}
)
```
### disableSSG
使用 `disableSSG` 中间件的路由不会被 `toSSG` 生成静态文件。
```ts
app.get('/api', disableSSG(), (c) => c.text('an-api'))
```
### onlySSG
使用 `onlySSG` 中间件的路由在执行 `toSSG` 后会被 `c.notFound()` 接管。
```ts
app.get('/static-page', onlySSG(), (c) => c.html(Welcome to my site
))
```
## 插件
通过插件可以扩展静态站点生成流程,它们通过钩子在不同阶段定制行为。
### 钩子类型
插件可使用以下钩子定制 `toSSG`:
```ts
export type BeforeRequestHook = (req: Request) => Request | false
export type AfterResponseHook = (res: Response) => Response | false
export type AfterGenerateHook = (
result: ToSSGResult
) => void | Promise
```
- **BeforeRequestHook**:在处理每个请求前调用,返回 `false` 可跳过该路由。
- **AfterResponseHook**:在获取响应后调用,返回 `false` 可跳过文件生成。
- **AfterGenerateHook**:在全部生成流程完成后调用。
### 插件接口
```ts
export interface SSGPlugin {
beforeRequestHook?: BeforeRequestHook | BeforeRequestHook[]
afterResponseHook?: AfterResponseHook | AfterResponseHook[]
afterGenerateHook?: AfterGenerateHook | AfterGenerateHook[]
}
```
### 基础插件示例
仅保留 GET 请求:
```ts
const getOnlyPlugin: SSGPlugin = {
beforeRequestHook: (req) => {
if (req.method === 'GET') {
return req
}
return false
},
}
```
按状态码筛选:
```ts
const statusFilterPlugin: SSGPlugin = {
afterResponseHook: (res) => {
if (res.status === 200 || res.status === 500) {
return res
}
return false
},
}
```
记录生成的文件:
```ts
const logFilesPlugin: SSGPlugin = {
afterGenerateHook: (result) => {
if (result.files) {
result.files.forEach((file) => console.log(file))
}
},
}
```
### 进阶插件示例
以下示例展示了如何创建一个生成 `sitemap.xml` 的插件:
```ts
// plugins.ts
import fs from 'node:fs/promises'
import path from 'node:path'
import type { SSGPlugin } from 'hono/ssg'
import { DEFAULT_OUTPUT_DIR } from 'hono/ssg'
export const sitemapPlugin = (baseURL: string): SSGPlugin => {
return {
afterGenerateHook: (result, fsModule, options) => {
const outputDir = options?.dir ?? DEFAULT_OUTPUT_DIR
const filePath = path.join(outputDir, 'sitemap.xml')
const urls = result.files.map((file) =>
new URL(file, baseURL).toString()
)
const siteMapText = `
${urls.map((url) => `${url}`).join('\n')}
`
fsModule.writeFile(filePath, siteMapText)
},
}
}
```
应用插件:
```ts
import app from './index'
import { toSSG } from 'hono/ssg'
import { sitemapPlugin } from './plugins'
toSSG(app, fs, {
plugins: [
getOnlyPlugin,
statusFilterPlugin,
logFilesPlugin,
sitemapPlugin('https://example.com'),
],
})
```
# Streaming 助手
Streaming 助手提供了一组用于返回流式响应的方法。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { stream, streamText, streamSSE } from 'hono/streaming'
```
## `stream()`
返回一个基础的流式响应(`Response` 对象)。
```ts
app.get('/stream', (c) => {
return stream(c, async (stream) => {
// 在终止时执行的处理。
stream.onAbort(() => {
console.log('Aborted!')
})
// 写入 Uint8Array。
await stream.write(new Uint8Array([0x48, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f]))
// 管道转发可读流。
await stream.pipe(anotherReadableStream)
})
})
```
## `streamText()`
返回带有 `Content-Type:text/plain`、`Transfer-Encoding:chunked` 以及 `X-Content-Type-Options:nosniff` 头部的流式响应。
```ts
app.get('/streamText', (c) => {
return streamText(c, async (stream) => {
// 写入携带换行符('\n')的文本。
await stream.writeln('Hello')
// 等待 1 秒。
await stream.sleep(1000)
// 写入不带换行的文本。
await stream.write(`Hono!`)
})
})
```
::: warning
在 Cloudflare Workers 中开发时,流式传输可能无法在 Wrangler 中正常工作。此时可以将 `Content-Encoding` 头设置为 `Identity`。
```ts
app.get('/streamText', (c) => {
c.header('Content-Encoding', 'Identity')
return streamText(c, async (stream) => {
// ...
})
})
```
:::
## `streamSSE()`
用于无缝推送 Server-Sent Events(SSE)。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
let id = 0
app.get('/sse', async (c) => {
return streamSSE(c, async (stream) => {
while (true) {
const message = `It is ${new Date().toISOString()}`
await stream.writeSSE({
data: message,
event: 'time-update',
id: String(id++),
})
await stream.sleep(1000)
}
})
})
```
## 错误处理
Streaming 助手的第三个参数是错误处理函数。该参数可选,如果未提供,错误会被输出到控制台。
```ts
app.get('/stream', (c) => {
return stream(
c,
async (stream) => {
// 在终止时执行的处理。
stream.onAbort(() => {
console.log('Aborted!')
})
// 写入 Uint8Array。
await stream.write(
new Uint8Array([0x48, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f])
)
// 管道转发可读流。
await stream.pipe(anotherReadableStream)
},
(err, stream) => {
stream.writeln('An error occurred!')
console.error(err)
}
)
})
```
回调执行完毕后,流会自动关闭。
::: warning
如果 Streaming 助手的回调函数抛出错误,将不会触发 Hono 的 `onError` 事件。
`onError` 用于在响应发送前拦截错误并覆盖响应。然而在回调执行时,流已经开始传输,因而无法再覆盖。
:::
# Testing 助手
Testing 助手提供了一些函数,帮助你更轻松地测试 Hono 应用。
## 导入
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { testClient } from 'hono/testing'
```
## `testClient()`
`testClient()` 接收一个 Hono 实例作为第一个参数,返回一个按路由类型定义好的对象,类似于 [Hono Client](/docs/guides/rpc#client)。借助它可以在测试中以类型安全的方式调用各路由,并享受编辑器的自动补全。
**关于类型推断的重要说明:**
为了让 `testClient` 正确推断路由类型并提供自动补全,**必须直接在 `Hono` 实例上通过链式调用定义路由**。
类型推断依赖 `.get()`、`.post()` 等链式调用中流动的类型。如果你按照传统的 “Hello World” 写法(`const app = new Hono(); app.get(...)`)在实例创建后再单独注册路由,`testClient` 就无法获取这些类型信息,也就无法提供类型安全的客户端能力。
**示例:**
以下示例可以正常推断类型,因为 `.get()` 直接链在 `new Hono()` 上:
```ts
// index.ts
const app = new Hono().get('/search', (c) => {
const query = c.req.query('q')
return c.json({ query: query, results: ['result1', 'result2'] })
})
export default app
```
```ts
// index.test.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { testClient } from 'hono/testing'
import { describe, it, expect } from 'vitest' // 或任意测试框架
import app from './app'
describe('Search Endpoint', () => {
// 基于应用实例创建测试客户端
const client = testClient(app)
it('should return search results', async () => {
// 使用带类型的客户端调用接口
// 如果路由中定义了查询参数,这里也会获得类型提示
// 并通过 .$get() 访问
const res = await client.search.$get({
query: { q: 'hono' },
})
// 断言
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
query: 'hono',
results: ['result1', 'result2'],
})
})
})
```
如需在测试请求中携带请求头,可将其作为第二个参数传入。该参数也支持 `init` 属性(类型为 `RequestInit`),便于设置请求头、方法、请求体等。关于 `init` 的更多信息,请参考 [这里](/docs/guides/rpc#init-option)。
```ts
// index.test.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { testClient } from 'hono/testing'
import { describe, it, expect } from 'vitest' // 或任意测试框架
import app from './app'
describe('Search Endpoint', () => {
const client = testClient(app)
it('should return search results', async () => {
// 在请求头中附带 token,并设置内容类型
const token = 'this-is-a-very-clean-token'
const res = await client.search.$get(
{
query: { q: 'hono' },
},
{
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${token}`,
'Content-Type': `application/json`,
},
}
)
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
query: 'hono',
results: ['result1', 'result2'],
})
})
})
```
# WebSocket 助手
WebSocket 助手为 Hono 应用提供服务端 WebSocket 支持。目前已提供 Cloudflare Workers/Pages、Deno 与 Bun 的适配器。
## 导入
::: code-group
```ts [Cloudflare Workers]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { upgradeWebSocket } from 'hono/cloudflare-workers'
```
```ts [Deno]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { upgradeWebSocket } from 'hono/deno'
```
```ts [Bun]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { upgradeWebSocket, websocket } from 'hono/bun'
// ...
export default {
fetch: app.fetch,
websocket,
}
```
:::
若使用 Node.js,可参考 [@hono/node-ws](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/node-ws)。
## `upgradeWebSocket()`
`upgradeWebSocket()` 会返回一个用于处理 WebSocket 的处理器。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket((c) => {
return {
onMessage(event, ws) {
console.log(`Message from client: ${event.data}`)
ws.send('Hello from server!')
},
onClose: () => {
console.log('Connection closed')
},
}
})
)
```
可用事件包括:
- `onOpen` —— 当前 Cloudflare Workers 尚未支持。
- `onMessage`
- `onClose`
- `onError`
::: warning
如果在使用 WebSocket 助手的路由上同时使用会修改头部的中间件(例如 CORS),可能会遇到 “无法修改不可变头部” 的错误,因为 `upgradeWebSocket()` 内部也会修改头部。使用 WebSocket 助手与中间件时请格外注意。
:::
## RPC 模式
通过 WebSocket 助手定义的处理器可配合 RPC 模式使用。
```ts
// server.ts
const wsApp = app.get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket((c) => {
// ...
})
)
export type WebSocketApp = typeof wsApp
// client.ts
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787')
const socket = client.ws.$ws() // 客户端的 WebSocket 对象
```
## 示例
以下示例展示了如何使用 WebSocket 助手。
### 服务端与客户端
```ts
// server.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { upgradeWebSocket } from 'hono/cloudflare-workers'
const app = new Hono().get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket(() => {
return {
onMessage: (event) => {
console.log(event.data)
},
}
})
)
export default app
```
```ts
// client.ts
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
import type app from './server'
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787')
const ws = client.ws.$ws(0)
ws.addEventListener('open', () => {
setInterval(() => {
ws.send(new Date().toString())
}, 1000)
})
```
### Bun + JSX
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { createBunWebSocket } from 'hono/bun'
import { html } from 'hono/html'
const { upgradeWebSocket, websocket } = createBunWebSocket()
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
{html`
`}
)
})
const ws = app.get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket((c) => {
let intervalId
return {
onOpen(_event, ws) {
intervalId = setInterval(() => {
ws.send(new Date().toString())
}, 200)
},
onClose() {
clearInterval(intervalId)
},
}
})
)
export default {
fetch: app.fetch,
websocket,
}
```
# 最佳实践
Hono 十分灵活,你可以按照自己的偏好编写应用。
不过,仍然有一些更值得遵循的最佳实践。
## 尽量不要创建“控制器”
能不写“Ruby on Rails 风格的控制器”时,就别写。
```ts
// 🙁
// 类似 RoR 的控制器
const booksList = (c: Context) => {
return c.json('list books')
}
app.get('/books', booksList)
```
问题出在类型上。例如,如果不写复杂的泛型,控制器内部无法推断路径参数。
```ts
// 🙁
// 类似 RoR 的控制器
const bookPermalink = (c: Context) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // 无法推断路径参数
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
}
```
因此你完全没必要写 RoR 风格的控制器,直接在路径定义后编写处理函数即可。
```ts
// 😃
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // 可以正确推断路径参数
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
})
```
## 使用模式验证请求
如果需要验证请求,请使用模式验证器,而不要手写验证逻辑。
```ts
import { z } from 'zod'
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
app.post(
'/auth',
zValidator(
'json',
z.object({
email: z.string().email(),
password: z.string().min(8),
})
),
async (c) => {
const { email, password } = c.req.valid('json')
return c.json({ email, password })
}
)
```
## 在调用 `app.get()` 之前定义配置
这是来自 JavaScript 模块的最佳实践:
在调用函数之前先定义配置对象。
```ts
const route = {
method: 'GET',
path: '/',
}
app.get(route, (c) => c.text('Hello'))
```
## 不要为了分组而重复使用 `app.route`
只有在需要为同一路径提供多个 HTTP 方法时,才应该使用 `app.route`。
如果只是想划分路由分组,就会显得多此一举。
```ts
const app = new Hono()
const books = app.route('/books')
books.get('/', (c) => c.json(['Hello']))
books.get('/:id', (c) => c.json({ id: c.req.param('id') }))
```
在这种情况下就显得冗余了。直接写成下面这样能得到相同的效果。
```ts
app.get('/books', (c) => c.json(['Hello']))
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => c.json({ id: c.req.param('id') }))
```
## 更倾向使用 `app.on` 而不是 `app.xxx`
Hono 提供了 `app.on`,可以为同一路径定义多个 HTTP 方法。建议使用 `app.on`,而不是 `app.xxx`。
```ts
app.on(['GET', 'POST'], '/books', (c) => {
return c.json(['Hello'])
})
```
## 使用 `c.req.param()` 而非 `c.req.param['id']`
请使用函数形式的 `c.req.param()`,而不是访问器 `c.req.param['id']`,以避免触发 getter。
```ts
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id')
return c.json({ id })
})
```
## 用模板字符串拼接响应
拼接响应文本时,请使用模板字符串,而不是字符串相加。
```ts
app.get('/hello/:name', (c) => {
const { name } = c.req.param()
return c.text(`Hello ${name}!`)
})
```
## 日志
使用 `console.log` 和 `console.error` 输出日志信息。
```ts
app.get('/hello', async (c) => {
const start = Date.now()
const res = await c.req.parseBody()
const end = Date.now()
console.log(`[${c.req.method}] ${c.req.path} - ${end - start}ms`)
return c.json(res)
})
```
## 用 `c.var` 复用逻辑
如果有重复使用的逻辑,可以通过 `c.set` 和 `c.var` 进行复用。
```ts
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
c.set('database', await getDatabase())
await next()
})
app.get('/users', async (c) => {
const db = c.var.database
const users = await db.users.findMany()
return c.json(users)
})
```
## 等待 Response
`Response` 只能读取一次。等待响应会消耗它。
```ts
app.get('/', async (c) => {
const res = await fetch('https://example.com')
const json = await res.json()
return c.json(json)
})
```
# Create-hono
以下是 `create-hono` 支持的命令行选项。这个项目初始化工具会在你执行 `npm create hono@latest`、`npx create-hono@latest` 或 `pnpm create hono@latest` 时运行。
> [!NOTE]
> **为什么需要这篇文档?** 安装与快速上手示例通常只展示最精简的 `npm create hono@latest my-app` 命令。其实 `create-hono` 提供了很多实用的参数,可以帮助你自动化并自定义项目创建过程(选择模板、跳过交互式提示、指定包管理器、使用本地缓存等)。
## 传递参数
使用 `npm create`(或 `npx`)时,传给初始化脚本的参数必须放在 `--` 之后。`--` 后面的所有内容都会转发给初始化器。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
# 将参数转发给 create-hono(npm 必须使用 `--`)
npm create hono@latest my-app -- --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [yarn]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
yarn create hono my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [pnpm]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
pnpm create hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [bun]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
bun create hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
```sh [deno]
# "--template cloudflare-workers" 会选择 Cloudflare Workers 模板
deno init --npm hono@latest my-app --template cloudflare-workers
```
:::
## 常用参数
| 参数 | 说明 | 示例 |
| :---------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | :----------------------------- |
| `--template ` | 选择一个起始模板,并跳过交互式模板提示。模板名称可能包括 `bun`、`cloudflare-workers`、`vercel` 等 | `--template cloudflare-workers` |
| `--install` | 模板创建完毕后自动安装依赖。 | `--install` |
| `--pm ` | 指定安装依赖时使用的包管理器。常见值:`npm`、`pnpm`、`yarn`。 | `--pm pnpm` |
| `--offline` | 使用本地缓存/模板,而不是获取最新的远程模板。适合离线环境或希望固定模板版本的场景。 | `--offline` |
> [!NOTE]
> 模板列表与可用选项由 `create-hono` 项目维护。本文仅汇总了最常用的参数——完整且权威的参考请查看下方仓库链接。
## 示例流程
### 最小化、交互式
```bash
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
命令会提示你选择模板和其他选项。
### 非交互式:指定模板与包管理器
```bash
npm create hono@latest my-app -- --template vercel --pm npm --install
```
该命令会基于 `vercel` 模板创建 `my-app`,使用 `npm` 安装依赖,并跳过所有交互式提问。
### 使用离线缓存(无网络)
```bash
pnpm create hono@latest my-app --template deno --offline
```
## 故障排查与提示
- 如果某个参数似乎没有生效,请确认在使用 `npm create`/`npx` 时是否加上了 `--` 进行转发。
- 想查看最新的模板与参数列表,可以直接查阅 `create-hono` 仓库,或者本地运行初始化工具并查看其帮助信息。
## 相关链接
- `create-hono` 仓库:[create-hono](https://github.com/honojs/create-hono)
# 示例
请参阅[示例章节](/examples/)。
# 常见问题
本指南整理了关于 Hono 的常见疑问及解决方式。
## Hono 是否提供官方的 Renovate 配置?
目前 Hono 团队没有维护 [Renovate](https://github.com/renovatebot/renovate) 的官方配置。
因此,请参考以下方式使用第三方的 renovate-config。
在你的 `renovate.json` 中写入:
```json
// renovate.json
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"github>shinGangan/renovate-config-hono" // [!code ++]
]
}
```
更多详情请参阅 [renovate-config-hono](https://github.com/shinGangan/renovate-config-hono) 仓库。
# 助手
助手(Helper)可以在开发应用时提供支持。与中间件不同,它们不会作为处理函数运行,而是提供便捷的实用功能。
例如,[Cookie 助手](/docs/helpers/cookie) 的使用方式如下:
```ts
import { getCookie, setCookie } from 'hono/cookie'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/cookie', (c) => {
const yummyCookie = getCookie(c, 'yummy_cookie')
// ...
setCookie(c, 'delicious_cookie', 'macha')
//
})
```
## 可用的助手
- [Accepts](/docs/helpers/accepts)
- [Adapter](/docs/helpers/adapter)
- [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
- [css](/docs/helpers/css)
- [Dev](/docs/helpers/dev)
- [Factory](/docs/helpers/factory)
- [html](/docs/helpers/html)
- [JWT](/docs/helpers/jwt)
- [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
- [Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
- [Testing](/docs/helpers/testing)
- [WebSocket](/docs/helpers/websocket)
# 客户端组件
`hono/jsx` 不仅支持服务端渲染,也支持在客户端运行。这意味着你可以在浏览器里构建交互式界面,我们把它称作客户端组件,或 `hono/jsx/dom`。
它既快又小。`hono/jsx/dom` 的计数器示例在 Brotli 压缩后只有 2.8KB,而 React 的同类示例则有 47.8KB。
本章介绍客户端组件特有的功能。
## 计数器示例
下面是一个简单的计数器示例,代码与 React 中的写法相同。
```tsx
import { useState } from 'hono/jsx'
import { render } from 'hono/jsx/dom'
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
Count: {count}
)
}
function App() {
return (
)
}
const root = document.getElementById('root')
render(, root)
```
## `render()`
你可以使用 `render()` 将 JSX 组件插入到指定的 HTML 元素中。
```tsx
render(, container)
```
## 与 React 兼容的 Hook
`hono/jsx/dom` 提供了与 React 兼容或部分兼容的 Hook。具体 API 可以参考 [React 文档](https://react.dev/reference/react/hooks)。
- `useState()`
- `useEffect()`
- `useRef()`
- `useCallback()`
- `use()`
- `startTransition()`
- `useTransition()`
- `useDeferredValue()`
- `useMemo()`
- `useLayoutEffect()`
- `useReducer()`
- `useDebugValue()`
- `createElement()`
- `memo()`
- `isValidElement()`
- `useId()`
- `createRef()`
- `forwardRef()`
- `useImperativeHandle()`
- `useSyncExternalStore()`
- `useInsertionEffect()`
- `useFormStatus()`
- `useActionState()`
- `useOptimistic()`
## `startViewTransition()` 系列
`startViewTransition()` 系列提供了原生的 Hook 与函数,帮助你更轻松地使用 [View Transitions API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/View_Transitions_API)。下面展示几种典型写法。
### 1. 最简单的示例
借助 `startViewTransition()`,可以非常简洁地调用 `document.startViewTransition` 来实现过渡效果。
```tsx
import { useState, startViewTransition } from 'hono/jsx'
import { css, Style } from 'hono/css'
export default function App() {
const [showLargeImage, setShowLargeImage] = useState(false)
return (
<>
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
{!showLargeImage ? (

) : (
)}
Hello Hono!
{props.messages.map((message) => {
return - {message}!!
})}
)
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
const messages = ['Good Morning', 'Good Evening', 'Good Night']
return c.html()
})
export default app
```
## 元数据提升
你可以在组件中直接书写 ``、`<link>`、`<meta>` 等文档元数据标签。框架会自动将这些标签提升到文档的 `<head>` 区域。对于 `<head>` 元素距离实际决定元数据的组件较远的情况,这一点尤为便利。
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content) => {
return c.html(
<html>
<head></head>
<body>{content}</body>
</html>
)
})
await next()
})
app.get('/about', (c) => {
return c.render(
<>
<title>About Page
about page content
)
})
export default app
```
## Fragment
使用 Fragment 可以在不增加额外节点的情况下包裹多个元素:
```tsx
import { Fragment } from 'hono/jsx'
const List = () => (
first child
second child
third child
)
```
如果配置正确,也可以写成 `<>`。
```tsx
const List = () => (
<>
first child
second child
third child
)
```
## `PropsWithChildren`
使用 `PropsWithChildren` 可以在函数组件中正确推断子元素类型。
```tsx
import { PropsWithChildren } from 'hono/jsx'
type Post = {
id: number
title: string
}
function Component({ title, children }: PropsWithChildren) {
return (
{title}
{children}
)
}
```
## 插入原始 HTML
如果需要直接插入 HTML,可以使用 `dangerouslySetInnerHTML`:
```tsx
app.get('/foo', (c) => {
const inner = { __html: 'JSX · SSR' }
const Div =
})
```
## 记忆化
通过 `memo` 记忆化生成的字符串,可以优化组件性能:
```tsx
import { memo } from 'hono/jsx'
const Header = memo(() => )
const Footer = memo(() => )
const Layout = (
)
```
## Context
使用 `useContext` 可以在组件树的任意层级共享数据,无需逐层传递 props。
```tsx
import type { FC } from 'hono/jsx'
import { createContext, useContext } from 'hono/jsx'
const themes = {
light: {
color: '#000000',
background: '#eeeeee',
},
dark: {
color: '#ffffff',
background: '#222222',
},
}
const ThemeContext = createContext(themes.light)
const Button: FC = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext)
return
}
const Toolbar: FC = () => {
return (
)
}
// ...
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## 异步组件
`hono/jsx` 支持异步组件,因此可以在组件中使用 `async`/`await`。当你使用 `c.html()` 渲染时,会自动等待异步结果。
```tsx
const AsyncComponent = async () => {
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 1000)) // 延迟 1 秒
return Done!
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## Suspense
提供了类似 React 的 `Suspense` 功能。
将异步组件包裹在 `Suspense` 中时,会先渲染备用内容(fallback),待 Promise 解析后再显示真实内容。你可以结合 `renderToReadableStream()` 使用。
```tsx
import { renderToReadableStream, Suspense } from 'hono/jsx/streaming'
//...
app.get('/', (c) => {
const stream = renderToReadableStream(
loading...}>
)
return c.body(stream, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=UTF-8',
'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked',
},
})
})
```
## ErrorBoundary
使用 `ErrorBoundary` 可以捕获子组件中的错误。
在下例中,如果抛出错误,就会展示 `fallback` 指定的内容。
```tsx
function SyncComponent() {
throw new Error('Error')
return Hello
}
app.get('/sync', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
)
})
```
`ErrorBoundary` 也可以与异步组件及 `Suspense` 搭配使用。
```tsx
async function AsyncComponent() {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000))
throw new Error('Error')
return Hello
}
app.get('/with-suspense', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
Loading...}>
)
})
```
## StreamingContext
`StreamingContext` 可用于为 `Suspense`、`ErrorBoundary` 等流式组件提供配置。例如在生成的 `
) : (
)}
Hello
)
})
```
为了正确构建脚本,可以参考以下 `vite.config.ts` 示例:
```ts
import pages from '@hono/vite-cloudflare-pages'
import devServer from '@hono/vite-dev-server'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig(({ mode }) => {
if (mode === 'client') {
return {
build: {
rollupOptions: {
input: './src/client.ts',
output: {
entryFileNames: 'static/client.js',
},
},
},
}
} else {
return {
plugins: [
pages(),
devServer({
entry: 'src/index.tsx',
}),
],
}
}
})
```
执行以下命令可同时构建服务端与客户端脚本:
```sh
vite build --mode client && vite build
```
## Cloudflare Pages 中间件
Cloudflare Pages 拥有与 Hono 不同的[中间件机制](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/middleware/)。在 `_middleware.ts` 中导出 `onRequest` 即可启用:
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
export async function onRequest(pagesContext) {
console.log(`You are accessing ${pagesContext.request.url}`)
return await pagesContext.next()
}
```
借助 `handleMiddleware`,可以将 Hono 中间件作为 Cloudflare Pages 中间件使用:
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
export const onRequest = handleMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
console.log(`You are accessing ${c.req.url}`)
await next()
})
```
还可以使用 Hono 内置或第三方中间件。例如,为页面添加基础认证可以使用 [Hono 的 Basic Auth 中间件](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)。
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
export const onRequest = handleMiddleware(
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
```
如果需要应用多个中间件,可以这样写:
```ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
// ...
export const onRequest = [
handleMiddleware(middleware1),
handleMiddleware(middleware2),
handleMiddleware(middleware3),
]
```
### 访问 `EventContext`
在 `handleMiddleware` 中可以通过 `c.env` 获取 [`EventContext`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/api-reference/#eventcontext) 对象。
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
export const onRequest = [
handleMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.env.eventContext.data.user = 'Joe'
await next()
}),
]
```
之后便可在处理函数中通过 `c.env.eventContext` 读取数据:
```ts
// functions/api/[[route]].ts
import type { EventContext } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { handle } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
// ...
type Env = {
Bindings: {
eventContext: EventContext
}
}
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: `Hello, ${c.env.eventContext.data.user}!`, // 'Joe'
})
})
export const onRequest = handle(app)
```
# Cloudflare Workers
[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com) 是运行在 Cloudflare CDN 上的 JavaScript 边缘运行时。
通过 [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/) 可以在本地开发,并只需几条命令就能发布。Wrangler 自带转译能力,因此可以直接编写 TypeScript 代码。
下面让我们使用 Hono 在 Cloudflare Workers 上创建第一个应用。
## 1. 环境准备
Cloudflare Workers 提供了启动模板,可用 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `cloudflare-workers` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
将 `src/index.ts` 修改如下:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Cloudflare Workers!'))
export default app
```
## 3. 运行
在本地启动开发服务器,然后访问 `http://localhost:8787`。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
### 修改端口
如果需要修改端口号,可参考以下文档更新 `wrangler.toml`/`wrangler.json`/`wrangler.jsonc`:
- [Wrangler Configuration](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#local-development-settings)
或通过 CLI 参数配置:
- [Wrangler CLI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#dev)
## 4. 部署
拥有 Cloudflare 账号后即可部署。在 `package.json` 中,请将 `$npm_execpath` 替换为所用的包管理器。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run deploy
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn deploy
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run deploy
```
```sh [bun]
bun run deploy
```
:::
完成以上步骤即可。
## 与其他事件处理器一起使用 Hono
在模块化 Worker 模式下,可以将 Hono 与其他事件处理器(例如 `scheduled`)结合使用。导出 `app.fetch` 作为模块的 `fetch` 处理器,并按需实现其他处理器:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
export default {
fetch: app.fetch,
scheduled: async (batch, env) => {},
}
```
## 提供静态文件
若需提供静态文件,可使用 Cloudflare Workers 的[静态资源功能](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/static-assets/)。在 `wrangler.toml` 中指定目录:
```toml
assets = { directory = "public" }
```
然后创建 `public` 目录并放置文件。例如 `./public/static/hello.txt` 可通过 `/static/hello.txt` 访问。
```
.
├── package.json
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ └── static
│ └── hello.txt
├── src
│ └── index.ts
└── wrangler.toml
```
## 类型支持
如果想获得 Workers 类型定义,需要安装 `@cloudflare/workers-types`。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i --save-dev @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add -D @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add -D @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [bun]
bun add --dev @cloudflare/workers-types
```
:::
## 测试
推荐使用 `@cloudflare/vitest-pool-workers` 进行测试,可参考 [examples 仓库](https://github.com/honojs/examples) 中的配置。
假设应用如下:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Please test me!'))
```
可以通过以下测试验证是否返回 `200 OK`:
```ts
describe('Test the application', () => {
it('Should return 200 response', async () => {
const res = await app.request('http://localhost/')
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
})
})
```
## 绑定(Bindings)
在 Cloudflare Workers 中可以绑定环境变量、KV 命名空间、R2 Bucket、Durable Object 等。通过在 `Hono` 泛型中传入绑定类型结构体,即可在 `c.env` 中获取并拥有完整类型信息。
```ts
type Bindings = {
MY_BUCKET: R2Bucket
USERNAME: string
PASSWORD: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
// 访问环境值
app.put('/upload/:key', async (c) => {
const key = c.req.param('key')
await c.env.MY_BUCKET.put(key, c.req.body)
return c.text(`Put ${key} successfully!`)
})
```
## 在中间件中使用变量
在模块化 Worker 模式下,如果希望在中间件中使用变量或机密变量(如 Basic Auth 中的用户名和密码),可以这样编写:
```ts
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
type Bindings = {
USERNAME: string
PASSWORD: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
// ...
app.use('/auth/*', async (c, next) => {
const auth = basicAuth({
username: c.env.USERNAME,
password: c.env.PASSWORD,
})
return auth(c, next)
})
```
同样适用于 Bearer 认证、JWT 认证等其他中间件。
## 通过 GitHub Actions 部署
在 CI 中将代码部署到 Cloudflare,需要先创建 Cloudflare Token。可在 [User API Tokens](https://dash.cloudflare.com/profile/api-tokens) 中管理。
如果是新建 Token,请选择 **Edit Cloudflare Workers** 模板;若使用已有 Token,请确保其拥有相应权限(Cloudflare Pages 与 Workers 的 Token 权限并不通用)。
随后在 GitHub 仓库的 `Settings -> Secrets and variables -> Actions -> Repository secrets` 中新增名为 `CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN` 的机密。
在项目根目录创建 `.github/workflows/deploy.yml` 并写入:
```yml
name: Deploy
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Deploy
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Deploy
uses: cloudflare/wrangler-action@v3
with:
apiToken: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
```
随后在 `wrangler.toml` 中、`compatibility_date` 行之后加入:
```toml
main = "src/index.ts"
minify = true
```
至此一切就绪,提交代码即可。
## 本地开发时加载环境变量
在项目根目录创建 `.dev.vars` 或 `.env` 文件,为本地开发配置环境变量。这些文件应采用 [dotenv](https://hexdocs.pm/dotenvy/dotenv-file-format.html) 格式,例如:
```
SECRET_KEY=value
API_TOKEN=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
```
> 更多信息请参见 Cloudflare 文档:
随后即可通过 `c.env.*` 在代码中读取这些变量。
::: info
默认情况下,Cloudflare Workers 中无法使用 `process.env`,建议通过 `c.env` 获取环境变量。如需使用 `process.env`,请启用 [`nodejs_compat_populate_process_env`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/compatibility-flags/#enable-auto-populating-processenv) 标志,或从 `cloudflare:workers` 导入 `env`。详细说明参见 [Cloudflare 文档:如何访问 `env`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/bindings/#how-to-access-env)。
:::
```ts
type Bindings = {
SECRET_KEY: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/env', (c) => {
const SECRET_KEY = c.env.SECRET_KEY
return c.text(SECRET_KEY)
})
```
在将项目部署到 Cloudflare 之前,别忘了在 Cloudflare Workers 的项目配置中设置对应的环境变量或机密。
> 更多信息请参考 Cloudflare 文档:
# Deno
[Deno](https://deno.com/) 是基于 V8 构建的 JavaScript 运行时,与 Node.js 不同。Hono 也能运行在 Deno 上。
你可以使用 TypeScript 编写 Hono 应用,借助 `deno` 命令运行,并部署到 Deno Deploy。
## 1. 安装 Deno
首先安装 `deno` 命令,具体方法请参考[官方文档](https://docs.deno.com/runtime/getting_started/installation/)。
## 2. 环境准备
Deno 提供了启动模板,可使用 [`deno init`](https://docs.deno.com/runtime/reference/cli/init/) 命令创建项目:
```sh
deno init --npm hono my-app --template=deno
```
进入 `my-app` 目录。Deno 会按需拉取依赖,无需显式安装 Hono。
```sh
cd my-app
```
## 3. Hello World
编辑 `main.ts`:
```ts [main.ts]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Deno!'))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
## 4. 运行
在本地启动开发服务器,然后访问 `http://localhost:8000`。
```sh
deno task start
```
## 修改端口
可以在 `main.ts` 中通过 `Deno.serve` 指定端口:
```ts
Deno.serve(app.fetch) // [!code --]
Deno.serve({ port: 8787 }, app.fetch) // [!code ++]
```
## 提供静态文件
从 `hono/deno` 引入 `serveStatic` 即可提供静态文件:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { serveStatic } from 'hono/deno'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('/static/*', serveStatic({ root: './' }))
app.use('/favicon.ico', serveStatic({ path: './favicon.ico' }))
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('You can access: /static/hello.txt'))
app.get('*', serveStatic({ path: './static/fallback.txt' }))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
上述代码可搭配以下目录结构使用:
```
./
├── favicon.ico
├── index.ts
└── static
├── demo
│ └── index.html
├── fallback.txt
├── hello.txt
└── images
└── dinotocat.png
```
### `rewriteRequestPath`
若需将 `http://localhost:8000/static/*` 映射到 `./statics`,可启用 `rewriteRequestPath`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
root: './',
rewriteRequestPath: (path) =>
path.replace(/^\/static/, '/statics'),
})
)
```
### `mimes`
通过 `mimes` 可以添加额外的 MIME 类型:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
mimes: {
m3u8: 'application/vnd.apple.mpegurl',
ts: 'video/mp2t',
},
})
)
```
### `onFound`
使用 `onFound` 可在文件命中时执行自定义逻辑:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
// ...
onFound: (_path, c) => {
c.header('Cache-Control', `public, immutable, max-age=31536000`)
},
})
)
```
### `onNotFound`
使用 `onNotFound` 可在文件缺失时自定义处理:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
onNotFound: (path, c) => {
console.log(`${path} is not found, you access ${c.req.path}`)
},
})
)
```
### `precompressed`
启用 `precompressed` 后,会检测 `.br`、`.gz` 等预压缩文件,并根据 `Accept-Encoding` 优先返回 Brotli,其次是 Zstd、Gzip;若均不存在,则返回原文件。
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
precompressed: true,
})
)
```
## Deno Deploy
Deno Deploy 是面向 JavaScript/TypeScript 应用的 Serverless 平台,支持 GitHub 等集成方式快速部署。Hono 同样适用于 Deno Deploy,详情请参见[官方文档](https://docs.deno.com/deploy/manual/)。
## 测试
在 Deno 中测试非常简单,可以使用 `Deno.test` 搭配 [@std/assert](https://jsr.io/@std/assert) 的 `assert` 或 `assertEquals`。
```sh
deno add jsr:@std/assert
```
```ts [hello.ts]
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { assertEquals } from '@std/assert'
Deno.test('Hello World', async () => {
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Please test me'))
const res = await app.request('http://localhost/')
assertEquals(res.status, 200)
})
```
执行以下命令运行测试:
```sh
deno test hello.ts
```
# Fastly Compute
[Fastly Compute](https://www.fastly.com/products/edge-compute) 是一套先进的边缘计算平台,可在全球网络上以你喜欢的语言运行代码。Hono 同样支持 Fastly Compute。
可以使用 [Fastly CLI](https://www.fastly.com/documentation/reference/tools/cli/) 在本地开发并通过几条命令发布应用。
## 1. 环境准备
Fastly Compute 提供启动模板,可通过 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `fastly` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `src/index.ts`:
```ts
// src/index.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { fire } from 'hono/service-worker'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Fastly!'))
fire(app)
```
## 3. 运行
在本地启动开发服务器,然后访问 `http://localhost:7676`。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run start
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn start
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run start
```
```sh [bun]
bun run start
```
:::
## 4. 部署
使用以下命令构建并部署到 Fastly 账号。首次部署时,CLI 会提示你在账户中创建新服务。
若尚无账号,请先[注册 Fastly 账号](https://www.fastly.com/signup/)。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run deploy
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn deploy
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run deploy
```
```sh [bun]
bun run deploy
```
:::
# Google Cloud Run
[Google Cloud Run](https://cloud.google.com/run) 是 Google Cloud 提供的 Serverless 平台。你可以根据事件触发运行代码,底层计算资源由 Google 自动管理。
Cloud Run 使用容器运行服务,这意味着你可以通过提供 Dockerfile 来选择任意运行时(例如 Deno 或 Bun)。如果没有提供 Dockerfile,Cloud Run 会使用默认的 Node.js Buildpack。
本指南假设你已有 Google Cloud 账号和计费账号。
## 1. 安装 CLI
使用 [gcloud CLI](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install) 能更高效地操作 Google Cloud 平台。
例如在 macOS 上,可通过 Homebrew 安装:
```sh
brew install --cask google-cloud-sdk
```
安装完成后进行身份验证:
```sh
gcloud auth login
```
## 2. 项目初始化
创建项目,并在提示时接受自动生成的项目 ID:
```sh
gcloud projects create --set-as-default --name="my app"
```
为方便重复使用,可保存项目 ID 与项目编号。项目创建成功可能需要约 30 秒,请稍候再执行 `gcloud projects list`。
```sh
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud projects list \
--format='value(projectId)' \
--filter='name="my app"')
PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects list \
--format='value(projectNumber)' \
--filter='name="my app"')
echo $PROJECT_ID $PROJECT_NUMBER
```
查看计费账号 ID:
```sh
gcloud billing accounts list
```
将计费账号与项目关联:
```sh
gcloud billing projects link $PROJECT_ID \
--billing-account=[billing_account_id]
```
启用所需的 API:
```sh
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com
```
为服务账号授予 Cloud Build 权限:
```sh
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member=serviceAccount:$PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \
--role=roles/run.builder
```
## 3. Hello World
通过 `create-hono` 初始化项目,选择 `nodejs` 模板:
```sh
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖:
```sh
cd my-app
npm i
```
将 `src/index.ts` 中的端口改为 `8080`:
```ts
import { serve } from '@hono/node-server'
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello Hono!')
})
serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
port: 3000 // [!code --]
port: 8080 // [!code ++]
}, (info) => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${info.port}`)
})
```
启动本地开发服务器,并在浏览器访问 `http://localhost:8080`:
```sh
npm run dev
```
## 4. 部署
执行以下命令启动部署,根据提示选择区域等信息:
```sh
gcloud run deploy my-app --source . --allow-unauthenticated
```
## 更换运行时
如果希望使用 Deno、Bun 或自定义 Node.js 镜像,请在项目中添加 `Dockerfile`(可选配 `.dockerignore`),构建所需的运行环境。
有关容器化的更多信息可参考:
- [Node.js](/docs/getting-started/nodejs#building-deployment)
- [Bun](https://bun.sh/guides/ecosystem/docker)
- [Deno](https://docs.deno.com/examples/google_cloud_run_tutorial)
# Lambda@Edge
[Lambda@Edge](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/edge/) 是亚马逊云服务推出的 Serverless 平台,可在 Amazon CloudFront 的边缘节点运行 Lambda 函数,从而自定义 HTTP 请求与响应的行为。
Hono 可以在 Node.js 18 及以上环境的 Lambda@Edge 上运行。
## 1. 环境准备
在 Lambda@Edge 上创建应用时,[CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-cdk.html) 有助于配置 CloudFront、IAM 角色、API Gateway 等资源。
使用 `cdk` CLI 初始化项目:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
npm i hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [yarn]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
yarn add hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [pnpm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
pnpm add hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [bun]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
bun add hono
mkdir lambda
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `lambda/index_edge.ts`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono on Lambda@Edge!'))
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## 3. 部署
编辑 `bin/my-app.ts`:
```ts
#!/usr/bin/env node
import 'source-map-support/register'
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import { MyAppStack } from '../lib/my-app-stack'
const app = new cdk.App()
new MyAppStack(app, 'MyAppStack', {
env: {
account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT,
region: 'us-east-1',
},
})
```
编辑 `lambda/cdk-stack.ts`:
```ts
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import * as cloudfront from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront'
import * as origins from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront-origins'
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda'
import { NodejsFunction } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda-nodejs'
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3'
export class MyAppStack extends cdk.Stack {
public readonly edgeFn: lambda.Function
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const edgeFn = new NodejsFunction(this, 'edgeViewer', {
entry: 'lambda/index_edge.ts',
handler: 'handler',
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
})
// 上传任意 HTML 文件
const originBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'originBucket')
new cloudfront.Distribution(this, 'Cdn', {
defaultBehavior: {
origin: new origins.S3Origin(originBucket),
edgeLambdas: [
{
functionVersion: edgeFn.currentVersion,
eventType: cloudfront.LambdaEdgeEventType.VIEWER_REQUEST,
},
],
},
})
}
}
```
最后运行以下命令部署:
```sh
cdk deploy
```
## Callback
如果想在通过 Basic Auth 验证后继续执行后续处理,可以调用 `c.env.callback()`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
import type { Callback, CloudFrontRequest } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
import { handle } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
type Bindings = {
callback: Callback
request: CloudFrontRequest
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get(
'*',
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
app.get('/', async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.env.callback(null, c.env.request)
})
export const handler = handle(app)
```
# Netlify
Netlify 提供静态网站托管与无服务器后端服务。[Edge Functions](https://docs.netlify.com/edge-functions/overview/) 可以让页面具备动态能力。
Edge Functions 支持使用 Deno 与 TypeScript 编写,并可通过 [Netlify CLI](https://docs.netlify.com/cli/get-started/) 轻松部署。借助 Hono,你可以为 Netlify Edge Functions 构建应用。
## 1. 环境准备
Netlify 提供了启动模板,可通过 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `netlify` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 目录。
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `netlify/edge-functions/index.ts`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
import { handle } from 'jsr:@hono/hono/netlify'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello Hono!')
})
export default handle(app)
```
## 3. 运行
使用 Netlify CLI 启动开发服务器,并访问 `http://localhost:8888`:
```sh
netlify dev
```
## 4. 部署
通过以下命令即可部署:
```sh
netlify deploy --prod
```
## `Context`
可以通过 `c.env` 访问 Netlify 的 `Context`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
import { handle } from 'jsr:@hono/hono/netlify'
// 引入类型定义
import type { Context } from 'https://edge.netlify.com/'
export type Env = {
Bindings: {
context: Context
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/country', (c) =>
c.json({
'You are in': c.env.context.geo.country?.name,
})
)
export default handle(app)
```
# Next.js
Next.js 是一个灵活的 React 框架,提供构建快速 Web 应用所需的基础能力。
在使用 Node.js 运行时时,可以在 Next.js 中运行 Hono。
在 Vercel 上部署时,借助 Vercel Functions 可以轻松将 Hono 与 Next.js 结合。
## 1. 环境准备
Next.js 提供启动模板,可通过 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `nextjs` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
如果使用 App Router,请编辑 `app/api/[[...route]]/route.ts`。更多支持的 HTTP 方法可参考[官方文档](https://nextjs.org/docs/app/building-your-application/routing/route-handlers#supported-http-methods)。
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/vercel'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello Next.js!',
})
})
export const GET = handle(app)
export const POST = handle(app)
```
## 3. 运行
启动本地开发服务器,并访问 `http://localhost:3000`。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
此时 `/api/hello` 会返回 JSON。如果继续构建 React 界面,即可基于 Hono 构成完整的全栈应用。
## 4. 部署
若已拥有 Vercel 账号,可直接关联 Git 仓库进行部署。
## Pages Router
若使用 Pages Router,需先安装 Node.js 适配器。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i @hono/node-server
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add @hono/node-server
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add @hono/node-server
```
```sh [bun]
bun add @hono/node-server
```
:::
然后在 `pages/api/[[...route]].ts` 中从 `@hono/node-server/vercel` 引入 `handle`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from '@hono/node-server/vercel'
import type { PageConfig } from 'next'
export const config: PageConfig = {
api: {
bodyParser: false,
},
}
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello Next.js!',
})
})
export default handle(app)
```
在 Pages Router 中使用该方式时,需要禁用 Vercel Node.js helpers。请在项目控制台或 `.env` 中设置:
```text
NODEJS_HELPERS=0
```
# Node.js
[Node.js](https://nodejs.org/) 是一个开源、跨平台的 JavaScript 运行时环境。
Hono 最初并未专为 Node.js 设计,但借助 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server) 也可以在 Node.js 上运行。
::: info
适配器支持 Node.js 18.x 及以上版本,具体要求如下:
- 18.x => 18.14.1+
- 19.x => 19.7.0+
- 20.x => 20.0.0+
总体而言,建议直接使用各大版本的最新版本。
:::
## 1. 环境准备
Node.js 提供启动模板,可通过 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `nodejs` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `src/index.ts`:
```ts
import { serve } from '@hono/node-server'
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Node.js!'))
serve(app)
```
如果需要优雅地关闭服务,可写成:
```ts
const server = serve(app)
// graceful shutdown
process.on('SIGINT', () => {
server.close()
process.exit(0)
})
process.on('SIGTERM', () => {
server.close((err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
process.exit(0)
})
})
```
## 3. 运行
在本地启动开发服务器,并访问 `http://localhost:3000`。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
:::
## 修改端口
可以通过 `port` 选项指定端口:
```ts
serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
port: 8787,
})
```
## 访问原生 Node.js API
可以通过 `c.env.incoming` 与 `c.env.outgoing` 获取 Node.js 原生对象:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { serve, type HttpBindings } from '@hono/node-server'
// 如果使用 HTTP/2,请改用 Http2Bindings
type Bindings = HttpBindings & {
/* ... */
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.json({
remoteAddress: c.env.incoming.socket.remoteAddress,
})
})
serve(app)
```
## 提供静态文件
可以使用 `serveStatic` 从本地文件系统提供静态资源。假设目录结构如下:
```
./
├── favicon.ico
├── index.ts
└── static
├── hello.txt
└── image.png
```
若想让 `/static/*` 路径对应 `./static` 下的文件,可编写:
```ts
import { serveStatic } from '@hono/node-server/serve-static'
app.use('/static/*', serveStatic({ root: './' }))
```
若要提供根目录的 `favicon.ico`,可使用 `path` 选项:
```ts
app.use('/favicon.ico', serveStatic({ path: './favicon.ico' }))
```
若希望 `/hello.txt` 或 `/image.png` 映射到 `./static/hello.txt`、`./static/image.png`,可以:
```ts
app.use('*', serveStatic({ root: './static' }))
```
### `rewriteRequestPath`
如果需要将 `http://localhost:3000/static/*` 映射到 `./statics`,可以启用 `rewriteRequestPath`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
root: './',
rewriteRequestPath: (path) =>
path.replace(/^\/static/, '/statics'),
})
)
```
## HTTP/2
Hono 也可以运行在 [Node.js http2 服务器](https://nodejs.org/api/http2.html) 上。
### 未加密的 HTTP/2
```ts
import { createServer } from 'node:http2'
const server = serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
createServer,
})
```
### 加密的 HTTP/2
```ts
import { createSecureServer } from 'node:http2'
import { readFileSync } from 'node:fs'
const server = serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
createServer: createSecureServer,
serverOptions: {
key: readFileSync('localhost-privkey.pem'),
cert: readFileSync('localhost-cert.pem'),
},
})
```
## 构建与部署
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run build
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn run build
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run build
```
```sh [bun]
bun run build
```
::: info
如果项目包含前端框架,可考虑使用 [Hono 的 Vite 插件](https://github.com/honojs/vite-plugins)。
:::
### Dockerfile
以下是示例 Node.js Dockerfile:
```Dockerfile
FROM node:22-alpine AS base
FROM base AS builder
RUN apk add --no-cache gcompat
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*json tsconfig.json src ./
RUN npm ci && \
npm run build && \
npm prune --production
FROM base AS runner
WORKDIR /app
RUN addgroup --system --gid 1001 nodejs
RUN adduser --system --uid 1001 hono
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/node_modules /app/node_modules
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/dist /app/dist
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/package.json /app/package.json
USER hono
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "/app/dist/index.js"]
```
# Service Worker
[Service Worker](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Service_Worker_API) 是在浏览器后台运行的脚本,可处理缓存、推送通知等任务。借助 Service Worker 适配器,可以让 Hono 应用作为浏览器中的 [FetchEvent](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/FetchEvent) 处理器。
本页示例使用 [Vite](https://vitejs.dev/) 创建项目。
## 1. 环境准备
首先创建项目目录并进入:
```sh
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
```
创建 `package.json`:
```json
{
"name": "my-app",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite dev"
},
"type": "module"
}
```
创建 `tsconfig.json`:
```json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020",
"module": "ESNext",
"lib": ["ES2020", "DOM", "WebWorker"],
"moduleResolution": "bundler"
},
"include": ["./"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
```
安装所需依赖。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i hono
npm i -D vite
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add hono
yarn add -D vite
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add hono
pnpm add -D vite
```
```sh [bun]
bun add hono
bun add -D vite
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `index.html`:
```html
Hello World by Service Worker
```
`main.ts` 用于注册 Service Worker:
```ts
function register() {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register('/sw.ts', { scope: '/sw', type: 'module' })
.then(
function (_registration) {
console.log('Register Service Worker: Success')
},
function (_error) {
console.log('Register Service Worker: Error')
}
)
}
function start() {
navigator.serviceWorker
.getRegistrations()
.then(function (registrations) {
for (const registration of registrations) {
console.log('Unregister Service Worker')
registration.unregister()
}
register()
})
}
start()
```
在 `sw.ts` 中使用 Hono 构建应用,并通过 Service Worker 适配器的 `handle` 将其注册到 `fetch` 事件,这样访问 `/sw` 时便由 Hono 接管:
```ts
// To support types
// https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/issues/14877
declare const self: ServiceWorkerGlobalScope
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/service-worker'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/sw')
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello World'))
self.addEventListener('fetch', handle(app))
```
### 使用 `fire()`
`fire()` 会自动调用 `addEventListener('fetch', handle(app))`,让代码更简洁:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { fire } from 'hono/service-worker'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/sw')
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello World'))
fire(app)
```
## 3. 运行
启动开发服务器。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
默认情况下,开发服务器运行在 `5173` 端口。访问 `http://localhost:5173/` 完成 Service Worker 注册,然后访问 `/sw` 查看 Hono 应用的响应。
# Supabase Edge Functions
[Supabase](https://supabase.com/) 是开源的 Firebase 替代方案,提供数据库、身份验证、存储以及如今的无服务器函数等能力。
Supabase Edge Functions 是在全球分发的服务端 TypeScript 函数,可在更接近用户的位置运行以提升性能。这些函数基于 [Deno](https://deno.com/),带来了更好的安全性以及现代化的 JavaScript/TypeScript 运行时体验。
以下是使用 Supabase Edge Functions 的快速指南:
## 1. 环境准备
### 前置条件
开始之前,请确保已安装 Supabase CLI。若尚未安装,可按照[官方文档](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/cli/getting-started) 操作。
### 创建新项目
1. 打开终端或命令行窗口。
2. 在本地目录中执行以下命令初始化 Supabase 项目:
```bash
supabase init
```
上述命令会在当前目录创建一个新的 Supabase 项目。
### 新增 Edge Function
3. 在项目内创建名为 `hello-world` 的 Edge Function:
```bash
supabase functions new hello-world
```
该命令会在项目中生成指定名称的 Edge Function。
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `supabase/functions/hello-world/index.ts`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
// 将此处替换为函数名称
const functionName = 'hello-world'
const app = new Hono().basePath(`/${functionName}`)
app.get('/hello', (c) => c.text('Hello from hono-server!'))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
## 3. 运行
在本地运行函数:
1. 启动 Supabase 环境并运行函数监视器:
```bash
supabase start # 启动 Supabase 全家桶
supabase functions serve --no-verify-jwt # 启动函数监听
```
`--no-verify-jwt` 参数用于在本地开发时跳过 JWT 校验。
2. 使用 cURL 或 Postman 请求 `http://127.0.0.1:54321/functions/v1/hello-world/hello`:
```bash
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:54321/functions/v1/hello-world/hello'
```
即可得到 “Hello from hono-server!” 的响应。
## 4. 部署
可通过以下命令一次性部署所有 Edge Functions:
```bash
supabase functions deploy
```
若只部署单个函数,可指定名称:
```bash
supabase functions deploy hello-world
```
更多部署方式请参考 Supabase 文档:[Deploying to Production](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/functions/deploy)。
# Vercel
Vercel 是一朵面向 AI 的云,为开发者提供构建、扩展与保护高速个性化 Web 所需的工具与基础设施。
Hono 可以零配置部署到 Vercel。
## 1. 环境准备
Vercel 提供了启动模板,可通过 `create-hono` 命令初始化项目。本示例选择 `vercel` 模板。
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
进入 `my-app` 并安装依赖:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
接下来会使用 Vercel CLI 在本地调试,如尚未安装请参考[Vercel CLI 文档](https://vercel.com/docs/cli) 进行全局安装。
## 2. Hello World
在项目的 `index.ts` 或 `src/index.ts` 中,将 Hono 应用作为默认导出:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
const welcomeStrings = [
'Hello Hono!',
'To learn more about Hono on Vercel, visit https://vercel.com/docs/frameworks/hono',
]
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text(welcomeStrings.join('\n\n'))
})
export default app
```
如果使用的是 `vercel` 模板,这些内容已经配置完成。
## 3. 运行
在本地启动开发服务器:
```sh
vercel dev
```
访问 `localhost:3000` 即可看到文本响应。
## 4. 部署
使用 `vercel deploy` 将应用部署到 Vercel:
```sh
vercel deploy
```
## 延伸阅读
可在 [Vercel 文档](https://vercel.com/docs/frameworks/backend/hono) 中了解更多关于 Hono 的信息。
# 基准测试
基准测试只是基准测试,但对我们而言十分重要。
## 路由器
我们测量了多款 JavaScript 路由器的性能。
例如,`find-my-way` 是 Fastify 内部使用、速度极快的路由器。
- @medley/router
- find-my-way
- koa-tree-router
- trek-router
- express(包含请求处理)
- koa-router
首先,我们为所有路由器注册了以下路由,
这些路由与真实世界中的案例十分接近。
```ts twoslash
interface Route {
method: string
path: string
}
// ---cut---
export const routes: Route[] = [
{ method: 'GET', path: '/user' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/user/comments' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/user/avatar' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/user/lookup/username/:username' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/user/lookup/email/:address' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/event/:id' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/event/:id/comments' },
{ method: 'POST', path: '/event/:id/comment' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/map/:location/events' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/status' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/very/deeply/nested/route/hello/there' },
{ method: 'GET', path: '/static/*' },
]
```
随后,我们向这些端点发送如下请求:
```ts twoslash
interface Route {
method: string
path: string
}
// ---cut---
const routes: (Route & { name: string })[] = [
{
name: 'short static',
method: 'GET',
path: '/user',
},
{
name: 'static with same radix',
method: 'GET',
path: '/user/comments',
},
{
name: 'dynamic route',
method: 'GET',
path: '/user/lookup/username/hey',
},
{
name: 'mixed static dynamic',
method: 'GET',
path: '/event/abcd1234/comments',
},
{
name: 'post',
method: 'POST',
path: '/event/abcd1234/comment',
},
{
name: 'long static',
method: 'GET',
path: '/very/deeply/nested/route/hello/there',
},
{
name: 'wildcard',
method: 'GET',
path: '/static/index.html',
},
]
```
让我们看看结果。
### Node.js 环境
以下截图展示了在 Node.js 环境下的结果。
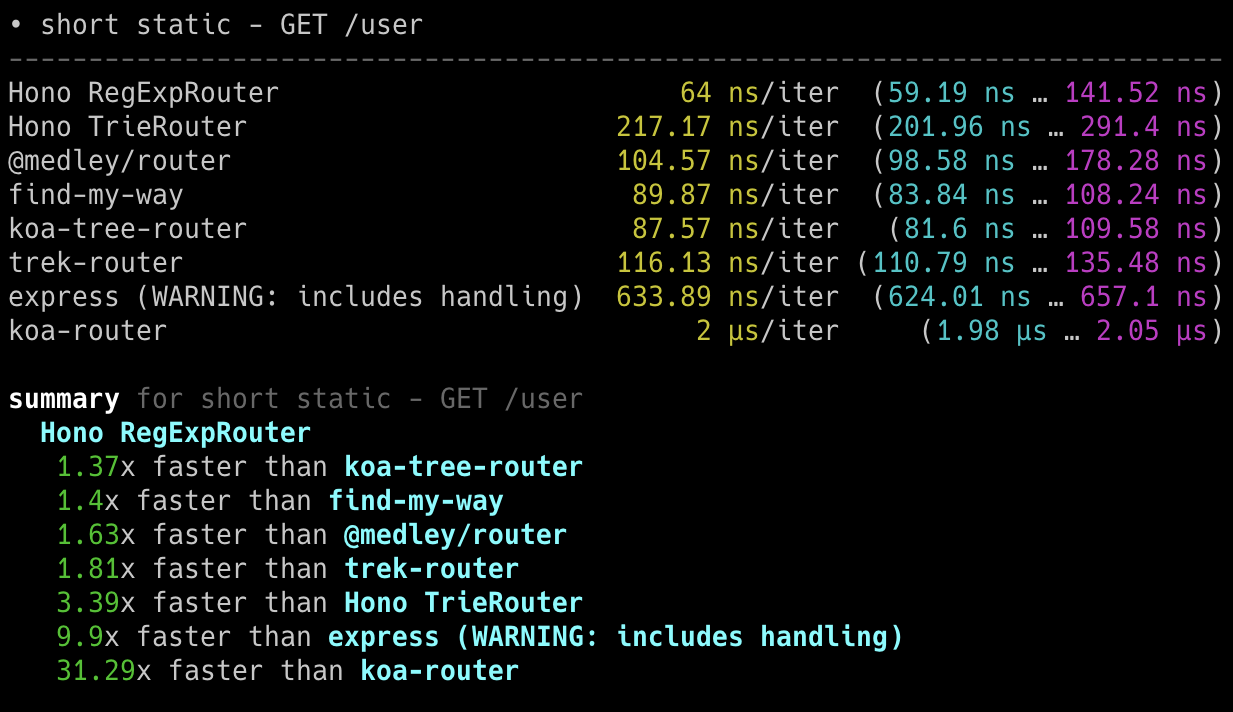
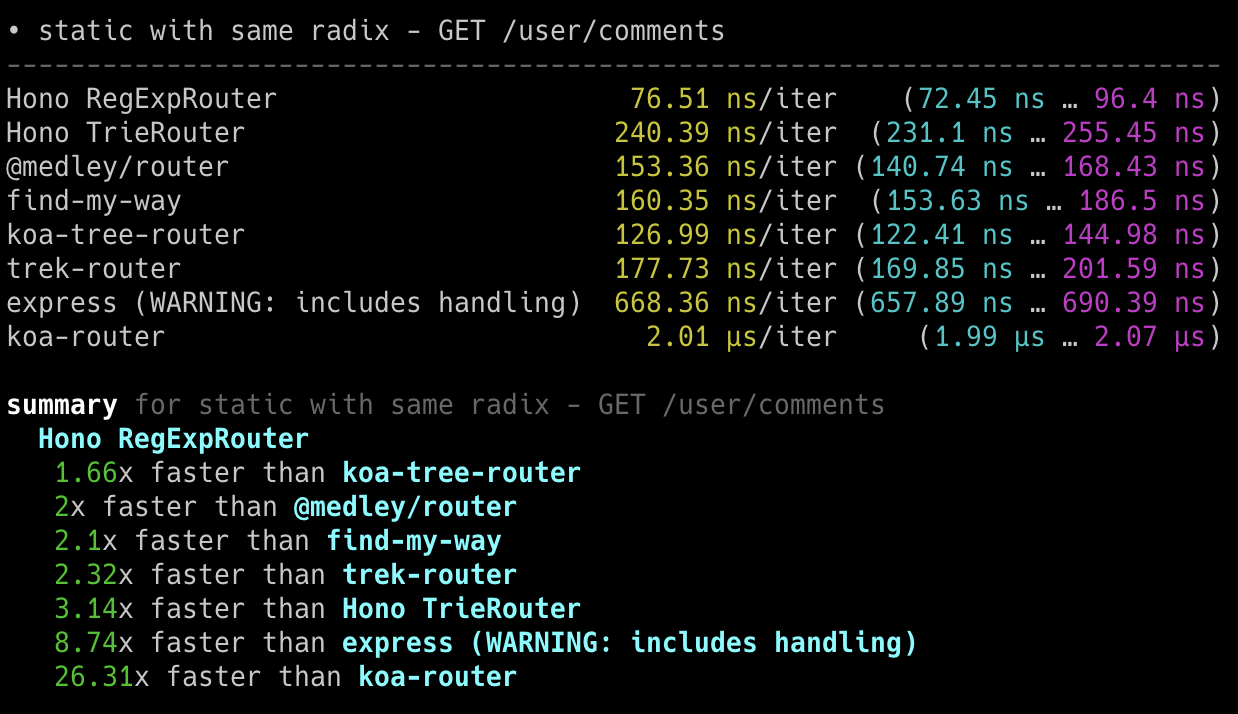
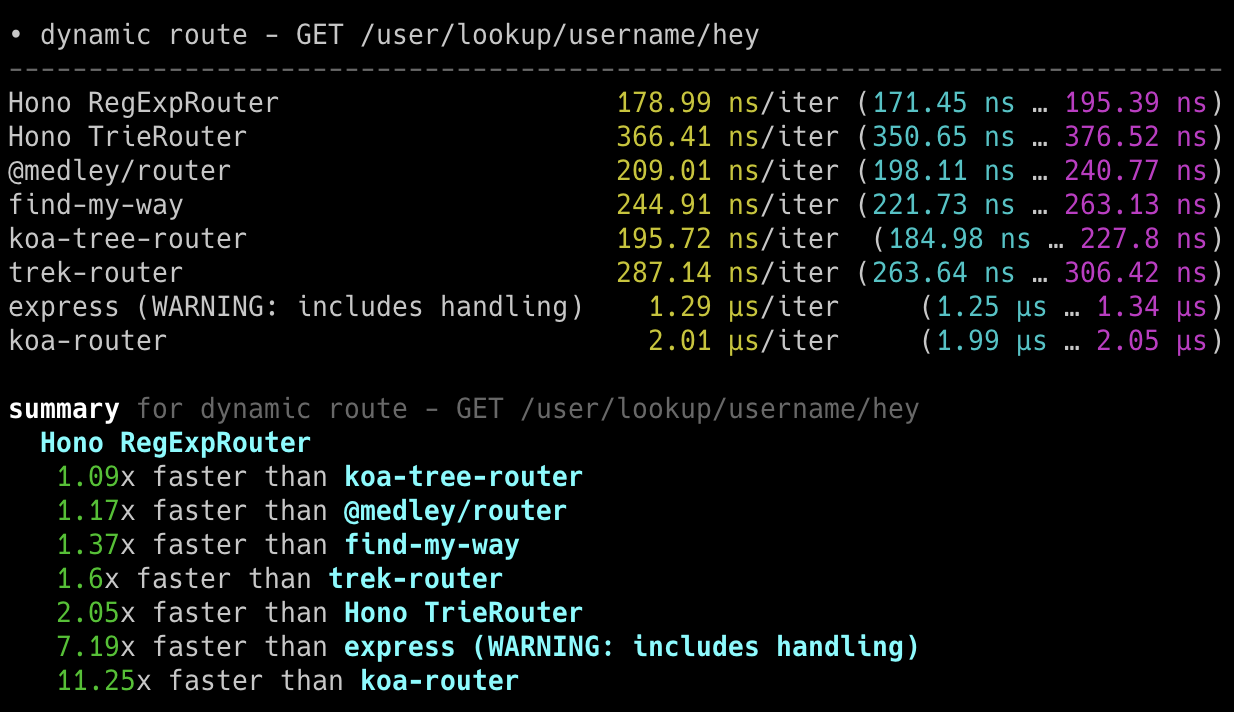
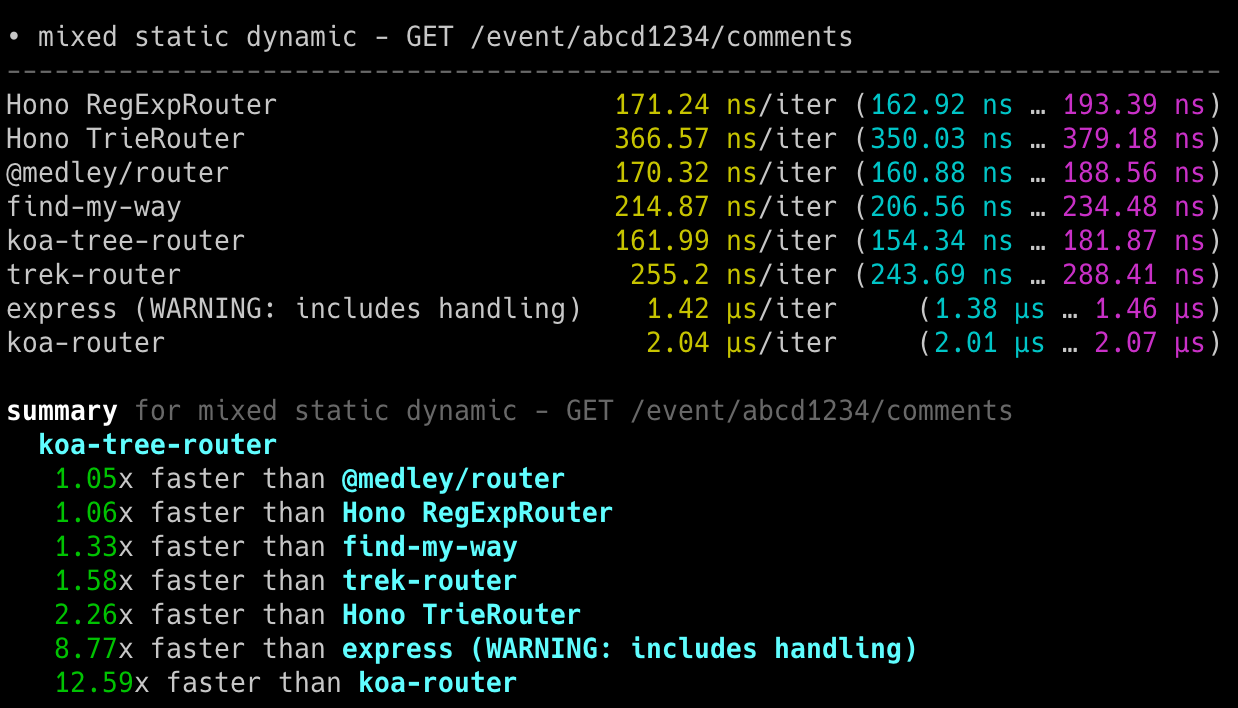
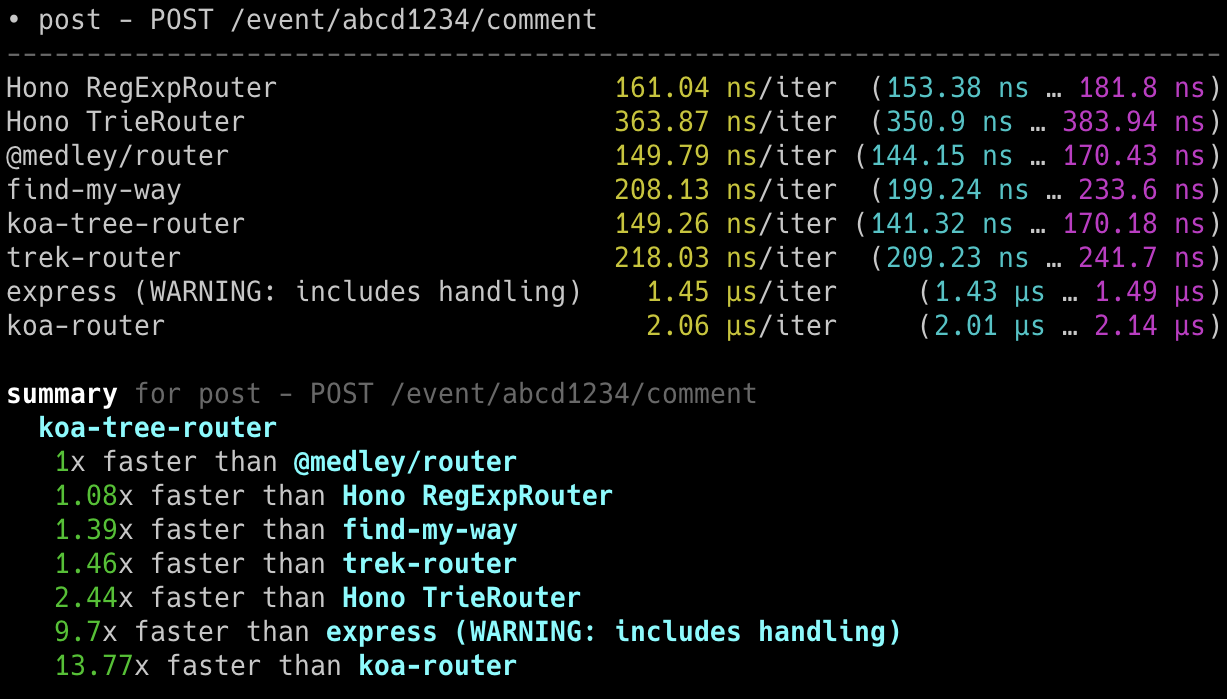
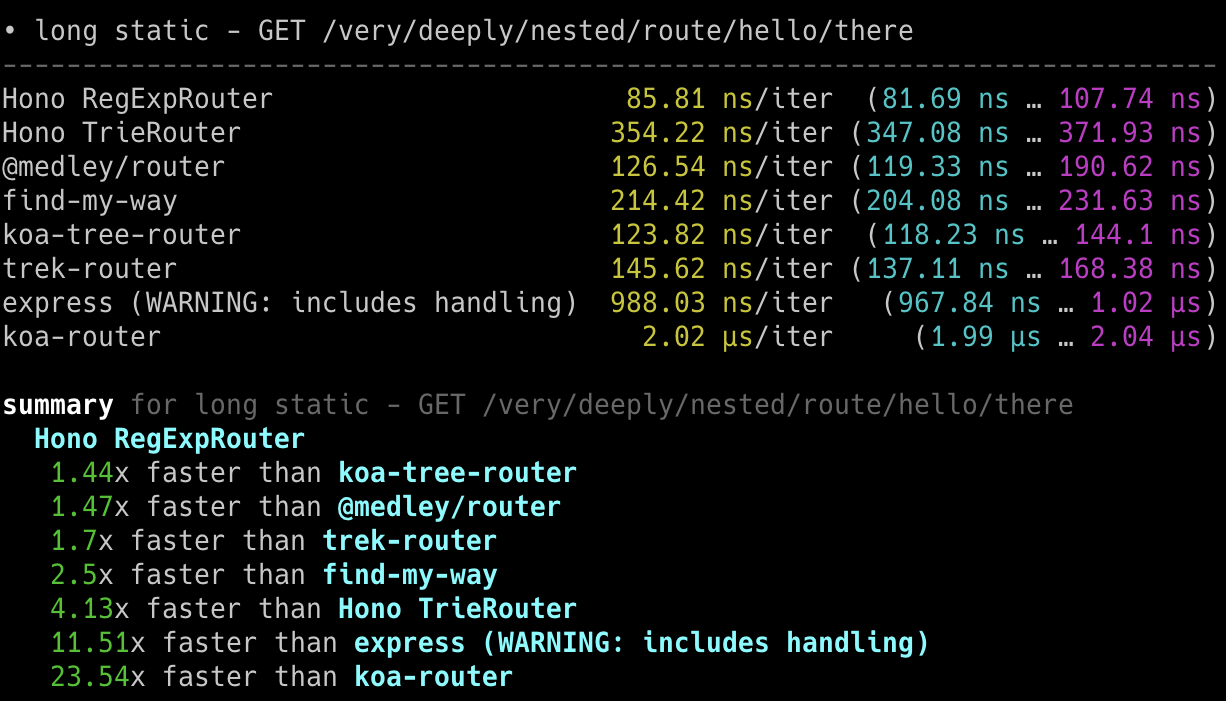
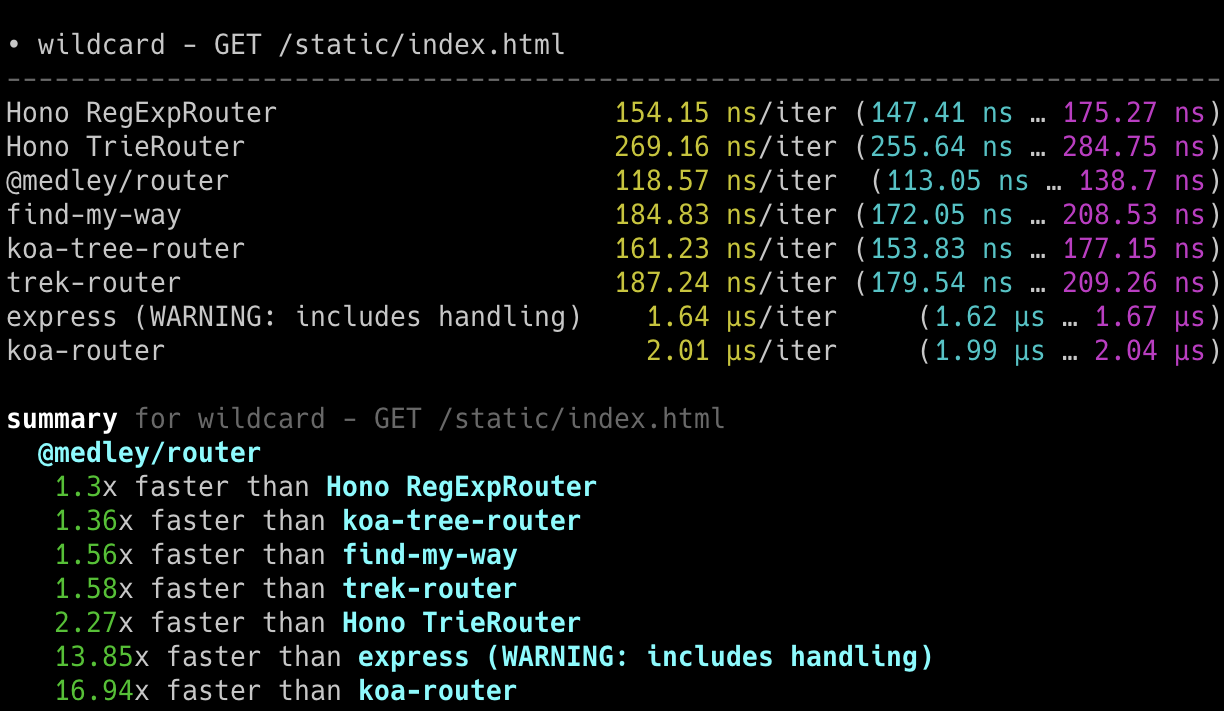
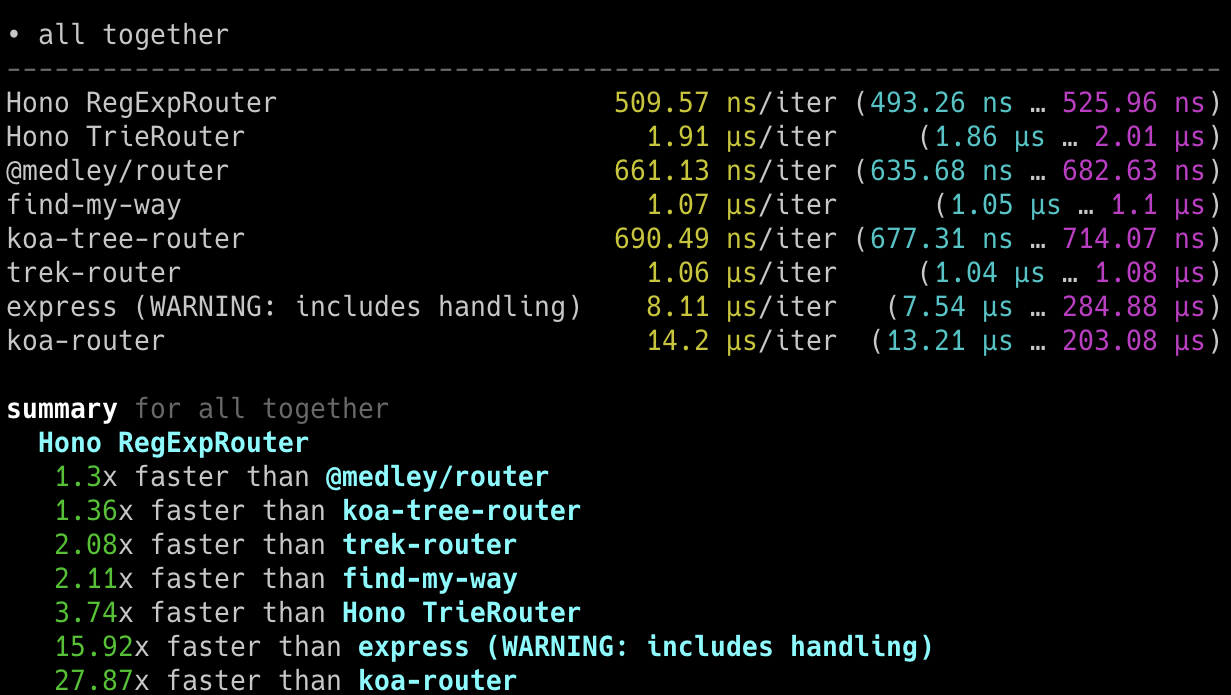
### Bun 环境
以下截图展示了在 Bun 环境下的结果。
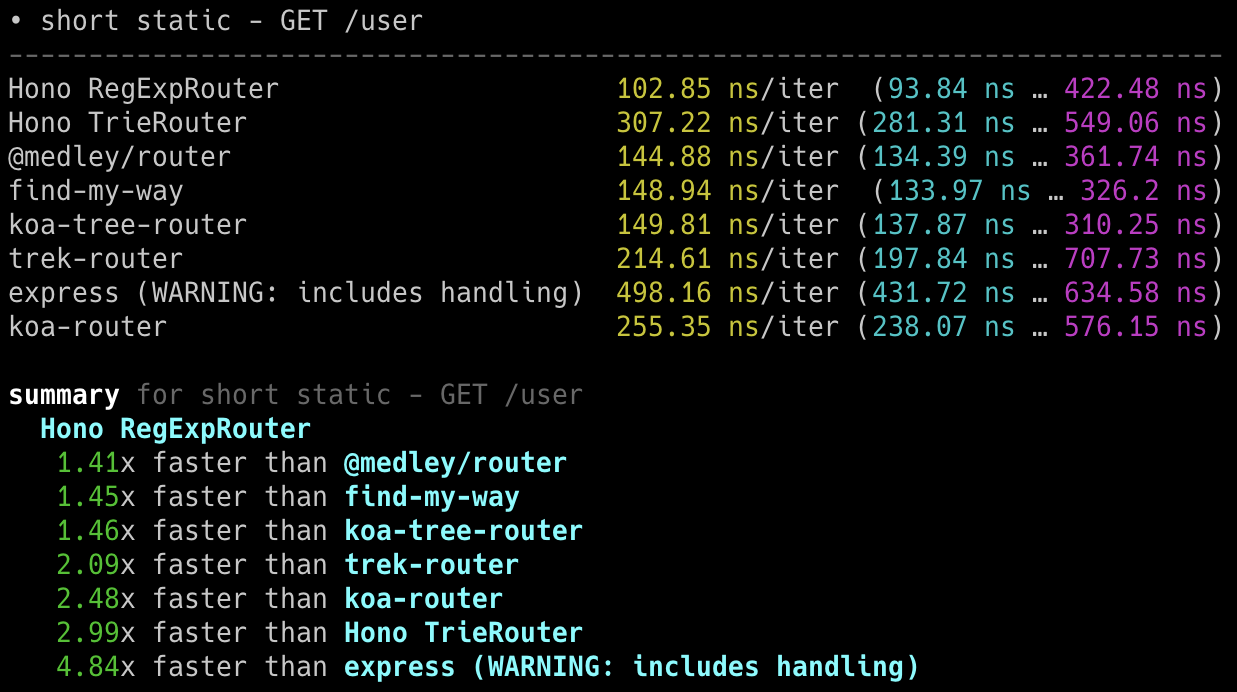
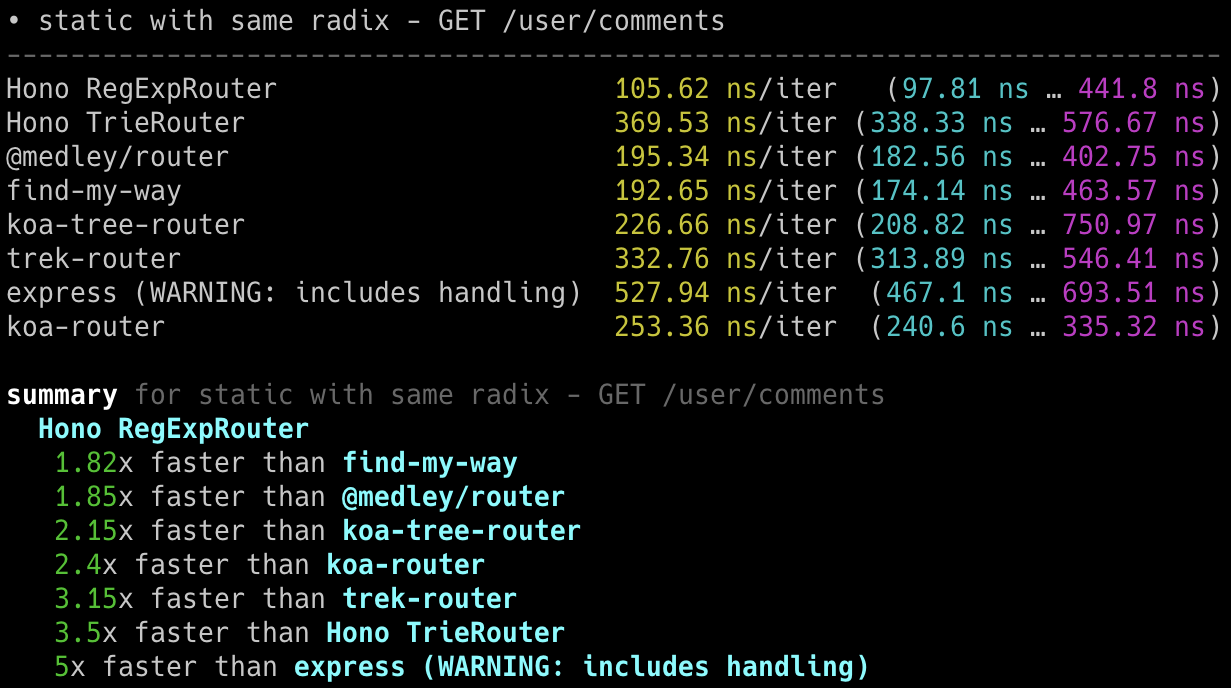
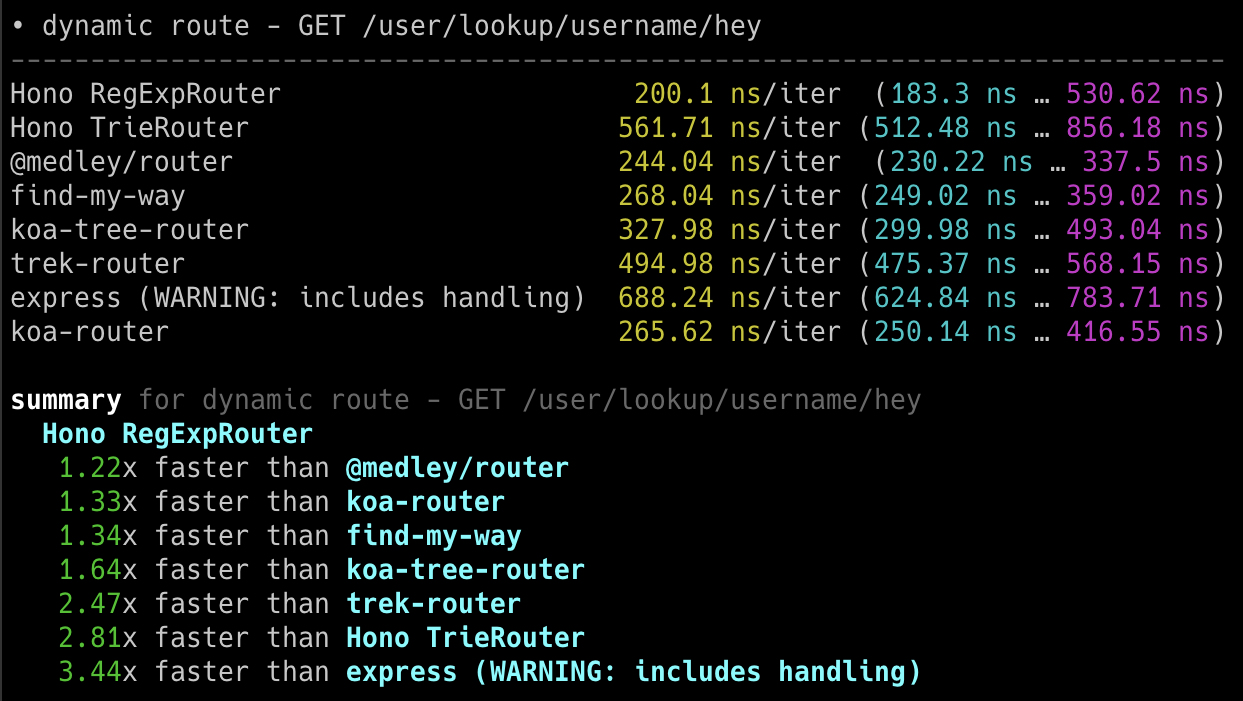
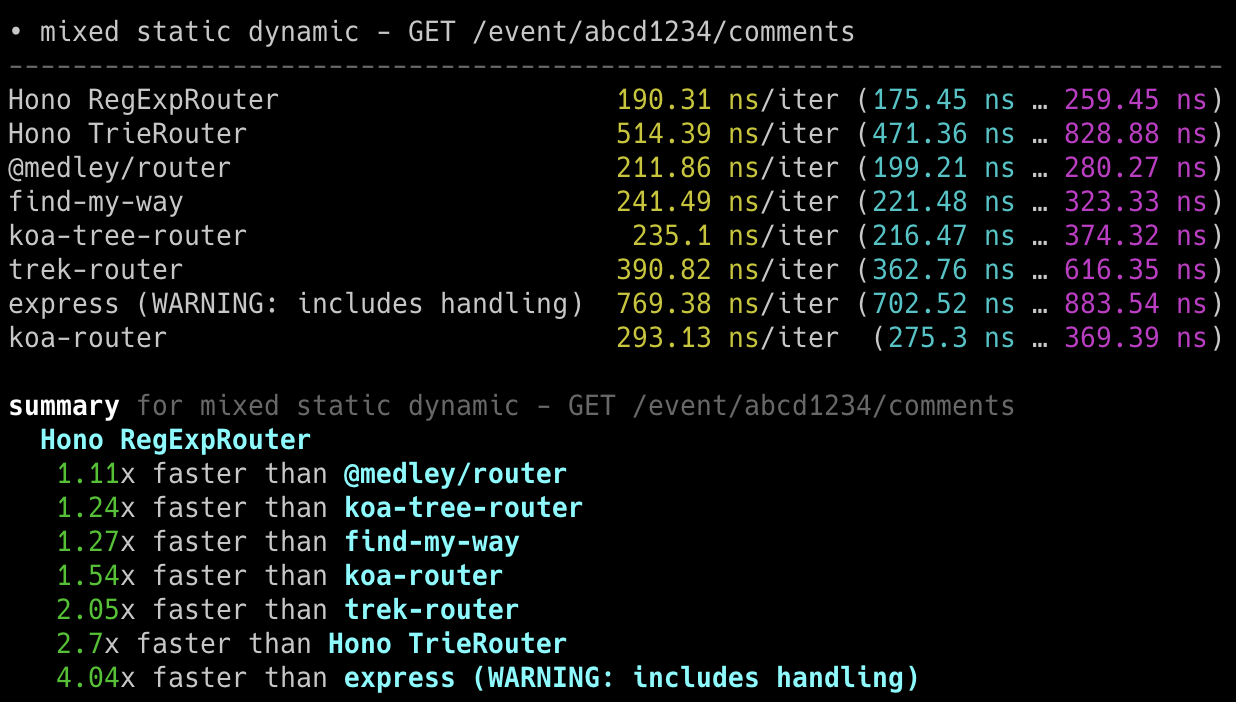
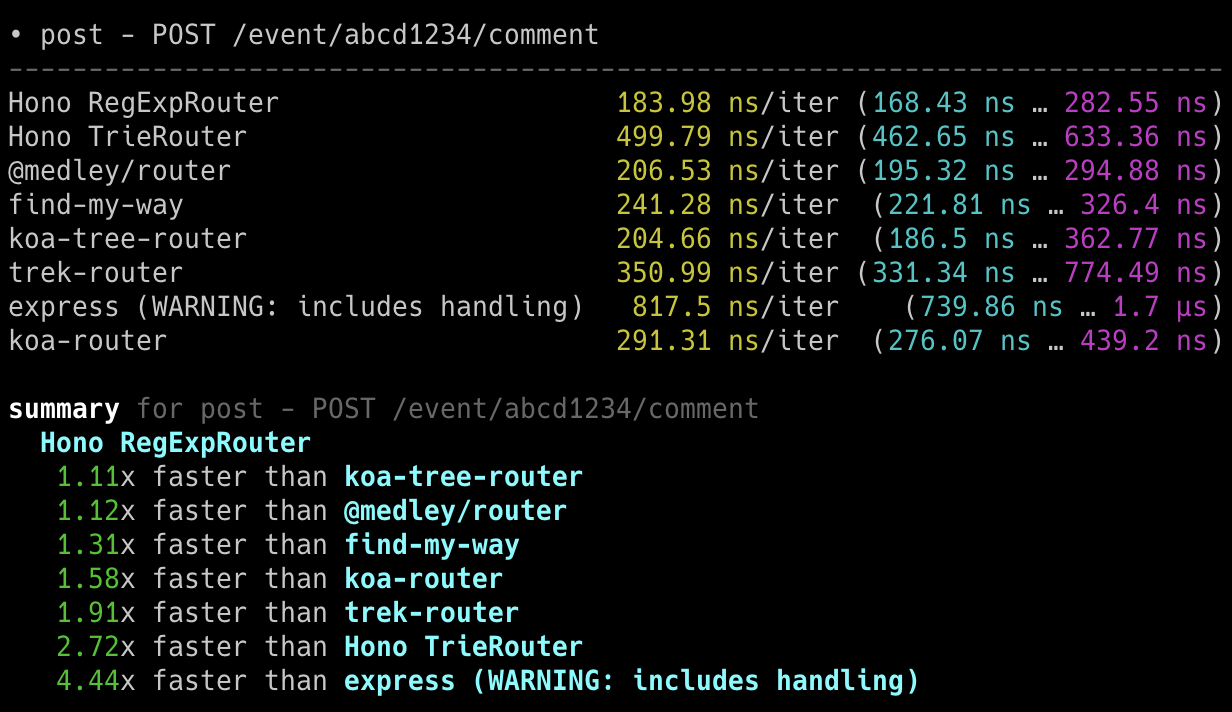
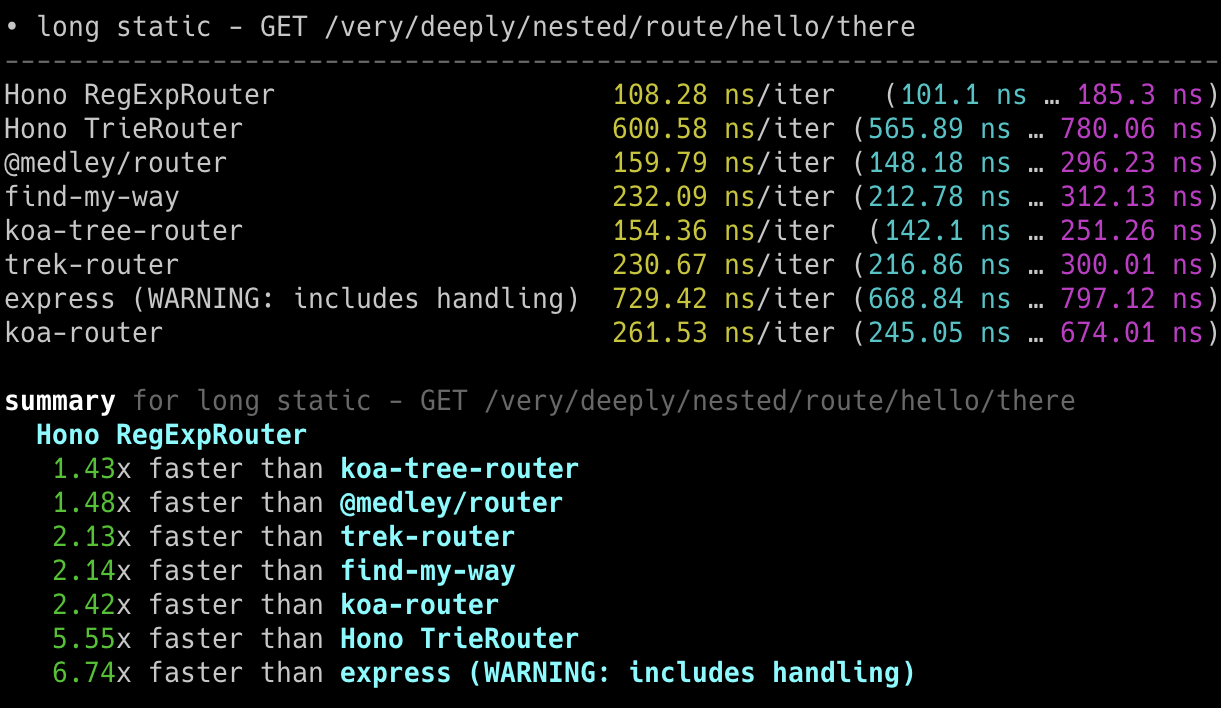
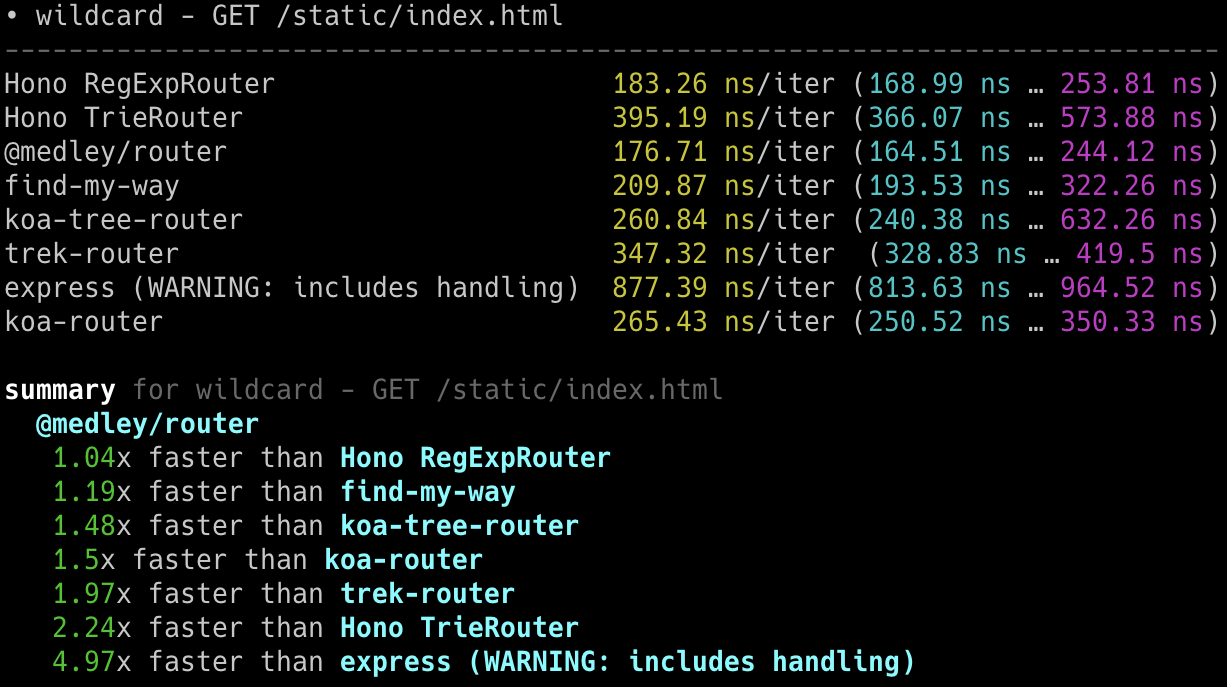
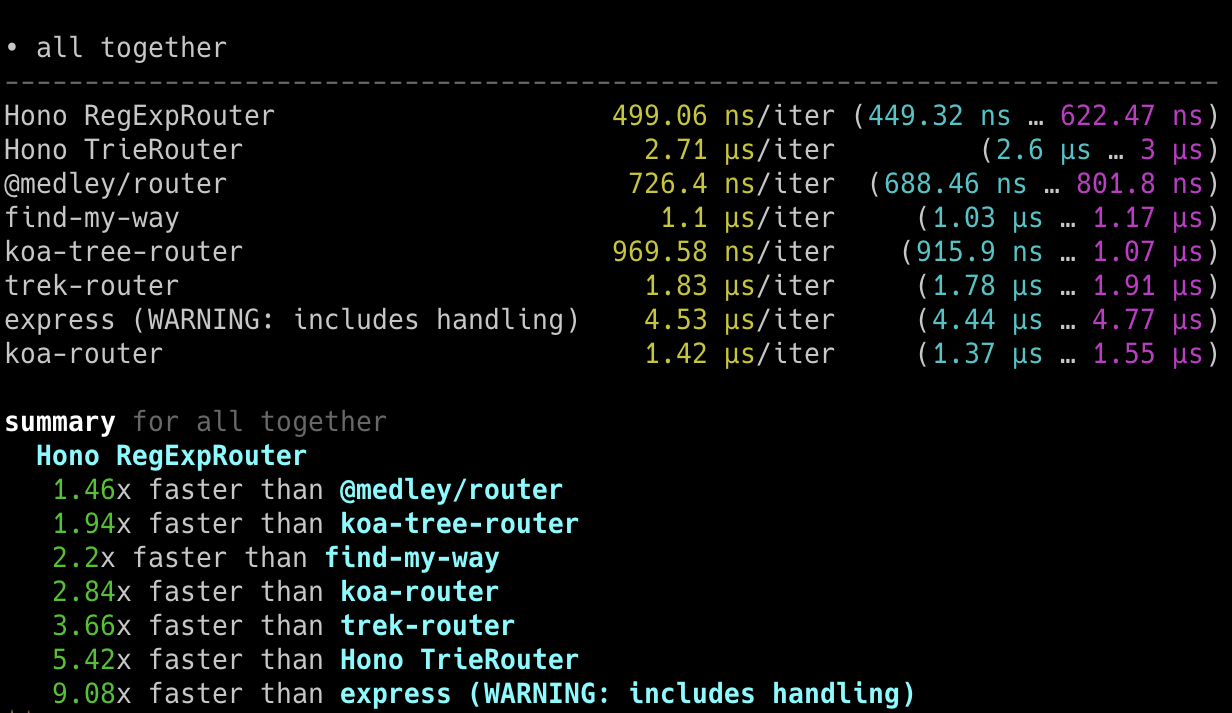
## Cloudflare Workers
**与其他 Cloudflare Workers 路由器相比,Hono 是最快的。**
- 测试机型:Apple MacBook Pro,32 GiB,M1 Pro
- 脚本来源:[benchmarks/handle-event](https://github.com/honojs/hono/tree/main/benchmarks/handle-event)
```
Hono x 402,820 ops/sec ±4.78% (80 runs sampled)
itty-router x 212,598 ops/sec ±3.11% (87 runs sampled)
sunder x 297,036 ops/sec ±4.76% (77 runs sampled)
worktop x 197,345 ops/sec ±2.40% (88 runs sampled)
Fastest is Hono
✨ Done in 28.06s.
```
## Deno
**与其他 Deno 框架相比,Hono 同样是最快的。**
- 测试机型:Apple MacBook Pro,32 GiB,M1 Pro,Deno v1.22.0
- 脚本来源:[benchmarks/deno](https://github.com/honojs/hono/tree/main/benchmarks/deno)
- 压测命令:`bombardier --fasthttp -d 10s -c 100 'http://localhost:8000/user/lookup/username/foo'`
| 框架 | 版本 | 结果 |
| --------- | :-----------: | -------------------: |
| **Hono** | 3.0.0 | **Requests/sec: 136112** |
| Fast | 4.0.0-beta.1 | Requests/sec: 103214 |
| Megalo | 0.3.0 | Requests/sec: 64597 |
| Faster | 5.7 | Requests/sec: 54801 |
# 开发者体验
若想打造优秀的应用,首先需要拥有出色的开发者体验。
所幸我们可以直接使用 TypeScript 为 Cloudflare Workers、Deno 与 Bun 编写应用,而无需额外转译成 JavaScript。
Hono 以 TypeScript 编写,让应用天然具备类型安全。
# 中间件
我们把返回 `Response` 的原语称为“处理器(Handler)”。
“中间件”在处理器之前或之后执行,用来处理 `Request` 与 `Response`,
结构就像一层层洋葱。
例如,下面的中间件可以为响应添加 “X-Response-Time” 请求头。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
const start = performance.now()
await next()
const end = performance.now()
c.res.headers.set('X-Response-Time', `${end - start}`)
})
```
借助这种简单的方式,我们可以编写自定义中间件,或复用内建与第三方中间件。
# 开发哲学
本节将介绍 Hono 的理念与哲学。
## 初衷
最初,我只是想在 Cloudflare Workers 上构建一个 Web 应用。
然而,当时缺乏一个适用于 Cloudflare Workers 的优秀框架,
于是我开始动手打造 Hono。
我认为这是一个学习如何用 Trie 树构建路由器的好机会。
后来朋友带来了一个快得不可思议的路由器——“RegExpRouter”。
还有朋友为我们编写了 Basic Authentication 中间件。
因为只使用 Web 标准 API,我们得以让 Hono 在 Deno 与 Bun 上运行。
当有人问“Bun 上有 Express 吗?”时,我们可以回答:“没有,但有 Hono。”
(虽然现在 Express 也能运行在 Bun 上了。)
我们还有朋友开发了 GraphQL 服务器、Firebase 鉴权以及 Sentry 中间件。
我们也拥有 Node.js 适配器。
整个生态正在蓬勃发展。
换句话说,Hono 飞快、功能丰富且随处可用。
我们希望 Hono 能成为 **Web 标准中的事实标准**。
# 路由器
路由器是 Hono 最重要的功能之一。
Hono 内建五种路由器。
## RegExpRouter
**RegExpRouter** 是 JavaScript 世界中最快的路由器。
虽然名字叫 “RegExp”,但它并不是 [path-to-regexp](https://github.com/pillarjs/path-to-regexp) 那样的 Express 风格实现。
后者使用线性循环,意味着每条路由都会逐一进行正则匹配,
路由越多性能越差。

Hono 的 RegExpRouter 会将路由模式转换成“一条巨大的正则表达式”,
只需一次匹配即可得到结果。
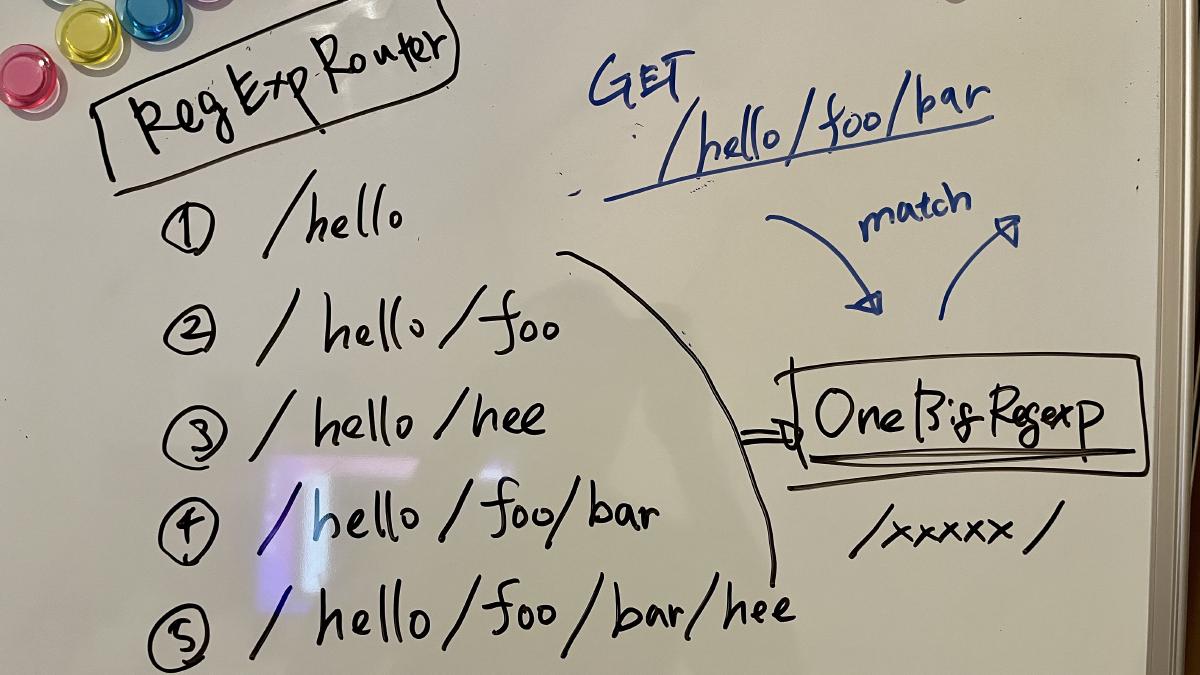
在多数场景下,这比使用诸如 radix-tree 等树形算法的方法更快。
不过,RegExpRouter 并不支持所有路由模式,
因此通常会与下文中支持全量路由模式的其他路由器搭配使用。
## TrieRouter
**TrieRouter** 基于 Trie 树算法实现。
与 RegExpRouter 一样,它也不依赖线性循环。
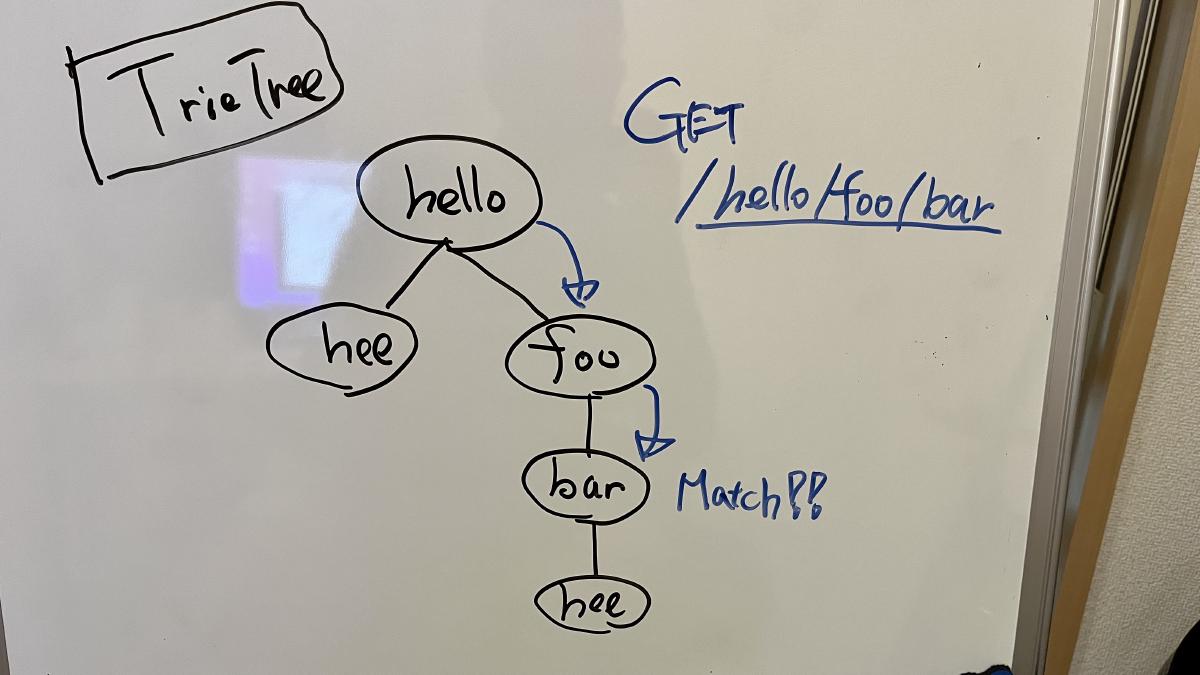
它虽然没有 RegExpRouter 那么快,但仍比 Express 的路由器快得多,
并且支持全部路由模式。
## SmartRouter
当你需要组合多种路由器时,**SmartRouter** 非常实用。
它会根据已注册的路由自动挑选最合适的路由器。
Hono 默认同时使用 SmartRouter、RegExpRouter 与 TrieRouter:
```ts
// Hono 内部代码。
readonly defaultRouter: Router = new SmartRouter({
routers: [new RegExpRouter(), new TrieRouter()],
})
```
应用启动后,SmartRouter 会依据路由配置检测最快的实现,并持续沿用。
## LinearRouter
RegExpRouter 虽然运行时极快,但在注册路由阶段略显缓慢,
因此不太适合每次请求都会初始化应用的环境。
**LinearRouter** 针对“一次性”场景做了优化。
它采用线性方式添加路由,无需编译字符串,
因此注册速度远快于 RegExpRouter。
下面这段基准测试包含了路由注册阶段:
```console
• GET /user/lookup/username/hey
----------------------------------------------------- -----------------------------
LinearRouter 1.82 µs/iter (1.7 µs … 2.04 µs) 1.84 µs 2.04 µs 2.04 µs
MedleyRouter 4.44 µs/iter (4.34 µs … 4.54 µs) 4.48 µs 4.54 µs 4.54 µs
FindMyWay 60.36 µs/iter (45.5 µs … 1.9 ms) 59.88 µs 78.13 µs 82.92 µs
KoaTreeRouter 3.81 µs/iter (3.73 µs … 3.87 µs) 3.84 µs 3.87 µs 3.87 µs
TrekRouter 5.84 µs/iter (5.75 µs … 6.04 µs) 5.86 µs 6.04 µs 6.04 µs
summary for GET /user/lookup/username/hey
LinearRouter
2.1x faster than KoaTreeRouter
2.45x faster than MedleyRouter
3.21x faster than TrekRouter
33.24x faster than FindMyWay
```
在 Fastly Compute 等环境中,建议搭配 `hono/quick` 预设使用 LinearRouter。
## PatternRouter
**PatternRouter** 是 Hono 中体积最小的路由器。
虽然 Hono 本身已经很小,但如果你在资源受限环境中需要进一步压缩体积,
可以使用 PatternRouter。
仅使用 PatternRouter 的应用体积不足 15KB。
```console
$ npx wrangler deploy --minify ./src/index.ts
⛅️ wrangler 3.20.0
-------------------
Total Upload: 14.68 KiB / gzip: 5.38 KiB
```
# Hono 技术栈
Hono 让简单的事情更简单,也让困难的事情变得简单。
它不仅适合返回 JSON,同样适合构建包含 REST API 服务器与客户端的全栈应用。
## RPC
Hono 的 RPC 功能允许你在几乎不改动代码的情况下共享 API 规范。
`hc` 生成的客户端会读取这些规范,并以类型安全的方式访问端点。
以下库共同构成了这一能力:
- Hono —— API 服务器
- [Zod](https://zod.dev) —— 校验器
- [Zod Validator Middleware](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator)
- `hc` —— HTTP 客户端
我们将这一整套组件称作 **Hono Stack**。
下面就用它来创建一个 API 服务器和一个客户端。
## 编写 API
首先,写一个接收 GET 请求并返回 JSON 的端点。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: `Hello!`,
})
})
```
## 使用 Zod 做校验
使用 Zod 校验查询参数的值。
```ts
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
import { z } from 'zod'
app.get(
'/hello',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
name: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
const { name } = c.req.valid('query')
return c.json({
message: `Hello! ${name}`,
})
}
)
```
## 共享类型
为了导出端点规范,只需导出其类型。
::: warning
为了让 RPC 正确推断路由,所有方法必须链式调用,并且端点或应用类型需从已声明的变量推断。详见 [RPC 最佳实践](https://hono.dev/docs/guides/best-practices#if-you-want-to-use-rpc-features)。
:::
```ts{1,17}
const route = app.get(
'/hello',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
name: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
const { name } = c.req.valid('query')
return c.json({
message: `Hello! ${name}`,
})
}
)
export type AppType = typeof route
```
## 客户端
接下来是客户端实现。
将 `AppType` 作为泛型传给 `hc` 生成客户端对象。
此时智能补全会自动提示端点路径与请求类型。
```ts
import { AppType } from './server'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const client = hc('/api')
const res = await client.hello.$get({
query: {
name: 'Hono',
},
})
```
`Response` 与 fetch API 保持兼容,但通过 `json()` 获取的数据自带类型。
```ts
const data = await res.json()
console.log(`${data.message}`)
```
共享 API 规范意味着你可以即时获知服务端的变更。
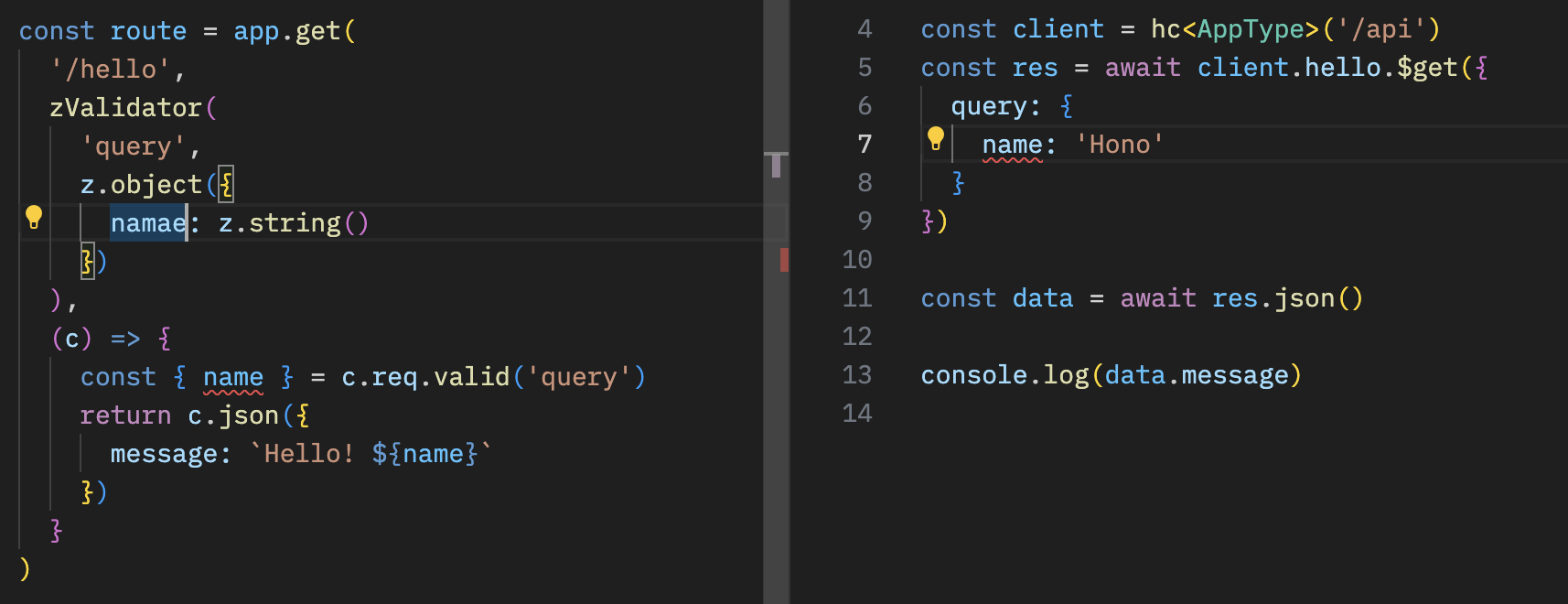
## 搭配 React
你可以使用 React 在 Cloudflare Pages 上构建应用。
以下是 API 服务器:
```ts
// functions/api/[[route]].ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { z } from 'zod'
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
const app = new Hono()
const schema = z.object({
id: z.string(),
title: z.string(),
})
type Todo = z.infer
const todos: Todo[] = []
const route = app
.post('/todo', zValidator('form', schema), (c) => {
const todo = c.req.valid('form')
todos.push(todo)
return c.json({
message: '创建成功!',
})
})
.get((c) => {
return c.json({
todos,
})
})
export type AppType = typeof route
export const onRequest = handle(app, '/api')
```
下面是结合 React 与 React Query 的客户端:
```tsx
// src/App.tsx
import {
useQuery,
useMutation,
QueryClient,
QueryClientProvider,
} from '@tanstack/react-query'
import { AppType } from '../functions/api/[[route]]'
import { hc, InferResponseType, InferRequestType } from 'hono/client'
const queryClient = new QueryClient()
const client = hc('/api')
export default function App() {
return (
)
}
const Todos = () => {
const query = useQuery({
queryKey: ['todos'],
queryFn: async () => {
const res = await client.todo.$get()
return await res.json()
},
})
const $post = client.todo.$post
const mutation = useMutation<
InferResponseType,
Error,
InferRequestType['form']
>({
mutationFn: async (todo) => {
const res = await $post({
form: todo,
})
return await res.json()
},
onSuccess: async () => {
queryClient.invalidateQueries({ queryKey: ['todos'] })
},
onError: (error) => {
console.log(error)
},
})
return (
{query.data?.todos.map((todo) => (
- {todo.title}
))}
)
}
```
# Web 标准
Hono 仅依赖 **Web 标准**(例如 Fetch)。
这些标准最初用于 `fetch` 函数,由处理 HTTP 请求与响应的基础对象构成。
除了 `Request` 与 `Response`,还有 `URL`、`URLSearchParam`、`Headers` 等。
Cloudflare Workers、Deno 与 Bun 同样构建在 Web 标准之上。
例如,下面的服务器会返回 “Hello World”,即可运行在 Cloudflare Workers 与 Bun 上。
```ts twoslash
export default {
async fetch() {
return new Response('Hello World')
},
}
```
Hono 完全依赖 Web 标准,因此只要运行时支持这些标准,Hono 就能在其上运行。
此外,我们还提供 Node.js 适配器。Hono 已在以下运行时中可用:
- Cloudflare Workers (`workerd`)
- Deno
- Bun
- Fastly Compute
- AWS Lambda
- Node.js
- Vercel(edge-light)
它同样适用于 Netlify 等平台,同一份代码可在所有平台运行。
Cloudflare Workers、Deno、Shopify 等团队发起了 [WinterCG](https://wintercg.org),
共同探讨如何通过 Web 标准实现“Web 互操作性”。
Hono 将紧随其步伐,迈向 **Web 标准的事实标准**。
# Context(上下文)
`Context` 对象会为每个请求创建,并在返回响应前一直存在。你可以向其中存放数据、设置响应头与状态码,并访问 HonoRequest 和 Response 对象。
## req
`req` 是 HonoRequest 的实例。详情见 [HonoRequest](/docs/api/request)。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
const userAgent = c.req.header('User-Agent')
// ...
// ---cut-start---
return c.text(`你好,${userAgent}`)
// ---cut-end---
})
```
## status()
可以通过 `c.status()` 设置 HTTP 状态码,默认值为 `200`。当状态码就是 `200` 时无需显式调用。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/posts', (c) => {
// 设置 HTTP 状态码
c.status(201)
return c.text('你的文章已经创建!')
})
```
## header()
可以为响应设置 HTTP 头。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
// 设置响应头
c.header('X-Message', '我的自定义消息')
return c.text('你好!')
})
```
## body()
返回一个 HTTP 响应。
::: info
**注意**:当返回文本或 HTML 时,推荐使用 `c.text()` 或 `c.html()`。
:::
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/welcome', (c) => {
c.header('Content-Type', 'text/plain')
// 返回响应主体
return c.body('感谢你的到访')
})
```
也可以这样写:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/welcome', (c) => {
return c.body('感谢你的到访', 201, {
'X-Message': '你好!',
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
})
})
```
返回结果与下面的 `Response` 对象相同。
```ts twoslash
new Response('感谢你的到访', {
status: 201,
headers: {
'X-Message': '你好!',
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
},
})
```
## text()
以 `Content-Type:text/plain` 渲染文本。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/say', (c) => {
return c.text('你好!')
})
```
## json()
以 `Content-Type:application/json` 渲染 JSON。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/api', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: '你好!' })
})
```
## html()
以 `Content-Type:text/html` 渲染 HTML。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html('你好!Hono!
')
})
```
## notFound()
返回一个 `Not Found` 响应。也可以使用 [`app.notFound()`](/docs/api/hono#not-found) 自定义内容。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/notfound', (c) => {
return c.notFound()
})
```
## redirect()
执行重定向,默认状态码为 `302`。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/redirect', (c) => {
return c.redirect('/')
})
app.get('/redirect-permanently', (c) => {
return c.redirect('/', 301)
})
```
## res
可以访问待返回的 Response 对象。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// Response 对象
app.use('/', async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.res.headers.append('X-Debug', '调试信息')
})
```
## set() / get()
可以在一次请求生命周期内读写任意键值对,从而在中间件之间或中间件与路由处理函数之间传递数据。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: { message: string } }>()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
c.set('message', 'Hono 超赞!!')
await next()
})
app.get('/', (c) => {
const message = c.get('message')
return c.text(`消息内容是「${message}」`)
})
```
将 `Variables` 作为泛型参数传给 `Hono` 构造函数,就能获得类型安全。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
type Variables = {
message: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: Variables }>()
```
`c.set` / `c.get` 的值只在同一个请求中有效,不能在不同请求之间共享或持久化。
## var
还可以通过 `c.var` 访问变量的值。
```ts twoslash
import type { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const result = c.var.client.oneMethod()
```
如果想编写提供自定义方法的中间件,可以这样写:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
// ---cut---
type Env = {
Variables: {
echo: (str: string) => string
}
}
const app = new Hono()
const echoMiddleware = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.set('echo', (str) => str)
await next()
})
app.get('/echo', echoMiddleware, (c) => {
return c.text(c.var.echo('你好!'))
})
```
若希望在多个处理函数中复用该中间件,可以结合 `app.use()`。这时需要将 `Env` 作为泛型传入 `Hono` 构造函数以确保类型安全。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { MiddlewareHandler } from 'hono/types'
declare const echoMiddleware: MiddlewareHandler
type Env = {
Variables: {
echo: (str: string) => string
}
}
// ---cut---
const app = new Hono()
app.use(echoMiddleware)
app.get('/echo', (c) => {
return c.text(c.var.echo('你好!'))
})
```
## render() / setRenderer()
可以在自定义中间件内调用 `c.setRenderer()` 设置布局。
```tsx twoslash
/** @jsx jsx */
/** @jsxImportSource hono/jsx */
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content) => {
return c.html(
{content}
)
})
await next()
})
```
随后就能通过 `c.render()` 在该布局内生成响应。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.render('你好!')
})
```
输出结果如下:
```html
你好!
```
此外,该特性还允许自定义渲染参数。为保持类型安全,可以这样定义类型:
```ts
declare module 'hono' {
interface ContextRenderer {
(
content: string | Promise,
head: { title: string }
): Response | Promise
}
}
```
下面演示了具体用法:
```ts
app.use('/pages/*', async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content, head) => {
return c.html(
{head.title}
{content}
)
})
await next()
})
app.get('/pages/my-favorite', (c) => {
return c.render(拉面和寿司
, {
title: '我的最爱',
})
})
app.get('/pages/my-hobbies', (c) => {
return c.render(看棒球
, {
title: '我的爱好',
})
})
```
## executionCtx
可以访问 Cloudflare Workers 特有的 [ExecutionContext](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/context/)。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono<{
Bindings: {
KV: any
}
}>()
declare const key: string
declare const data: string
// ---cut---
// ExecutionContext 对象
app.get('/foo', async (c) => {
c.executionCtx.waitUntil(c.env.KV.put(key, data))
// ...
})
```
## event
还可以访问 Cloudflare Workers 特有的 `FetchEvent`。这曾用于“Service Worker”语法,但现在已经不再推荐。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
declare const key: string
declare const data: string
type KVNamespace = any
// ---cut---
// 类型定义以辅助类型推断
type Bindings = {
MY_KV: KVNamespace
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
// FetchEvent 对象(仅在使用 Service Worker 语法时可用)
app.get('/foo', async (c) => {
c.event.waitUntil(c.env.MY_KV.put(key, data))
// ...
})
```
## env
在 Cloudflare Workers 中,绑定到 Worker 的环境变量、密钥、KV 命名空间、D1 数据库、R2 存储桶等统称为 Binding。
无论类型如何,这些 Binding 都可以作为全局变量使用,并通过 `c.env.BINDING_KEY` 访问。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
type KVNamespace = any
// ---cut---
// 类型定义以辅助类型推断
type Bindings = {
MY_KV: KVNamespace
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
// Cloudflare Workers 的环境对象
app.get('/', async (c) => {
c.env.MY_KV.get('my-key')
// ...
})
```
## error
当处理函数抛出异常时,错误对象会存放在 `c.error`,你可以在中间件中访问它。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
await next()
if (c.error) {
// 执行自定义逻辑...
}
})
```
## ContextVariableMap
例如,如果希望在特定中间件生效时为变量补充类型定义,可以扩展 `ContextVariableMap`:
```ts
declare module 'hono' {
interface ContextVariableMap {
result: string
}
}
```
然后即可在中间件中使用:
```ts twoslash
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
// ---cut---
const mw = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.set('result', '一些值') // result 是字符串
await next()
})
```
在处理函数中,该变量会被推断为正确的类型:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: { result: string } }>()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
const val = c.get('result') // val 是字符串
// ...
return c.json({ result: val })
})
```
# HTTPException
当出现严重错误时,Hono(以及许多生态中的中间件)可能会抛出 `HTTPException`。这是 Hono 自定义的 `Error`,用于简化[返回错误响应](#handling-httpexceptions)的流程。
## 抛出 HTTPException
你可以通过指定状态码并设置消息或自定义响应来主动抛出 `HTTPException`。
### 自定义消息
对于简单的 `text` 响应,只需设置错误的 `message`。
```ts twoslash
import { HTTPException } from 'hono/http-exception'
throw new HTTPException(401, { message: '未授权' })
```
### 自定义 Response
如需返回其他类型的响应或设置响应头,可以使用 `res` 选项。_注意:构造函数中传入的状态码将用于生成响应。_
```ts twoslash
import { HTTPException } from 'hono/http-exception'
const errorResponse = new Response('未授权', {
status: 401, // 这里的状态码会被忽略
headers: {
Authenticate: 'error="invalid_token"',
},
})
throw new HTTPException(401, { res: errorResponse })
```
### 错误原因(Cause)
无论哪种方式,你都可以使用 [`cause`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Error/cause) 选项将任意数据附加到 `HTTPException` 中。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono, Context } from 'hono'
import { HTTPException } from 'hono/http-exception'
const app = new Hono()
declare const message: string
declare const authorize: (c: Context) => Promise
// ---cut---
app.post('/login', async (c) => {
try {
await authorize(c)
} catch (cause) {
throw new HTTPException(401, { message, cause })
}
return c.redirect('/')
})
```
## 处理 HTTPException
可以通过 [`app.onError`](/docs/api/hono#error-handling) 统一处理未被捕获的 `HTTPException`。异常对象包含 `getResponse` 方法,会根据错误的 `status` 以及错误 `message` 或抛出时传入的[自定义响应](#custom-response)生成新的 `Response`。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
import { HTTPException } from 'hono/http-exception'
// ...
app.onError((error, c) => {
if (error instanceof HTTPException) {
console.error(error.cause)
// 获取自定义响应
return error.getResponse()
}
// ...
// ---cut-start---
return c.text('发生未知错误')
// ---cut-end---
})
```
::: warning
**`HTTPException.getResponse` 并不会读取 `Context`**。如果需要包含 `Context` 中已设置的响应头,需要手动将它们合并到新的 `Response` 中。
:::
# 应用 - Hono
`Hono` 是核心对象。
它会在一开始被导入,并贯穿整个应用程序。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
//...
export default app // for Cloudflare Workers or Bun
```
## 方法
`Hono` 实例提供以下方法:
- app.**HTTP_METHOD**(\[path,\]handler|middleware...)
- app.**all**(\[path,\]handler|middleware...)
- app.**on**(method|method[], path|path[], handler|middleware...)
- app.**use**(\[path,\]middleware)
- app.**route**(path, \[app\])
- app.**basePath**(path)
- app.**notFound**(handler)
- app.**onError**(err, handler)
- app.**mount**(path, anotherApp)
- app.**fire**()
- app.**fetch**(request, env, event)
- app.**request**(path, options)
其中前面几项用于定义路由,详见[路由章节](/docs/api/routing)。
## 未找到(Not Found)
`app.notFound` 可以自定义未找到时返回的响应。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.notFound((c) => {
return c.text('Custom 404 Message', 404)
})
```
:::warning
`notFound` 仅会由顶层应用触发。详情请参阅此[问题](https://github.com/honojs/hono/issues/3465#issuecomment-2381210165)。
:::
## 错误处理
`app.onError` 能捕获未处理的异常并返回自定义响应。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.onError((err, c) => {
console.error(`${err}`)
return c.text('Custom Error Message', 500)
})
```
::: info
当父应用和路由同时注册了 `onError` 处理器时,会优先使用路由级处理器。
:::
## fire()
::: warning
**`app.fire()` 已被弃用**。请改用 `hono/service-worker` 中的 `fire()`。详情参见[Service Worker 文档](/docs/getting-started/service-worker)。
:::
`app.fire()` 会自动添加全局的 `fetch` 事件监听器。
对于遵循 [Service Worker API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Service_Worker_API) 的运行环境(例如[非 ES 模块的 Cloudflare Workers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/reference/migrate-to-module-workers/))来说这会很有用。
`app.fire()` 会为你执行以下代码:
```ts
addEventListener('fetch', (event: FetchEventLike): void => {
event.respondWith(this.dispatch(...))
})
```
## fetch()
`app.fetch` 是应用程序的入口。
在 Cloudflare Workers 中可以这样使用:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
type Env = any
type ExecutionContext = any
// ---cut---
export default {
fetch(request: Request, env: Env, ctx: ExecutionContext) {
return app.fetch(request, env, ctx)
},
}
```
或者直接:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
export default app
```
Bun:
```ts
export default app // [!code --]
export default { // [!code ++]
port: 3000, // [!code ++]
fetch: app.fetch, // [!code ++]
} // [!code ++]
```
## request()
`request` 方法非常适合用于测试。
你可以传入 URL 或路径来发送 GET 请求,`app` 会返回一个 `Response` 对象。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
declare const test: (name: string, fn: () => void) => void
declare const expect: (value: any) => any
// ---cut---
test('GET /hello is ok', async () => {
const res = await app.request('/hello')
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
})
```
你也可以传入 `Request` 对象:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
declare const test: (name: string, fn: () => void) => void
declare const expect: (value: any) => any
// ---cut---
test('POST /message is ok', async () => {
const req = new Request('Hello!', {
method: 'POST',
})
const res = await app.request(req)
expect(res.status).toBe(201)
})
```
## mount()
`mount()` 让你可以在 Hono 应用中挂载其他框架构建的应用。
```ts
import { Router as IttyRouter } from 'itty-router'
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// 创建 itty-router 应用
const ittyRouter = IttyRouter()
// 处理 `GET /itty-router/hello`
ittyRouter.get('/hello', () => new Response('来自 itty-router 的问候'))
// Hono 应用
const app = new Hono()
// 挂载!
app.mount('/itty-router', ittyRouter.handle)
```
## strict 模式
严格模式默认开启(值为 `true`),会将以下路由视为不同路径:
- `/hello`
- `/hello/`
`app.get('/hello')` 不会匹配 `GET /hello/`。
如果将 strict mode 设为 `false`,上述两个路径将被视为同一路由。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const app = new Hono({ strict: false })
```
## router 选项
`router` 选项用于指定路由器。默认值是 `SmartRouter`。如果想使用 `RegExpRouter`,可以在创建 Hono 实例时传入:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
import { RegExpRouter } from 'hono/router/reg-exp-router'
const app = new Hono({ router: new RegExpRouter() })
```
## 泛型
可以通过泛型参数声明 Cloudflare Workers 的 Binding 类型,以及 `c.set`/`c.get` 中使用的变量类型。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
type User = any
declare const user: User
// ---cut---
type Bindings = {
TOKEN: string
}
type Variables = {
user: User
}
const app = new Hono<{
Bindings: Bindings
Variables: Variables
}>()
app.use('/auth/*', async (c, next) => {
const token = c.env.TOKEN // token 的类型是 `string`
// ...
c.set('user', user) // user 应当是 `User`
await next()
})
```
# API
Hono 的 API 十分简洁。
它只是由符合 Web 标准的扩展对象组成。
因此你可以很快掌握它。
本节将按照下列顺序介绍 Hono 的 API:
- Hono 对象
- 路由
- Context 对象
- 中间件
# 预设路由器
Hono 提供多种路由器,分别针对不同的使用场景进行了优化。
你可以在创建 Hono 实例时通过构造函数选择具体的路由器。
为便于常见场景的使用,框架内置了若干**预设(Preset)**,这样就无需在每次实例化时都手动指定路由器。
所有预设导出的 `Hono` 类本质一致,差异仅在于默认绑定的路由器,因此它们可以互换使用。
## `hono`
用法:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
```
路由器:
```ts
this.router = new SmartRouter({
routers: [new RegExpRouter(), new TrieRouter()],
})
```
## `hono/quick`
用法:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono/quick'
```
路由器:
```ts
this.router = new SmartRouter({
routers: [new LinearRouter(), new TrieRouter()],
})
```
## `hono/tiny`
用法:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono/tiny'
```
路由器:
```ts
this.router = new PatternRouter()
```
## 应该选择哪种预设?
- `hono`:推荐用于大多数场景。虽然注册阶段比 `hono/quick` 略慢,但启动后性能优异,适用于基于 **Deno**、**Bun**、**Node.js** 的长生命周期服务器。在 **Cloudflare Workers**、**Deno Deploy** 等使用 V8 隔离的环境中同样表现稳定,因为实例在启动后会保持一段时间。
- `hono/quick`:面向每次请求都会重新初始化应用的环境,例如 **Fastly Compute**,因此更适合这些平台。
- `hono/tiny`:体积最小的路由器包,适用于资源受限的运行环境。
# HonoRequest
`HonoRequest` 是从 `c.req` 获取的对象,用于包装 [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) 实例。
## param()
获取路径参数的值。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// 捕获的参数
app.get('/entry/:id', async (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id')
// ^?
// ...
})
// 一次性获取全部参数
app.get('/entry/:id/comment/:commentId', async (c) => {
const { id, commentId } = c.req.param()
// ^?
})
```
## query()
获取查询字符串参数。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// 查询参数
app.get('/search', async (c) => {
const query = c.req.query('q')
// ^?
})
// 一次性获取全部参数
app.get('/search', async (c) => {
const { q, limit, offset } = c.req.query()
// ^?
})
```
## queries()
获取同名查询参数的多个值,例如 `/search?tags=A&tags=B`
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/search', async (c) => {
// tags 的类型是 string[]
const tags = c.req.queries('tags')
// ^?
// ...
})
```
## header()
获取请求头的值。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
const userAgent = c.req.header('User-Agent')
// ^?
return c.text(`你的 User-Agent 是 ${userAgent}`)
})
```
::: warning
当 `c.req.header()` 不带参数调用时,返回对象的所有键都会被转换为**小写**。
若要读取带有大写名称的请求头,请使用 `c.req.header("X-Foo")`。
```ts
// ❌ 不会生效
const headerRecord = c.req.header()
const foo = headerRecord['X-Foo']
// ✅ 可行
const foo = c.req.header('X-Foo')
```
:::
## parseBody()
解析 `multipart/form-data` 或 `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` 类型的请求体。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.parseBody()
// ...
})
```
`parseBody()` 支持以下场景:
**单文件**
```ts twoslash
import { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const body = await c.req.parseBody()
const data = body['foo']
// ^?
```
`body['foo']` 的类型为 `(string | File)`。
如果上传了多个文件,会保留最后一个。
### 多文件
```ts twoslash
import { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const body = await c.req.parseBody()
body['foo[]']
```
`body['foo[]']` 始终是 `(string | File)[]`。
必须带上 `[]` 后缀。
### 同名的多个文件或字段
当存在允许多选的文件输入 ``,或有多个同名复选框 `` 时:
```ts twoslash
import { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const body = await c.req.parseBody({ all: true })
body['foo']
```
`all` 选项默认关闭。
- 如果 `body['foo']` 对应多个文件,将解析为 `(string | File)[]`。
- 如果 `body['foo']` 是单个文件,将解析为 `(string | File)`。
### 点符号
当 `dot` 选项设为 `true` 时,返回值会根据点语法构建层级。
假设收到如下数据:
```ts twoslash
const data = new FormData()
data.append('obj.key1', 'value1')
data.append('obj.key2', 'value2')
```
启用 `dot: true` 后即可得到结构化结果:
```ts twoslash
import { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const body = await c.req.parseBody({ dot: true })
// body 为 `{ obj: { key1: 'value1', key2: 'value2' } }`
```
## json()
解析 `application/json` 类型的请求体。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.json()
// ...
})
```
## text()
解析 `text/plain` 类型的请求体。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.text()
// ...
})
```
## arrayBuffer()
将请求体解析为 `ArrayBuffer`。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.arrayBuffer()
// ...
})
```
## blob()
将请求体解析为 `Blob`。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.blob()
// ...
})
```
## formData()
将请求体解析为 `FormData`。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.post('/entry', async (c) => {
const body = await c.req.formData()
// ...
})
```
## valid()
获取校验后的数据。
```ts
app.post('/posts', async (c) => {
const { title, body } = c.req.valid('form')
// ...
})
```
可用的目标如下:
- `form`
- `json`
- `query`
- `header`
- `cookie`
- `param`
参见[验证章节](/docs/guides/validation)了解使用示例。
## routePath
::: warning
**v4.8.0 起已弃用**:该属性已废弃,请改用 [Route Helper](/docs/helpers/route) 提供的 `routePath()`。
:::
可以在处理函数中这样获取已注册的路径:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
return c.json({ path: c.req.routePath })
})
```
访问 `/posts/123` 时会返回 `/posts/:id`:
```json
{ "path": "/posts/:id" }
```
## matchedRoutes
::: warning
**v4.8.0 起已弃用**:该属性已废弃,请改用 [Route Helper](/docs/helpers/route) 提供的 `matchedRoutes()`。
:::
它会在处理函数中返回匹配到的路由,便于调试。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(async function logger(c, next) {
await next()
c.req.matchedRoutes.forEach(({ handler, method, path }, i) => {
const name =
handler.name ||
(handler.length < 2 ? '[处理函数]' : '[中间件]')
console.log(
method,
' ',
path,
' '.repeat(Math.max(10 - path.length, 0)),
name,
i === c.req.routeIndex ? '<- 从这里响应' : ''
)
})
})
```
## path
请求的路径名。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/about/me', async (c) => {
const pathname = c.req.path // `/about/me`
// ...
})
```
## url
请求的完整 URL 字符串。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/about/me', async (c) => {
const url = c.req.url // `http://localhost:8787/about/me`
// ...
})
```
## method
请求使用的方法名称。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/about/me', async (c) => {
const method = c.req.method // `GET`
// ...
})
```
## raw
原始的 [`Request`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) 对象。
```ts
// 适用于 Cloudflare Workers
app.post('/', async (c) => {
const metadata = c.req.raw.cf?.hostMetadata?
// ...
})
```
# 路由
Hono 的路由灵活且直观。
我们一起来看看。
## 基础用法
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// HTTP 方法
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('GET /'))
app.post('/', (c) => c.text('POST /'))
app.put('/', (c) => c.text('PUT /'))
app.delete('/', (c) => c.text('DELETE /'))
// 通配符
app.get('/wild/*/card', (c) => {
return c.text('GET /wild/*/card')
})
// 任意 HTTP 方法
app.all('/hello', (c) => c.text('任意方法 /hello'))
// 自定义 HTTP 方法
app.on('PURGE', '/cache', (c) => c.text('PURGE 方法 /cache'))
// 多个方法
app.on(['PUT', 'DELETE'], '/post', (c) =>
c.text('PUT 或 DELETE /post')
)
// 多个路径
app.on('GET', ['/hello', '/ja/hello', '/en/hello'], (c) =>
c.text('你好')
)
```
## 路径参数
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/user/:name', async (c) => {
const name = c.req.param('name')
// ^?
// ...
})
```
或一次性获取全部参数:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/posts/:id/comment/:comment_id', async (c) => {
const { id, comment_id } = c.req.param()
// ^?
// ...
})
```
## 可选参数
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// 将匹配 `/api/animal` 和 `/api/animal/:type`
app.get('/api/animal/:type?', (c) => c.text('动物!'))
```
## 正则表达式
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/post/:date{[0-9]+}/:title{[a-z]+}', async (c) => {
const { date, title } = c.req.param()
// ^?
// ...
})
```
## 匹配带斜杠的片段
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/posts/:filename{.+\\.png}', async (c) => {
//...
})
```
## 链式路由
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app
.get('/endpoint', (c) => {
return c.text('GET /endpoint')
})
.post((c) => {
return c.text('POST /endpoint')
})
.delete((c) => {
return c.text('DELETE /endpoint')
})
```
## 分组
你可以使用另一个 Hono 实例组织路由,再通过 `route` 方法挂载到主应用。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const book = new Hono()
book.get('/', (c) => c.text('列出书籍')) // GET /book
book.get('/:id', (c) => {
// GET /book/:id
const id = c.req.param('id')
return c.text('查看书籍:' + id)
})
book.post('/', (c) => c.text('创建书籍')) // POST /book
const app = new Hono()
app.route('/book', book)
```
## 不改变基础路径的分组
你也可以在保持原有基础路径的情况下组合多个实例。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const book = new Hono()
book.get('/book', (c) => c.text('列出书籍')) // GET /book
book.post('/book', (c) => c.text('创建书籍')) // POST /book
const user = new Hono().basePath('/user')
user.get('/', (c) => c.text('列出用户')) // GET /user
user.post('/', (c) => c.text('创建用户')) // POST /user
const app = new Hono()
app.route('/', book) // 处理 /book
app.route('/', user) // 处理 /user
```
## 基础路径
可以为应用指定基础路径。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const api = new Hono().basePath('/api')
api.get('/book', (c) => c.text('列出书籍')) // GET /api/book
```
## 搭配主机名的路由
在路径中带上主机名也可以正常工作。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const app = new Hono({
getPath: (req) => req.url.replace(/^https?:\/([^?]+).*$/, '$1'),
})
app.get('/www1.example.com/hello', (c) => c.text('你好 www1'))
app.get('/www2.example.com/hello', (c) => c.text('你好 www2'))
```
## 使用 `host` 请求头路由
如果在 Hono 构造函数中设置 `getPath()`,就能利用 `host` 请求头进行路由判断。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
const app = new Hono({
getPath: (req) =>
'/' +
req.headers.get('host') +
req.url.replace(/^https?:\/\/[^/]+(\/[^?]*).*/, '$1'),
})
app.get('/www1.example.com/hello', (c) => c.text('你好 www1'))
// 以下请求将匹配上面的路由:
// new Request('http://www1.example.com/hello', {
// headers: { host: 'www1.example.com' },
// })
```
利用这一点,你甚至可以根据 `User-Agent` 等请求头调整路由逻辑。
## 路由优先级
处理函数和中间件会按照注册顺序执行。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/book/a', (c) => c.text('a')) // a
app.get('/book/:slug', (c) => c.text('common')) // common
```
```
GET /book/a ---> `a`
GET /book/b ---> `common`
```
一旦命中了某个处理函数,请求就会停止继续匹配。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('*', (c) => c.text('common')) // common
app.get('/foo', (c) => c.text('foo')) // foo
```
```
GET /foo ---> `common` // 不会再派发 foo
```
如果希望中间件优先执行,需要将其写在处理函数之前。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(logger())
app.get('/foo', (c) => c.text('foo'))
```
若想提供“_兜底_”处理函数,请将其写在其他处理函数之后。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/bar', (c) => c.text('bar')) // bar
app.get('*', (c) => c.text('fallback')) // fallback
```
```
GET /bar ---> `bar`
GET /foo ---> `fallback`
```
## 分组顺序
需要注意,分组时顺序错误往往不易察觉。
`route()` 会把第二个参数(例如 `three` 或 `two`)中已有的路由加入到自身(`two` 或 `app`)的路由表中。
```ts
three.get('/hi', (c) => c.text('hi'))
two.route('/three', three)
app.route('/two', two)
export default app
```
这样会返回 200:
```
GET /two/three/hi ---> `hi`
```
但如果顺序弄错,就会返回 404。
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
const two = new Hono()
const three = new Hono()
// ---cut---
three.get('/hi', (c) => c.text('hi'))
app.route('/two', two) // `two` 尚未注册路由
two.route('/three', three)
export default app
```
```
GET /two/three/hi ---> 404 Not Found
```
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}
 ) : (
)}
) : (
)}